Abstract
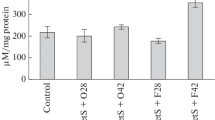
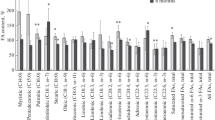
The levels of lipid peroxides in circulatory lipoproteins increased with chronic administration of ethanol or acetaldehyde. Low density lipoprotein showed a greater increase in its content of lipid peroxides than very low density lipoprotein or high density lipoprotein. However, very low density lipoprotein was more prone to lipid peroxidationin vitro than low density lipoprotein or high density lipoprotein. The effect of acetaldehyde was more marked than that of ethanol. Lipoproteins of control and hyperlipemic groups were partially protected against peroxidation by butyrated hydroxytoluene and serum high density lipoprotein of normal rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LPO:
-
Lipid peroxide
- VLDL:
-
very low density lipoprotein
- LDL:
-
low density lipoprotein
- HDL:
-
high density lipoprotein
- BHT:
-
butyrated hydroxytoluene
References
Burstein, M. and Legmann, P. (1982) inMonographs in atherosclerosis. Lipoprotein precipitations (ed. T. B. Clarkson) (London, Paris: S. Karger) pp 78–82.
Chander, R., Kapoor, N. K. and Singh, C. (1987)J. Biosci.,12, 55.
Di Luzio, N. R. (1973)Fed. Proc.,32, 1875.
Evensen, S. A., Galdal, K. S. and Nilsen, E. (1983)Atherosclerosis,49, 23.
Fink, R., Clemens, M. R., Major, D. H., Parlos, P., Cawood, P., Norden, A. G., Iversen, S. A. and Dormandy, T, L. (1985)Lancet,2, 291.
Gianturco, S. H., Eskin, S. G., Navarro, L. T., Lahart, G. J., Smith, L. C. and Golto, A. M. Jr. (1980)Biochim. Biophys. Acta,618, 143.
Harta, J., Nagata, M., Sasaki, E., Ishiguro, I. and Ohta, Y. (1983)Biochem. Pharmacol.,32, 1795.
Henriksen, T., Evensen, S. A. and Carlander, B. (1979)Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest.,39, 369.
Hessler, J. R., Robertson, A. L. and Chisolm, G. M. (1979)Atherosclerosis,32, 213.
Jurgens, G., Lang, J. and Esterbauer, H. (1986)Biochim. Biophys. Acta,875, 103.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. and Randall, R. J. (1951)J. Biol. Chem.,193, 265.
Mizukami, M., Aono, J., Sakai, K., Hata, S. and Nakano, M. (1984)Arzneim. Forsch.,34, 569.
Morel, D. W., Hessler, J. R. and Chisolm, G. M. (1983)J. LipidRes.,24, 1070.
Morgan, M. Y. (1982)Br. Med. Bull.,38, 21.
Narula, J. and Wasir, H. S. (1985)Indian Heart J.,37, 323.
Ohkawa, H. and Ohishi, N. (1978)J. Lipid Res.,19, 1053.
Ramakrishnan, S. (1984)J. Sci. Ind. Res.,43, 284.
Ross, R. and Harker, L. (1976)Science,193, 1094.
Vadivelu, N. and Ramakrishnan, S. (1986)Indian J. Med. Res.,83, 46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chander, R., Kapoor, N.K. & Singh, C. Lipid peroxidation of hyperlipemic rat serum lipoproteins in chronic ethanol and acetaldehyde administration. J Biosci 13, 269–274 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02712151
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02712151