Summary
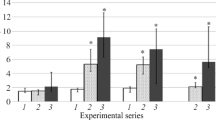
Epithelial cell enriched primary cultures were established from the rat and the rabbit epididymis. Epithelial cell aggregates, obtained after pronase digestion of minced epididymis, attached to the culture dish and after 72 h in vitro spread out to form discrete patches of cells. These cells have an epithelioid morphology and form a monolayer of closely apposed polygonal cells where DNA synthesis, as judged by [3H]thymidine uptake, is very low. Inl-valine medium the nonepithelial cell contamination was no more than 10% in rat and rabbit epididymal primary cultures. The labeling index of rat epididymal cells cultured ind-valine medium was significantly lower than that of cells cultured inl-valine medium. In contrast, the labeling index of rabbit epididymal cells cultured ind-valine medium was significantly higher than that of cells cultured inl-valine medium. Cytosine arabinoside decreased the number of labeled cells in bothl-valine andd-valine cultures. From these results, it appears thatd-valine is a selective agent for rat epididymal epithelial cells, but not for rabbit epithelial cells, and that cytosine arabinoside is a simple and effective means to control the proliferation of fibroblast-like cells in both rat and rabbit epididymal cell cultures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reid, B. L.; Cleland, K. W. The structure and function of the epididymis. I. the history of the rat epididymis. Aust. J. Zool. 5: 223–246; 1957.
Hamilton, D. W. Structure and function of the epithelium lining the ductuli efferentes, ductus epididymidis, and ductus deferens in the rat. Greep, R. O.; Astwood, E. B. eds. Handbook of physiology. Endocrinology. Vol. 5. Washington, D.C.: American Physiological Society; 1975: 259–301.
Sun, E. L.; Flickinger, C. J. Development of cell types and of regional differences in the postnatal rat epididymis. Am. J. Anat. 154: 27–56; 1979.
Nicander, L. On the regional history and cytochemistry of the ductus epididymis in rabbits. Acta Morphol. Neerl. Scand. 1: 99–118; 1957.
Jones, R.; Hamilton, D. W.; Fawcett, D. W. Morphology of the epithelium of the extratesticular rete testis, ductuli efferentes and ductus epididymidis of the adult male rabbit. Am. J. Anat. 156: 373–400; 1979.
Klinefelter, G. R.; Amann, R. P. Isolation of principal cells and basal cells by elutriation of suspensions of rat epididymal tissue. Int. J. Androl. 3: 287–300; 1980.
Olson, G. E.; Jonas-Davies, J.; Hoffman, L. H.; Orgebin-Crist, M.-C. Structural characterization of isolated rat epididymal epithelial cells. Gamete Res. 6: 161–178; 1982.
Gilbert, S. F.; Migeon, B. R.d-Valine as a selective agent for normal human and rodent epithelial cells in culture. Cell 5: 11–17; 1975.
Lenoz, L.; Sternberg, S. S.; Phillips, F. S. Cytotoxic effects of 1-α-d-arabinofuronosyl-5-fluorocytosine and of 1-α-d-arabinofuronosyl-cytosine in proliferating tissues in mice. Cancer Res. 29: 1790–1798; 1969.
Olson, G. E.; Jonas-Davies, J.; Hoffman, L. H.; Orgebin-Crist, M.-C. Structural features of cultured epithelial cells from the adult rat epididymis. J. Androl. 4: 347–360; 1983.
Kopriwa, B. W.; Leblond, C. P. Improvements in the coating technique of radioautography. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 10: 269–285; 1962.
Clermont, Y. Incorporation of thymidine-H3 in epithelial cells of the ductus epididymis in albino rats (abstr.). Anat. Rec. 139: 217; 1961.
Kierszenbaum, A. L.; Lea, O.; Petrusz, P.; French, F.; Tres, L. L. Isolation, culture, and immunocytochemical characterization of epididymal epithelial cells from pubertal and adult rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78: 1675–1679; 1981.
Klinefelter, G. R.; Amann, R. P.; Hammerstedt, R. H. Culture of principal cells from the caput epididymidis. Biol. Reprod. 26: 885–901; 1982.
White, M. T.; Hu, A. S. L.; Hamamoto, S. T.; Nandi, S. In vitro analysis of proliferating epithelial cell populations from the mouse mammary gland: fibroblast-free growth and serial passage. In Vitro 14: 271–281; 1978.
Tung, P. S.; Lacroix, M.; Fritz, I. B. Effects of cytosine arabinoside on properties of testicular preparations in culture. Biol. Reprod. 22: 1255–1261; 1980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was sponsored by grants from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, Bethesda, MD (HD-03820, HD-11816, HD-05797), and the Mellon Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orgebin-Crist, M.C., Jonas-Davies, J., Storey, P. et al. Effect ofd-valine and cytosine arabinoside on [3H]thymidine incorporation in rat and rabbit epididymal epithelial cell cultures. In Vitro 20, 45–52 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02633331
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02633331