Abstract
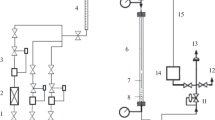
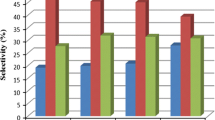
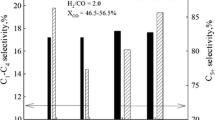
A three-phase slurry reactor has been employed to increase the CO2 conversion and decrease the selectivity of CO in the direct hydrogénation of CO2 to hydrocarbons, as it is beneficial for removal of the heat generated due to highly exothermic nature of the reaction. Experiments were conducted over iron-based catalysts (Fe-Cu-K-Al, dp,=45-75 Μm) in a slurry reactor. It was found that the slurry reactor is preferable to the fixed bed reactor. The productivity and selectivity of hydrocarbons in the slurry reactor appeared to be better than that in the fixed bed reactor for the hydrogénation of CO2. The CO2 conversion was increased with increasing reaction temperature (275-300 ‡C), pressure (1-2.5 MPa) or H2/CO2 ratio (2-5) in the three-phase slurry reactor. The CO2 conversion was increased with increasing the amount of CO2 fed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando, H., Xu, Q., Fujiwara, M., Matsumura, Y. and Souma, Y., “Hydro-carbon Synthesis from CO2 over Fe-Cu Catalysts”,Catal. Today,45, 229 (1998).
Aresta, M., “Perspectives of Carbon Dioxide Utilization in the Synthe-sis of Chemicals. Coupling Chemistry with Biotechnology”, Pro-ceedings of the 4th ICCDU, Kyoto, Japan, Sep. 7-11,114, Elsevier Science B.V. (1997).
Barrault, J., Forquy, C., Menezo, J. C. and Maurel, R., “Hydrocondensa-tion of CO2 (CO) over Supported Iron Catalysts”,React. Kinet. Catal. Lett.,17, 373(1981).
Bukur, D. B. and Lang, X., “Highly Active and Stable Iron Fischer-Trop-sch Catalyst for Synthesis Gas Conversion to Liquid Fuels”,Ind. Eng. Chem.Res.,38, 3270 (1999).
Choi, P. H., Jun, K. W., Lee, S. J., Choi, M. J. and Lee, K. W., “Hydro-génation of Carbon Dioxide over Alumina Supported Fe-K Cata-lysts”,Catal. Lett.,40, 115 (1996).
Choi, M. J., Kim, J. S., Kim, H. K., Kang, Y., Lee, S. B. and Lee, K. W., “Reduction Characteristics of CO2 over Fe-K Based Catalysts”,Korean J. Chem. Eng.,18, 646 (2001).
Dry, M. E, “The Sasol Route to Fuels”,CHEMTECH,Dec., 744 (1982).
Halmann, M., “Chemical Fixation of Carbon Dioxide: Methods for Re-cycling CO2 into Useful Products”, CRC Press, Inc., New York (1993).
Hong, J. S., Hwang, J. S., Jun, K. W., Sur, J. C and Lee, K. W., “Deacti-vation Study on a Coprecipitated Fe-Cu-K-Al Catalyst in CO2 Hy-drogénation”,Appl. Catal.,218, 53 (2001).
Jager, B. and Espinoza, R, “Advances in Low Temperature Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis”,Catal. Today,23, 17 (1995).
Kang, Y., Cho, Y. J., Woo, K. J. and Kim, S. D., “Diagnosis of Bubble Distribution and Mass Transfer in Pressurized Bubble Column with Viscous Liquid Medium”,Chem. Eng. Sci.,54, 4887 (1999).
Kim, S. D. and Kang, Y., “Heat and Mass Transfer in Three-Phase Flu-idized Bed Reactors-an Overview”,Chem. Eng. Sci.,52, 3639 (1997).
Lee, M. D., Lee, J. F. and Chang, C. S., “Hydrogénation of Carbon Di-oxide on Unpromoted and Potassium Iron Catalysts”,Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn.,62, 2756 (1989).
Nam, S. S., Lee, S. J, Kim, H., Jun, K. W., Choi, M. J. and Lee, K. W., “Catalytic Conversion of Carbon Dioxide into Hydrocarbons over Zinc Promoted Iron Catalysts”,Energy Convers. Mgmt.,38, 397 (1997).
Raje, A. P. and Davis, B. H., “Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis over Iron-Based Catalysts in a Slurry Reactor. Reaction Rates, Selectivities and Im-plications for Improving Hydrocarbon Productivity”,Catal. Today,36, 335 (1997).
Riedel, T., Schaub, G., Jun, K. W. and Lee, K. W., “Kinetics of CO2 Hy-drogenation on a K-Promoted Fe Catalyst”,Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.,40, 1355 (2001).
Sanders, E., Ledakowicz, S. and Deckwer, W. D., “Fischer-Tropsch Syn-thesis in Bubble Column Slurry Reactors on Fe/K-CatalysÇCana-dian J.Chem. Eng.,64, 133 (1986).
Tan, Y., Fujiwara, M., Ando, H., Xu, Q. and Souma, Y., “Syntheses of Isobutene and Branched Higher Hydrocarbons from Carbon Diox-ide and Hydrogen over Composite Catalysts”,Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.,38, 3225 (1999).
Xiaoding, X. and Moulijin, J. A., “Mitigation of CO2 by Chemical Con-version: Plausible Chemical Reactions and Promising Products”,Energy & Fuels,10, 350 (1996).
Xu, L., Wang, Q., Liang, D., Wang, X., Lin, L., Cui, W. and Xu, Y., “The Promotions of MnO and K2O to Fe/Silicate-2 Catalyst for the Pro-duction of Light Alkenes from CO2 Hydrogénation”,Appl. Catal.,173, 19 (1998).
Yan, S. R, Jun, K. W, Hong, J. S., Lee, S. B., Choi, M. J. and Lee, K. W., “Slurry-Phase CO2 Hydrogénation to Hydrocarbons over a Precipi-tated Fe-Cu-Al/K Catalyst: Investigation of Reaction Conditions”,Korean J. Chem. Eng.,16, 357 (1999).
Yan, S. R., Jun, K. W, Hong, J. S., Choi, M. J. and Lee, K. W., “Promo-tion Effect of Fe-Cu Catalyst for the Hydrogenation of CO2 and Ap-plication to Slurry Reactor”,Appl. Catal.,194, 63 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JS., Lee, SB., Kang, MC. et al. Promotion of CO2 hydrogénation to hydrocarbons in three-phase catalytic (Fe-Cu-K-Al) slurry reactors. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 20, 967–972 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02697307
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02697307