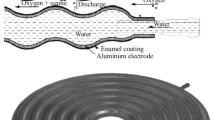
Abstract
Based on crystallizing alkaline boron-titanium-silicate glasses with oxide additives of the R2O type, ground and cover chemically stable enamels for steel have been developed, which exhibit high chemical resistance and high electrical conductivity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Safety Regulations with Respect to Static Electricity in Chemical, Petrochemical, and Oil Refining Industries [in Russian], Khimiya, Moscow (1973).
V. V. Tavgen’ and L. G. Khodskii, “On certain properties of glasses in the Na2O B2O3 - TiO2 - SiO2 system,”Vestsi AN BSSR, Ser. Khim. Navuk, No. 1, 53 57 (1978).
V. V. Tavgen’ and L. G. Khodskii, “On reduction processes in alkaline boron-titanium-silicate glasses fired on steel substrate,”Vestsi AN BSSR, Ser. Khim. Navuk, No. 6, 117–121 (1979).
V. V. Tavgen’ and L. G. Khodskii, “Electrical conductivity of rutile-bearing glass ceramic materials doped with R2O5 oxides,”Vestsi AN BSSR. Ser. Khim. Navuk, No. 2, 101–104 (1981).
K. Hauffe,Reactions Inside Solid Bodies and on Their Surfaces, Part 1 [Russian translation], IL, Moscow (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Steklo i Keramika, No. 5, pp. 33–34, May, 2000.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tavgen’, V.V. Glass ceramic enamels with increased conductivity. Glass Ceram 57, 183–184 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02681272
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02681272