Abstract
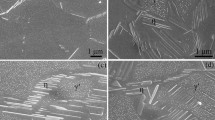
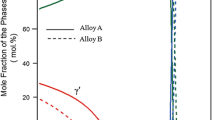
Recent studies on the room-temperature fracture behavior of Ni3Al-Zr alloys after preexposure at elevated temperatures show various types of intergranular failure. In the presently studied Ni78Al21Zr1B0.2 alloy, a strong intergranular fracture tendency at room temperature has been found after preexposure at 750 °C, which is caused by the grain boundary precipitation in this alloy. After short-term exposure above 1200 °C and bending fracture at room temperature, the alloy also suffers intergranular embrittlement due to grain boundary melting. The intergranular fracture appearance is quite different from that observed in a previous study for a Ni77.4Al22Zr0.6B0.2 alloy after air exposure for 100 hours at 1200 °C. In that case, the intergranular fracture was accompanied by grain boundary diffusion (invasion) and segregation of oxygen. The mechanisms of these types of grain boundary failure are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.H. Chuang, Y.C. Pan, and S.E. Hsu:Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 1801–09.
K. Aoki and O. Izumi:J. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1979, vol. 43, pp. 1190–96.
C.T. Liu, CL. White, and J.A. Horton:Acta Metall., 1985, vol. 33, pp. 213–29.
S. Taniguchi, T. Shibata, and H. Tsuruoka:Oxid. Met., 1986, vol. 26, pp. 1–18.
Y. Mishima, S. Ochiai, N. Hanao, M. Yodogawa, and T. Suzuki:Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met., 1986, vol. 27, pp. 656–64.
S.E. Hsu, N.N. Hsu, C.H. Tong, P.H. Hu, and J.Y. Ma:Proc. of the 1986 Annual Conf. of the Chinese Society for Materials Science, June 21–22, 1986, Taichung, Taiwan, 1986, pp. 423–29.
S.Y. Lee, S.J. Liu, C.H. Tong, and S.E. Hsu: Proc. of the1987 Annual Conf. of the Chinese Society for Materials Science, May 23–24, 1987, Hsinchu, Taiwan, pp. 303–07.
W. Dienst: inHoch-Temperatur-Werkstoffe, Werkstofftechnische Verlag, Karlsruhe, Germany, 1978, p. 115.
A.U. Seybolt and J.H. Westbrook:Acta Metall., 1964, vol. 12 pp. 449–58..
P.A. Turner, R.T. Pascoe, and C.W.A. Newey:J. Mater. Sci., 1966, vol. 1, pp. 113–15.
P.A. Turner, R.T. Pascoe, and C.W.A. Newey:J. Mater. Sci., 1967, vol. 2, p. 197.
A.U. Seybolt and J.H. Westbrook:J. Mater. Sci., 1967, vol. 2, pp. 196–97.
Binary Alloy Phase Diagram, T.B. Massalski, J.L. Murray, L.H. Bennett, and H. Baker, eds., ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1986, p. 1779.
J.D. Kuenzly and D.L. Douglass:Oxid. Met., 1974, vol. 8, pp. 139–78.
R.F. Decker and C.T. Sims: inThe Superalloys, C.T. Sims and W.C. Hagel, eds., John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York, NY, 1972, p. 33.
T.H. Chuang:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1991, vol. A141, pp. 169–78.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Formerly Doctoral Candidate, Institute of Materials Science and Engineering, National Taiwan University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chuang, T.H., Pan, Y.C. On the mechanisms of high-temperature intergranular embrittlements of Ni3Al-Zr Alloys. Metall Trans A 23, 1187–1193 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02665050
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02665050