Abstract
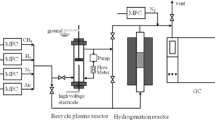
Methane, the major constituent of natural gas, was converted to higher hydrocarbons by a microwave plasma. The yield of C2+ products increased from 29.2 % to 42.2% with increasing plasma power and decreasing flow rate of methane. When catalysts were used in the plasma reactor, the selectivities of ethylene and acetylene increased, while the yield of C2+ remained constant. Among various catalysts used, Fe catalyst showed the highest ethylene selectivity of 30 %. And when the actual natural gas was introduced, more C2+ products were obtained (46%). This is due to the ethane and propane in the natural gas. Applying electric field inductance for evolving the high plasma, we obtained high C2+ products of 63.7 % when Pd-Ni bimetal catalyst was used.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang, J. H. and Suib, S. L., “Methane Dimerization via Microwave Plasmas”,Res. Chem. Intermed.,20(1), 133 (1994).
Ioffe, M. S., Pollington, S. D. and Wan, K. S. J., “High-Power Pulsed Radio-Frequency and Microwave Catalytic Processes: Selective Production of Acetylene from the Reaction of Methane over Carbon”,J. Catal.,151, 349 (1995).
Kizling, M. B. and Järås, S. G., “A Review of the Use of Plasma Techniques in Catalyst Preparation and Catalytic Reactions”,Applied Catalysis A: General,147, 1 (1996).
McCarty, R. L., “Chemical Synthesis from Free Radicals Produced in Microwave Fields”,J. Chem. Phys.,22, 1360 (1954).
Suib, S. L. and Zerger, R. P., “A Direct, Continuous, Low-Power Catalytic Conversion of Methane to Higher Hydrocarbons via Microwave Plasmas”,J. Catal.,139, 383 (1993).
Suib, S.L. and Zerger, R.P., US Patent 5, 015349, 1991.
Wan, J. K. S., “Microwaves and Chemistry: The Catalysis of an Exciting Marriage”,Res. Chem. Intermed.,19(2), 147 (1993).
Wan, J. K. S., US Patent4, 574038, 1986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, W., Baek, Y., Pang, H. et al. A direct catalytic conversion of natural gas to C2+ hydrocarbons by microwave plasma. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 15, 500–504 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02707099
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02707099