Abstract
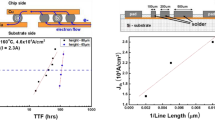
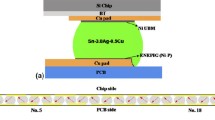
Electromigration may affect the reliability of flip-chip solder joints. Eutectic solder is a two-phase alloy, so its electromigration behavior is different from that in aluminum or copper interconnects. In addition, a flipchip solder joint has a built-in currentcrowding configuration to enhance electromigration failure. To better understand electromigration in SnPb and lead-free solder alloys, the authors prepared solder lines in v-grooves etched on Si (001). This article discusses the results of those tests and compares the electromigration failure modes of eutectic SnPb and SnAgCu flip-chip solder joints along with the mean-timeto-failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Brandenburg and S. Yeh,Proceedings of Surface Mount International Conference and Exhibition (Edina, MN: SMTA, 1998), pp. 337–344.
C.Y. Liu et al.,Appl. Phys. Lett., 75 (1) (1999), pp. 58–60.
C.Y. Liu, C. Chen, and K.N. Tu,J. Appl. Phys., 88 (2000), pp. 5703–5709.
Q.T. Huynh et al.,J. Appl. Phys., 89 (2001), pp. 4332–4335.
T.Y. Tom Lee, T.Y. Lee, and K.N. Tu,2001 IEEE ECTC Proceedings (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2001), pp. 558–563.
T.Y. Lee et al.,J. Appl. Phys., 89 (2001), pp. 3189–3194.
T.Y. Lee, K.N. Tu, and D. R. Frear,J. Appl. Phys., 89 (2001), pp. 4502–4508.
H. Gan and K.N. Tu, Accepted for2002 IEEE ECTC Proceedings (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2002).
W.J. Choi et al., Accepted for2002 IEEE ECTC Proceedings (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2002).
E.C.C. Yeh et al.,Appl. Phys. Lett., 80 (4) (2002), pp. 580–582.
X. Gu (unpublished Master degree thesis work, UCLA, 2001).
The International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductor (San Jose, CA: Semiconductor Industry Assoc., 1999).
I.A. Blech and C. Herring,Appl. Phys. Lett., 29 (1976), pp. 131–133.
K.N. Tu,Phys. Rev. B, 49 (1992), pp. 1409–1412.
D. Gupta, K. Vieregge, and W. Gust,Acta Mater., 47 (1) (1999), pp. 5–12.
H.B. Huntington,Diffusion in Solids: Recent Developments, ed. A.S. Nowick and J.J. Burton (New York: Academic, 1961), pp. 303–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gan, H., Choi, W.J., Xu, G. et al. Electromigration in solder joints and solder lines. JOM 54, 34–37 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02701847
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02701847