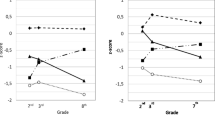
Abstract
The major findings of several research projects that investigated dyslexic college students are summarized in this paper. Consistent findings of these investigations led to the following conclusions. 1) Developmental dyslexia is a syndrome made up of the following four symptoms: slow rate of reading, error-prone oral reading, poor written spelling, and grammatically incorrect writing; 2) all these symptoms could be traced to a poor mastery of the grapheme-phoneme relational rules; 3) developmental dyslexia can be found in subjects who appear to have adequate oral language skills; 4) ex-dyslexics who appear to be “poor spellers but good readers” have subtle reading deficits; and 5) the 20 dyslexic subjects investigated appear to constitute a homogeneous group which raises questions regarding dyslexia subtypes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaron, P. G., Baxter, C. F., and Lucenti, J. 1980. Developmental dyslexia and acquired alexia: Two sides of the same coin?Brain and Language 11:1–11.
Aaron, P. G., Baker, C., and Hickox, G. 1982. In search of the third dyslexia.Neuropsychologia 20:203–208.
Aaron, P. G., Bommarito, T., and Baker, C. 1984. The three phases of developmental dyslexia.In R. N. Malathesha and H. Whitaker (eds.).Dyslexia: A global issue. The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff.
Aaron, P. G., Olsen, J., and Baker, C. 1985a. Dyslexic college student—Is he also dysphasic?Cognitive Neuropsychology 2:115–147.
Aaron, P. G., Tully, N., and Baker, C. 1985b. Specific reading disability and general reading disability. (Unpublished manuscript).
Aaron, P. G. 1985c. The paradoxical relationship between developmental dyslexia and intelligence.Perceptual and Motor Skills 61:1251–1261.
Bissex, G. L. 1980.Gnys at Wrk: A child learns to write and read. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Blank, M., and Bruskin, C. 1984. The reading of content and noncontent words by dyslexics.In S. J. White and V. Teller, (eds.). Discourses in reading and linguistics.Annals of the New York Academy of Science 443:59–70.
Bock, K. J. 1982. Toward a cognitive psychology of syntax: Information processing contributions to sentence formation.Psychological Review 89:(1),1–47.
Boder, E. 1973. A diagnostic approach based on three atypical reading-spelling patterns.Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 15:663–687.
Boder, E., and Jarrico, S. 1982.Boder Reading and Spelling Pattern Test: A diagnostic screening test for developmental dyslexia. New York: Grune and Stratton.
Bradley, D., Garrett, M., and Zurif, E. 1980. Syntactic deficits in Broca’s aphasia.In D. Caplan (ed.).Biological Studies of Mental Process. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Cherry, C. 1953. Some experiments on the recognition of speech with one and two ears.Journal of Acoustic Society of America 25:975–979.
Chomsky, C. 1969. The acquisition of syntax in children from 5 to 10.Research Monograph No. 57. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
Coltheart, M. 1978. Lexical access in simple reading tasks.In G. Underwood, (ed.).Strategies in Information Processing. London: Academic Press.
Coltheart, M., Masterson, J., Byngs, J., Prior, E., and Riddoch, B. 1983. Surface dyslexia.Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology 35:469–495.
Cook, L. 1981. Misspelling analysis in dyslexia. Observation of developmental strategy shifts.Bulletin of the Orton Society 31:123–134.
Cromer, R. F. 1970. Children are nice to understand: Surface structure clues for the recovery of deep structure.British Journal of Psychology 61:397–408.
Doehring, D. G., Trites, R. L., Patel, P. G., and Fiedorowicz, C. 1981.Reading Disabilities: The interaction of reading, language, and neuropsychological deficits. New York: Academic Press.
Durrell, D. D. 1955.Durrell Analysis of Reading Disability. New York: Harcourt, Brace, Jovanovich.
Ellis, A. W. 1985. The cognitive neuropsychology of developmental and acquired dyslexia: A critical survey.Cognitive Neuropsychology 2:169–205.
Frith, U. 1980. Unexpected spelling problems.In U. Frith (ed.).Cognitive Processes in Spelling. London: Academic Press.
Gibson, E. J., and Guinet, L. 1971. Perception of inflections in brief visual presentations of words.Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior 10:182–189.
Jorm, A. F. 1983.The Psychology of Reading and Spelling Disabilities. London: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
Kean, M. L. 1977. The linguistic interpretation of aphasic syndromes. Agrammatism in Broca’s aphasia, an example.Cognition 5:9–46.
Kleiman, G. M. 1975. Speech recoding in reading.Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior 14:323–329.
Kroll, N. E., Parks, T., Parkensen, S. R., Bieber, S. L., and Johnson, A. L. 1970. Short-term memory while shadowing: Recall of visually and aurally presented letters.Journal of Experimental Psychology 85:220–224.
Lee, L. 1974.Developmental Sentence Analysis. Evanston, IL: Northwestern University Press.
Liberman, I. Y., Liberman, A. M., Mattingly, I. Y., and Shankweiler, D. 1980. Orthography and the beginning reader.In J. F. Kavanaugh and R. L. Venezky (eds.).Orthography, Reading, and Dyslexia. Baltimore, MD: University Park Press.
Malatesha, R. N., and Dougan, D. R. 1982. Clinical subtypes of developmental dyslexia: resolution of an irresolute problem.In R. N. Malatesha and P. G. Aaron, (eds.).Reading Disorders: Varieties and treatments. New York: Academic Press.
Malatesha, R. N., Phillips, S. and Aaron, P. G. 1986. Specific spelling disability and specific reading disability—are they dissociable? Unpublished manuscript.
Marslen-Wilson, W. P. 1975. Sentence perception as an interactive parallel process.Science 189:226–288.
Mattis, S., French, J., and Rapin, I. 1975. Dyslexia in children and adults: Three independent neuropsychological syndromes.Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 17:150–163.
Mitchell, D. C. 1982.The Process of Reading. New York: John Wiley.
Moats, L. C. 1983. A comparison of the spelling errors of older dyslexic and second grade normal children.Annals of Dyslexia 33:121–140.
Perfetti, E. A., and Hogaboam, T. 1975. Relationship between single word decoding and reading comprehension skill.Journal of Educational Psychology 67:461–469.
Phillips, S., Taylor, B., and Aaron, P. G. 1985. Developmental dyslexia: Subtypes or substages? Paper presented at theIndiana Psychological Association Meeting, October, 1985, Indianapolis.
Pirozzolo, F. J. 1979.The Neuropsychology of Developmental Reading Disorders. New York: Praeger.
Snowling, M. J. 1980. The development of grapheme-phoneme correspondence in normal and dyslexic readers.Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 29:294–305.
Sticht, T. G. 1984. Rate of comprehending by listening and reading.In J. Flood, (ed.).Understanding Reading Comprehension. Newark, DL.: International Reading Association.
Thompson, L. 1969. Language disabilities in men of eminence.Bulletin of the Orton Society XIX:113–120.
Venezky, R. L. 1970.The Structure of English Orthography. The Hague: Mouton.
Wijk, A. 1966.Rules of Pronunciation for the English Language: An account of the relationship between English spelling and pronunciation. London: Oxford University Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aaron, P.G., Phillips, S. A decade of research with dyslexic college students: A summary of findings. Annals of Dyslexia 36, 44–66 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02648021
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02648021