Abstract
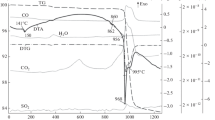
Chalcopyrite reacts readily with SO3 at about 100°C to form water-soluble sulfates; the reaction is approximately: 3CuFeS2+26SO3→3CuSO4+FeSO4+Fe2(SO4)3+25SO2 The presence of about 4 pct O2 in the gas phase greatly accelerates the reaction presumably due to the complete transformation of ferrous into ferric sulfate in an extremely porous form: 2CuFeS2+17SO3+1/2O2→2CuSO4+Fe2(SO4)3+16SO2 A stoichiometric mixture of SO2+1/2O2 behaves towards chalcopyrite in nearly the same way as SO3 although only in the temperature range 350° to 700°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. W. Sommer and H. H. Kellogg:Trans. TMS-AIME, 1959, vol. 215, pp. 742–44.
H. Jonas and H. Guth:German Patent 940115 (1956).
F. Habashi and R. Dugdale:Z. Anorg. Allgem. Chem., 1971, vol. 380, pp. 322–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
FATHI HABASHI and RAYMOND DUGDALE, formerly with the Anaconda Co., Tucson, Ariz.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Habashi, F., Dugdale, R. The action of sulfur trioxide on chalcopyrite. Metall Trans 4, 1553–1556 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02668007
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02668007