Summary
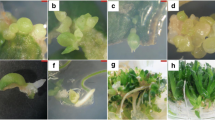
The Ringo Rose cultivar of zonal geranium (Pelargonium x hortorum Bailey) has been shown to be morphogenetically unresponsive. Attempts to improve somatic embryogenesis using various seed stress treatments before germination proved ineffective. However, bacterial contamination of one of the seed-stress treatments led to infected explants that had a significant increase in frequency of high-quality somatic embryos. The co-cultivation of explants with the isolated bacterium (tentatively identified asBacillus sp.) was found to be repeatable, and potentially represents a novel way to improve morphogenesis in geranium and possibly other species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrios, G. N. Plant pathology. San Diego, CA: Academic Press; 1988:79–86.
Barwale, U. B.; Kerns, H. R.; Widholm, J. M. Plant regeneration from callus cultures of several soybean genotypes via embryogenesis and organogenesis. Planta 167:473–481; 1988.
Brown, D. C. W. Germplast determination ofin vitro somatic embryogenesis in alfalfa. HortScience 23:526–531; 1988.
Cassells, A. C. The effect of 2,3,5-triiodobenzoic acid on caulogenesis in callus cultures of tomato andPelargonium. Physiol. Plant. 46:159–164; 1979.
Dunbar, K. B.; Stephens, C. T. Shoot regeneration of hybrid seed geranium (Pelargonium x hortorum) and regal geranium (Pelargonium x domesticum) from primary callus cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 19:13–21; 1989.
Gill, R.; Gerrath, J.; Saxena, P. K. High-frequency direct somatic embryogenesis in thin layer cultures of hybrid seed geranium. Can. J. Bot. 71:408–413; 1993.
Gill, R.; Senaratna, T.; Saxena, P. K. Thidiazuron-induced somatic embryogenesis enhances viability of hydrogel-encapsulated somatic embryos of geranium. J. Plant Physiol (in press); 1994.
Hodges, T. K.; Kamo, K. K.; Imbrie, C. W., et al. Genotype specificity of somatic embryogenesis and regeneration in maize. Bio/Technology 4:219–223; 1986.
Keyes, G. J.; Collins, B. G.; Taylor, L. N. Genetic variation in tissue cultures of red clover. Theor. Appl. Genet. 58:265–271; 1980.
Kiyosue, T.; Takano, K.; Kamada, H., et al. Induction of somatic embryogenesis in carrot by heavy metal ions. Can. J. Bot. 68:2301–2303; 1990.
Marsolais, A. A.; Wilson, D. P. M.; Tsujita, M. J.; Senaratna, T. Somatic embryogenesis and artificial seed production in Zonal (Pelargonium ×hortorum) and Regal (Pelargonium ×domesticum) geranium. Can. J. Bot. 169:1188–1193; 1991.
Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15:473–479; 1962.
Ou, G.; Wang, W. C.; Nguyen, H. T. Inheritance of somatic embryogenesis and organ regeneration from immature embryo cultures of winter wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 78:137–142; 1989.
Pillai, S. K.; Hildebrandt, A. C. Geranium plants differentiated in vitro from stem tip and callus cultures. Plant Dis. Rep. 52:600–601; 1968.
Redenbaugh, K.; Slade, D.; Viss, P., et al. Encapsulation of somatic embryos in synthetic seed coats. HortScience 22:803–809; 1987.
Slimmon, T.; Qureshi, J. A.; Saxena, P. K. Phenylacetic acid induced somatic embryogenesis in cultured hypocotyl explants of geranium (Pelargonium x hortorum Baily). Plant Cell Rep. 10:587–589; 1991.
Theiler, R.In vitro culture of shoot tips ofPelargonium species. Acta Hortic. 78:403–409; 1977.
Thorpe, T. A.In vitro somatic embryogenesis. ISI Atlas Sci. Anim. Plant Sci. 1:81–88; 1988.
Visser, C.; Qureshi, J. A.; Gill, R., et al. Morphoregulatory role of thidiazuron: substitution of auxin and cytokinin requirement for the induction of somatic embryogenesis in geranium hypocotyl cultures. Plant Physiol. 99:1704–1707; 1992.
Wake, H.; Umetsu, H.; Ozeki, Y.; et al. Extracts of marine cyanobacteria stimulated somatic embryogenesis ofDaucus carota L. Plant Cell Rep. 9:655–658; 1991.
Wake, H.; Akasaka, A.; Umetsu, H., et al. Promotion of plantlet formation from somatic embryos of carrot treated with a high molecular weight extract from a marine cyanobacterium. Plant Cell Rep. 11:62–65; 1992.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Visser-Tenyenhuis, C., Murthy, B.N.S., Odumeru, J. et al. Modulation of somatic embryogenesis in hypocotyl-derived cultures of geranium (Pelargonium X hortorum bailey) CV ringo rose by a bacterium. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Plant 30, 140–143 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02632203
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02632203