Abstract
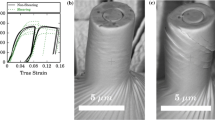
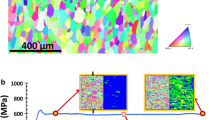
Tantalum plate produced by a forging-rolling sequence was subjected to high plastic shear strains(γ = 1 → 5.5) at high strain rates (∼4 × 104 s-1) in two experimental configurations: (a) a special hat-shaped geometry and (b) thin disks deformed in a split Hopkinson bar. In parallel experiments, the constitutive behavior of the same material was established through quasi-static and dynamic compression tests at ambient and elevated temperatures. The microstructure generated at high strain rates and retained by rapid cooling from a narrow (200-μm) deformation band progresses from dislocated, to elongated cells, to banded structures, and finally, to subgrains as the shear strain increases from 0 to 5.5. The temperature rise predictions from the constitutive description of the material indicate that the temperature reaches values of 800 K, and it is proposed that thermal energy is sufficient to produce a significant reorganization of the deformation substructure, leading to a recovered structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.W. Armstrong, V. Ramachandran, and F.J. Zerilli: inAdvances in Materials and Their Applications, P. Rama Rao, ed., Wiley Eastern Ltd., New Delhi, 1988, p. 201.
A. Seeger:Phil. Mag., 1956, vol. 1, pp. 651–62.
J.E. Dorn and S. Rajnak:Trans. AIME, 1964, vol. 230, pp. 1052–64.
L.A. Gypen and A. Deruyttere:J. Less-Common Met., 1982, vol. 86, pp. 219–40.
M. Werner:Phys. Status Solidi, 1987, vol. 104, pp. 63–78.
H. Koizumi, H.O.K. Kirchner, and T. Suzuki:Ada Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 41, pp. 3483–93.
F.J. Zerilli and R.W. Armstrong:J. Appl. Phys., 1986, vol. 61, pp. 1816–25.
F.J. Zerilli and R.W. Armstrong:J. Appl. Phys., 1990, vol. 68, pp. 1580–91.
J.H. Bechtold:Acta Metall, 1955, vol. 3, pp. 249–54.
A. Gilbert, D. Hull, W.S. Owen, and C.N. Reid:J. Less-Common Met, 1962, vol. 4, pp. 399–408.
T.E. Mitchell and W.A. Spitzig:Acta Metall, 1965, vol. 13, pp. 1169–79.
B.L. Mordike and G. Rudolf:J. Mater. Sci, 1967, vol. 2, pp. 332–38.
K.G. Hoge and A.K. Mukherjee:J. Mater. Sci., 1977, vol. 12, pp. 1666–72.
D. Lassila and G.T. Gray III:J. Phys., Colloq., 1991, vol. 1, pp. 19–26.
A.C. Gurevitch, L.E. Murr, H.K. Shih, C.-S. Niou, A.H. Advani, D. Manuel, and L. Zernow:Mater. Charact, 1993, vol. 30, pp. 201–16.
H.K. Shih, L.E. Murr, C.-S. Niou, and L. Zernow:Scripta. Metall. Mater., 1993, vol. 29, pp. 1291–96.
L.E. Murr, H.K. Shih, and C.-S. Niou:Mater. Charact, 1994, vol. 33, pp. 65–74.
C. Feng and P. Kumar:J. Met., 1989, vol. 41, pp. 40–45.
J.B. Clark, R.K. Garrett, Jr., T.L. Jungling, R.A. Vandermeer, and C.L. Vold:Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 2039–48.
J.B. Clark, R.K. Garrett, T.L. Jungling, and R.I. Asfahani:Metall. Trans. A, 1992, vol. 23A, pp. 2183–91.
L.W. Meyer and S. Manwaring: inMetallurgical Applications of Shock-Wave and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena, L.E. Murr, K.P. Staudhammer, and M.A. Meyers, eds., Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, 1986, p. 657.
M.A. Meyers, G. Subhash, B.K. Kad, and L. Prasad:Mech. Mater., 1994, vol. 17, pp. 175–99.
U.R. Andrade, M.A. Meyers, K.S. Vecchio, and A.H. Chokshi:Acta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 42, pp. 3183–95.
M.A. Meyers, U.R. Andrade, and A.H. Chokshi:Metall. Mater. Trans., in press.
S. Nemat-Nasser, J.B. Isaacs, and J.E. Starrett:Proc. R. Soc. London A, 1991, vol. A20, pp. 371–91.
S. Nemat-Nasser, Y.-F. Li, and J.B. Isaacs:Mech. Mater., 1994, vol. 17, pp. 111–34.
G.R. Johnson and W.H. Cook: inProc. 7th Int. Symp. on Ballistics, The Hague, The Netherlands, 1983, pp. 1–7.
G.R. Johnson and T.J. Holmquist:J. Appl. Phys., 1988, vol. 64, pp. 3901–10.
C.L. Wittman, CM. Lopatin, J.P. Swensen, and T.J. Holmquist: inHigh Strain Rate Behavior of Refractory Metals and Alloys, R. Asfahani, E. Chen, and A. Crowson, eds., TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1992, pp. 167–78.
T.W. Wright:J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1990, vol. 38, pp. 515–30.
T.W. Wright:Mech. Mater., 1994, vol. 17, pp. 215–22.
R.E. Reed-Hill:Physical Metallurgy Principles, 2nd ed., PWS Engineering, Boston, MA, 1973, pp. 284–90.
W. Köck and P. Paschen:J Met, 1989, vol. 41 (10), pp. 33–39.
D. Beckenhauer, P. Niessen, and P. Pick:J. Mater. Sci. Lett, 1993, vol. 12, pp. 449–50.
L.E. Murr, C.-S. Niou, and C. Feng:Scripta Metall. Mater., 1994, vol. 31, pp. 297–302.
M.J. Worswick, N. Qiang, P. Niessen, and R.J. Pick: inShock-Wave and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena in Materials, M.A. Meyers, L.E. Murr, and K.P. Staudhammer, eds., Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, 1992, pp. 87–95.
C.L. Wittman, R.K. Garrett, J.B. Clark, and CM. Lopatin: inShock- Wave and High-Strain-Rate Phenomena in Materials, M.A. Meyers, L.E. Murr, and K.P. Staudhammer, eds., Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, 1992, pp. 925–33.
C.O. Mgbokwere, S.R. Nutt, and J. Duffy:Mech. Mater., 1994, vol. 17, pp. 97–110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article is based on a presentation made in the symposium “Dynamic Behavior of Materials,” presented at the 1994 Fall Meeting of TMS/ASM in Rosemont, Illinois, October 3-5, 1994, under the auspices of the TMS-SMD Mechanical Metallurgy Committee and the ASM-MSD Flow and Fracture Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyers, M.A., Chen, Y.J., Marquis, F.D.S. et al. High-strain, high-strain-rate behavior of tantalum. Metall Mater Trans A 26, 2493–2501 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02669407
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02669407