Abstract
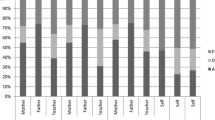
Seven locus of control scales—two designed for adults and five for children—were administered to about 200 adolescents. A content analysis revealed very little overlap between the scales which had practically no effect on the correlations between them. Correlations between the five children’s locus of control scale scores were highly significant, and nearly all greater than .50, but the two adult scales showed very little significant correlations either with each other, or any of the children’s scales. A number of demographic variables were correlated with total scale scores of which age was the most significant. The results are discussed in terms of the multidimensional nature of the concept, psychometric evaluation of locus of control beliefs in different age groups and the specificity of the concept in general.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman, A., & Hays, T. (1973). Relation between belief in after-life and locus of control.Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 41, 318.
Calhoun, L., Johnson, R., & Boardman, W. (1975). Attribution of depression to internal-external and stable-unstable causes: Preliminary investigations.Psychological Reports, 36, 463–466.
Cherlin, A., & Bourque, L. (1974). Dimensionality and reliability of the Rotter I-E scale.Sociometry, 37, 565–582.
Collins, B. (1974). Four components of the Rotter internal-external scale: belief in a difficult world, a just world, a predictable world and a politically responsive world.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 29, 381–391.
Crandall, V., Katkovsky, W., & Crandall, V. (1965). Children’s beliefs in their own control of reinforcement in intellectually-academic achievement situations.Child Development, 36, 91–109.
Dalquist, L., & Ottinger, D. (1983). Locus of control and peer status: A scale for children’s perceptions of social interactions.Journal of Personality Assessment, 47, 278–287.
Davis, J. (1983). Does authority generalize? Locus of control perceptions in Anglo-American and Mexican-American adolescents.Political Psychology, 4, 101–120.
Feather, N. (1975).Values in Education and Society. New York: Free Press.
Franklin, R. (1963). Youth’s expectancies about internal vs external control reinforcement related to N variables. Unpublished doctoral thesis. University of Purdue.
Frantz, R. (1980). The effect of early labour market experience upon internal-external locus of control among male workers.Journal of Youth and Adolescence.
Furnham, A. (1982). Locus of control and theological beliefs.Journal of Psychology and Theology, 10, 130–136.
Furnham, A. (1986). Economic locus of control.Human Relations, 39, 29–43.
Furnham, A., & Henderson, M. (1982). A content analysis of four personality inventories.Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38, 818–825.
Furnham, A., & Henderson, M. (1984). Assessing assertiveness: A content and correlational analysis of five assertiveness inventories.Behavioural Assessment, 6, 79–88.
Gurin, P., Gurin, G., Lao, R., & Beattie, M. (1969). Internal-external control in the motivation dynamics of Negro youth.Journal of Social Issues, 25, 29–53.
James, W., & Rotter, J. (1958). Partial and 100% reinforcement under chance and skill conditions.Journal of Experimental Psychology, 55, 397–403.
Klandermans, P. (1983) Rotters Internal/External Scale and socio-political action-taking: The balance of 20 year’s research.European Journal of Social Psychology, 13, 399–415.
Lau, R. (1982). Origins of health locus of control beliefs.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 42, 322–334.
Lau, R., & Ware, J. (1981). Refinements in the measurement of health-specific locus-of-control beliefs.Medical Care, 19, 1147–1158.
Lawler, E. (1971).Pay and organizational effectiveness. A psychological review. New York: McGraw Hill.
Levensohn, H. (1974). Activism and powerful others: Distinctions within the concept of internal-external control.Journal of Personality Assessment, 38, 377–383.
Louden, D. (1978). Internal vs external control in Asian and West Indian adolescents in Britain.Journal of Adolescence, 1, 283–296.
Ludenia, K., & Donham, G. (1983). Dental out patients: Health locus of control correlates.Journal of Clinical Psychology, 39, 854–858.
Mirels, H. (1970). Dimensions of internalvs. external control.Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 34, 226–228.
Mischel, W., Zeiss, R., & Zeiss, A. (1974). Internal-external control and persistence: Validation and implications of the Stanford preschool internal-external scale.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 29, 265–278.
Nowicki, S., & Strickland, B. (1973). A locus of control scale for children.Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 40, 148–155.
Parcel, G., & Meyer, M. (1978). Development of an instrument to measure children’s health locus of control.Health Education Monographs, 6, 149–159.
Paulus, D., & Christie, R. (1981). Spheres of control: An interactionsist approach to assessment of perceived control. In H. Lefcourt (Ed.),Research with the locus of control construct (Vol. 1). New York: Academic Press.
Paulus, D. (1983). Sphere-specific measures of perceived control.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 44, 1253–1265.
Phares, E. (1957). Expecting changes in skill and chance situations.Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 54, 339–342.
Phares, E. (1976).Locus of control in personality. Morristown: General Learning Press.
Phares, E. (1984).Research with the locus of control construct. Vol. 1 and 2. New York: Academic Press.
Rotter, J. (1966). Generalized expectances for internal versus external control of reinforcement.Psychological Monographs, 80, 509.
Saltzer, E. (1982). The weight locus of control (WLOC) scale: A specific measure for obesity research.Journal of Personality Assessment, 46, 620–628.
Sanger, S., & Walker, H. (1972). Dimensions of internal-external control and the women’s liberation movement.Journal of Social Issues, 28, 115–129.
Schneider, J., & Parsons, O. (1970). Categories on the locus of control scale and cross-cultural comparisons in Denmark and the United States.Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 2, 131–138.
Sexton, P., Leak, G., & Toemies, F. (1980). Relationship of locus of control and modernity to certainty of religious beliefs.Psychological Reports, 46, 1285–1286.
Snyder, M. (1974). Self-monitoring of expressive behavior.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 30, 526–537.
Sosis, R., Strickland, B., & Haley, W. (1980). Perceived locus of control and beliefs about astrology.Journal of Social Psychology, 110, 65–71.
Spector, P. (1982). Behavior in organizations as a function of employees’ locus of control.Psychological Bulletin, 91, 482–497.
Tanaka-Matsumi, J., & Kameoka, V. (1986). Reliabilities and concurrent validities of popular self-report measures of depression, anxiety and social desirability.Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 54, 320–333.
Wallston, K., & Wallston, B. (1981). Health locus of control scales. In H. Lefcourt (Ed.),Research with the locus of control construct (Vol. 1). New York: Academic Press.
Wallston, K., Wallston, B., & Devellis, R. (1978). Development of the multidimensional health locus of control (MHLC) scale.Health Education Monographs, 6, 160–169.
Waters, L., Bathis, N., & Waters, C. (1975). Protestant ethic attitudes among college students.Educational and Psychological Measurement, 35, 447–450.
Weiner, B. (1980).Human motivation. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston.
Weiner, B., Beckhauser, H., Meyer, W., & Cook, R. (1972). Causal ascriptions and achievement behavior: A conceptual analysis of effort and reanalysis of locus of control.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 21, 239–248.
Wood, D., & Letak, J. (1982). A mental-health locus of control scale.Personality and Individual Differences, 3, 84–87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furnham, A. A content and correlational analysis of seven locus of control scales. Current Psychology 6, 244–255 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02686651
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02686651