Abstract
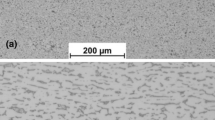
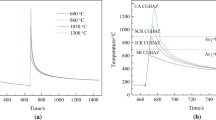
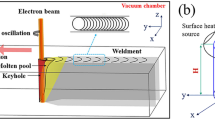
The effect of microstructural characteristics on fracture behaviour mechanism for electron beam welding of Ti-6Al-4V was investigated. The results indicated that the welded microstructure composed of coarse needle α + β phases presenting disordered and multidirectional short needle morphology to make fracture mechanism complex. The coarse grains in weld seam with microhardness 536 HV were easy to be fractured in the region where welding heat input was ≥ 68.8 kJ/m. There exists flat curves of Ti, Al and V, Fe concentration distribution fluctuation to cause microstructural amplitude-modulated decomposition to increase the joint ductility and cleavage strength. The uneven distribution of the partial micropores located at the interior of the specimen acting as crack initiation sites lead to non-linear branch propagating path. The α + β interlaced structure results in the fracture location near α/β interface. The existence of stacking fault structure caused pile-up of dislocation to produce micropores to be new fracture initiation sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Xiaofeng, Han Zhong and Lou Xinfang 1999Trans. Non-ferrous Met. Soc. China 9 535
Dance B G I 1995Weld Res. 41 19
Han Zhong, Lin Haochao and Chen Xiaofeng 1999J. Chinese Electron Microsc. Soc. 18 536
Irving Bob 1994Weld. J. 73 31
Jinkeun Oh, Nack J. Kim and Sunghak Lee 2003Mater. Sci. Eng. A340 232
Keshava Murthy K and Sundaresan S 1998J. Mater. Sci. 33 817
Messler R W 1981Weld. J. 60 79S
Qi Yunlian, Deng Ju and Hong Quan 2000Mater. Sci. Eng. A280 177
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huiqiang, W., Jicai, F. & Jingshan, H. Microstructure evolution and fracture behaviour for electron beam welding of Ti-6Al-4V. Bull Mater Sci 27, 387–392 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704777
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02704777