Abstract
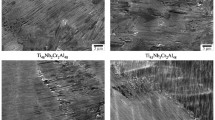
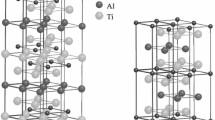
A detailed study has been carried out to determine the crystal structure of a stable Ti-rich second phase seen in Ll2 Al3Ti-base alloys and the effect of the phase on the mechanical properties. As determined by energy-dispersive X-ray analysis in a scanning electron microscope (SEM), the phase contains not only Ti and Al in a 2:1 ratio, but also N. Using the X-ray powder diffraction technique and computer simulations, the phase was identified to be Ti2NAl, which has a hexagonal structure (Cr2CAl-type) with lattice parametersa = 2.995 Å andc = 13.61 Å. The formation of the phase does not seem to be dependent on the Al/Ti ratio but appears to be controlled by the amount of N existing in the Ti starting material. Based on experimental observations of cracks formed in Ll2 Al3Ti specimens deformed in compression or fracturedin situ in an Auger microscope, it was found that a small volume fraction of the Ti2NAl precipitates plays an important role in the early stages of brittle failure: cracks often initiate within the second phase or at the interface between the second phase and the Ll2 matrix.
Similar content being viewed by others
Rererences
Z.L. Wu, D.P. Pope, and V. Vitek:Scripta Metall., 1990, vol. 24, pp. 2187–90.
Z.L. Wu, D.P. Pope, and V. Vitek:Scripta Metall., 1990, vol. 24, pp. 2191–96.
V. Ya, Markiv, V.V. Burnashova, and V.P. Ryabov:Akad. Nauk. Ukr. SSR Metall., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 103–10.
A. Siebold:Z. Metallkd., 1981, vol. 72, pp. 712–19.
S. Mazdiyasm, D.B. Miracle, D.M. Dimiduk, M.G. Mendiratta, and P.R. Subramaniam:Scripta Metall., 1989, vol. 23, pp. 327–31.
A. Raman and K. Schubert:Z. Metallkd., 1965, vol. 56, pp. 99–104.
K.S. Kumar:Int. Mater. Rev., 1990, vol. 35, pp. 293–327.
A. Loiseau and A. Lasalmonie:Acta Crystallogr., 1983, vol. 39, pp. 580–87.
A. Loiseau and A. Lasalmonie:Mater. Sci. Eng., 1984, vol. 67, pp. 163–68.
M.J. Kaufman, D.G. Konitzer, R.D. Shull, and H.L. Fraser:Scripta Metall., 1986, vol. 20, pp. 103–08.
W. Jeitschko, H. Nowotny, and F. Benesovsky:Monatsh. Chem., 1963, vol. 94, pp. 672–76.
Z.L. Wu, D.P. Pope, and V. Vitek:Acta Metall., 1994, vol. 42, pp. 519–26.
R. Vaughan:Energy-Dispersion X-ray Microanalysis, Kevex Instruments, Inc., San Carlos, CA, 1989.
P. Villars and L.D. Calvert:Pearson’s Handbook of Crystallographic Data for Intermetallic Phases 2, ASM, Metals Park, OH, 1985.
P.B. Hirsch, A. Howie, R.B. Nicholson, D.W. Pashley, and M.J. Whelan:Electron Microscopy of Thin Crystals, Butterworth, London, 1967.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Z.L., Pope, D.P. & VITEK, V. Ti2NAI in L12 AI3Ti- base alloys. Metall Mater Trans A 26, 521–524 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02663902
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02663902