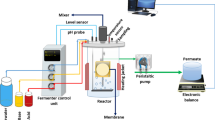
Abstract
A new approach to a membrane hybrid system by pre-coating the hollow fiber membrane with powdered activated carbons (PAC) was evaluated for its ability to minimize the fouling of the membrane and to remove organic material from wastewater. This preliminary study evaluates the performance of a microfiltration membrane coated with three kinds of PACs: wood based (WB), charcoal based (CB) and coconut based (HA). Broadly, two scenarios were evaluated: one with low amounts of PAC coated on the membrane and another at higher amounts of PAC coating. The results indicate that the pre-coated membrane can effectively arrest the fouling agents in the wastewater in reaching the membrane pores and thereby limit membrane fouling. Interestingly, it was also found that, without any pre-treatment or addition of PAC in the tank, the pre-coated membrane also had the ability to retain organic materials. For the hollow fiber microfilter membrane used in the study having surface area of 2.58×10-03 m2 surface area, pre-coating the membrane individually with 458 mg of HA-PAC, 497 mg of WB-PAC and 906 mg CB-PAC, the reduction in permeate flux was as little as 14–20% after 8 hours of each operation and the maximum organic removals was about 76%, for all the three kinds of PAC coatings. The type of PAC coated on the membrane and the amount coated could be the key factors in deciding the performance of the system. Although further studies are required, it is evident that the PAC pre-coated membrane system has great potential in successfully reducing membrane fouling, which could improve membrane life, enhance process performance and reduce membrane cleaning time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adham, S. S., Snoeyink, V. L., Clark, M. M. and Bersillon, J.-L., “Predicting and Verifying Organics Removal by PAC in an Ultrafiltration System,”J. AWWA,83, 81 (1991).
APHA,Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed., American Public Health Association, Washington, DC (1998).
AWWA Membrane Technology Research Committee, “Committee Report: Membrane Process in Potable Water Treatment,”J. AWWA,84, 59 (1992).
Brink, L. E. S., Elbers, S. J.G., Robbertsen, T. and Both, P., “The Anti-Fouling action of Polymers Preadsorbed on Untrafiltration and Microfiltration Membranes,”J. Memebr. Sci.,76, 281 (1993).
Crozes, G., Anselme, C. and Mallevialle, J., “Effect of Adsorption of Organic Matter on Fouling of Ultrafiltration Membranes,”J. Membr. Sci.,84, 61 (1993).
Jacangelo, J. G., Laine, J.-M., Cummings, E.W. and Adham, S. S., “UF with Pretreatment for Removing DBP Precursors,”J. AWWA,87, 100 (1995).
Kaiya, Y., Itoh, Y., Fujita, K. and Takizawa, S., “Study on Fouling Materials in the Membrane Treatment Process for Potable Water,”Desalination,106, 71 (1996).
Konieczny, K. and Klomfas, G., “Using Activated Carbon to Improve Natural Water Treatment by Porous Membranes,”Desalination,147, 109 (2002).
Kuberkar, V. and Davis, R.H., “Modeling of Fouling Reduction by Secondary Membranes,”J. Membr. Sci.,168, 243 (2000).
Lebeau, T., Lelievre, C., Buisson, H., Cleret, D., Van de Venter, L.W. and Cote, P., “Immersed Membrane Filtration for the Production of Drinking Water: Combination with PAC for NOM and SOCs Removal,”Desalination,117, 219 (1998).
Lim, A. L. and Bai, R., “Membrane Fouling and Cleaning in Microfiltration of Activated Sludge Wastewater,”J. Membr. Sci.,216, 279 (2003).
Ma, H., Bowman, C.N. and Davis, R.H., “Membrane Fouling Reduction by Backpulsing and Surface Modification,”J. Membr. Sci.,173, 191 (2000).
Thiruvenkatachari, R., Shim, W.G., Lee, J.W. and Moon, H., “Effect of Powdered Activated Carbon Type on the Performance of Adsorption-Microfiltration Submerged Hollow Fiber Membrane Hybrid System,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,21(5), 1044 (2004).
van Oers, C.W., Vorstman, M.A.G. and Kerkhof, P. J.A. M., “Solute Rejection in the Presence of a Deposited Layer during Ultrafiltration,”J. Membr. Sci.,107, 173 (1995).
Wakeman, R. J. and Williams, C. J., “Additional Techniques to Improve Microfiltration,”Sep. Purif. Technol.,26, 3 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thiruvenkatachari, R., Shim, W.G., Lee, J.W. et al. Powdered activated carbon coated hollow fiber membrane: Preliminary studies on its ability to limit membrane fouling and to remove organic materials. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 22, 250–255 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02701493
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02701493