Abstract
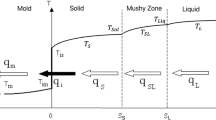
Rapid melting and solidification of a semi-infinite substrate subjected to a high intensity heat flux over a circular region on its bounding surface moving with a constant velocity is considered. General expressions are developed for the coefficients in the finite difference equation governing the heat transfer in moving orthogonal curvilinear coordinate systems. These expressions are reduced to their specific forms in terms of dimensionless nodal temperature and enthalpy for a moving oblate spheroidal coordinate system. Quasisteady state conditions are assumed and the thermal properties of the substrate in the liquid and solid phase are considered constant and equal. It is also assumed that the substrate melts and solidifies at a single temperature. Temperature distributions in the molten region and the adjacent heat affected zone are computed along with the liquid-solid interface shape, its velocity and other important solidification variables. Both uniform and Gaussian heat flux distributions within the circular region are considered. The results are presented in their most general form—in terms of dimensionless numbers when possible. Specific criteria for the melting of the substrate are established. It is shown that the three variables, absorbed heat fluxq, the radius of the circular regiona and the velocity of the moving fluxU, could be combined into two independent variables. That is, the dimensionless temperature distribution in the metal pool and the solid substrate remain the same as long as the productsqa andUa orU/q are kept constant. The effect of these variables on cooling rate in the liquid and the ratio of temperature gradient to growth rate at the solid-liquid interface are discussed using an aluminum substrate as an example.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. C. Hsu, S. Chakravorty, and R. Mehrabian:Met. Trans. B, 1978 vol. 9B, p. 221.
S. C. Hsu, S. Kou, and R. Mehrabian:Met. Trans. B, 1980 vol. 11B, p. 29.
D. Rosenthal:Weld. J., 1941 vol. 20, Research Supplement, p. 2205.
G. E. Schneider, A. B. Strong, and M. M. Yovanovich:Proceedings of International Symposium on Computer Methods for Partial Differntial Equations, R. Vichnevetsky, ed., pp. 312–17, AICA, New Brunswick, NJ, 1975.
F. B. Hilderbrand:Advanced Calculus for Applications, Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 1962.
N. Shamsunder and E. M. Sparrow:J. Heat Transfer, 1975, p. 333.
G. Horvay and J. W. Cahn:Acta Metall., 1961, vol. 9, p. 695.
G. E. Nash and M. E. Glicksman:Acta Metall., 1974, vol. 22, p. 1283.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
S. KOU and S. C. HSU, formerly Research Associate and Graduate Student, respectively, at the University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois.
R. MEHRABIAN, formerly Professor in the Department of Metallurgy and Mining Engineering and the Department of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois .
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kou, S., Hsu, S.C. & Mehrabian, R. Rapid melting and solidification of a surface due to a moving heat flux. Metall Trans B 12, 33–45 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02674756
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02674756