Abstract
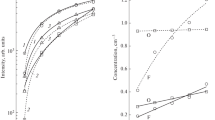
Silicon and silicon dioxide have been Reactive Ion Etched in a CF4 plasma using a diode sputtering configuration to achieve etching. Pressures ranged from 20 to 100 millitorr and power densities to the RF cathode were between 0.1 and 1.0 W/cm2. The effect of cathode material on the quality of etched surfaces and on etch rates has been investigated. It has been observed that the etch rate of silicon decreases as the area of silicon exposed to the plasma is increased and that this silicon loading effect is strongly influenced by the material covering the balance of the cathode. For instance, the silicon loading effect is much more pronounced when silicon dioxide rather than aluminum is used to cover the balance of the cathode. This silicon loading effect was investigated further by varying RF power. It was found that loading a silicon dioxide covered cathode with silicon wafers decreases the dependence of silicon etch rate on power. The silicon dioxide etch rate and its dependence on RF power are the same whether silicon, silicon dioxide or aluminum is used to cover the balance of the cathode. Possible explanations for these experimental results will be discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.N. Yu, R.H. Dennard, T.H.P. Chang, CM. Osburn, V. DiLonardo and H.E. Luhn, J. Vac. Sci. Technol.12, 1197 (1975).
J. Bondur, J. Vac. Sci. Technol.13, 1023 (1976).
G. Schwartz, L.B. Zielinski and T. Schopen, “Reaction Ion Etching”, inEtching for Pattern Definition, p. 122 (The Electrochemical Society, Inc., 1976).
R. Heinecke, Solid State Electronics18, 1146 (1975).
A.B. Burg, “Volatile Inorganic Fluorides”, inFlurorine Chemistry, Vol. 1, ed. by J.H. Simons (Academic Press, New York, 1950).
H. Abe, Proceedings of the Sixth Conference on Solid State Devices, J. Japan Soc. Appl. Phys.44, 289 (1975).
R.W. Kirk, “Applications of Plasma Technology to the Fabrication of Semiconductor Devices”, inTechniques and Applications of Plasma Chemistry, p. 357, ed. by J.R. Hollahan (Wiley and Sons, New York, 1974).
J. Keller and D. Weston, “Photoresist Loss and Etch Rates of Silicon Dioxide and Silicon Nitride During Plasma Processing”, Kodak Microelectronic Seminar, 1975.
G. Schwartz, private communication (1975).
R. Kumar and C. Ladas, “Characterization of Plasma-Etching for Semiconductor Applications”, IEDM Tech. Digest, p. 27, 1975.
N. Chou, private communication (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ephrath, L.M. The effect of cathode materials on reactive ion etching of silicon and silicon dioxide in a CF4 plasma. J. Electron. Mater. 7, 415–428 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02655646
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02655646