Summary
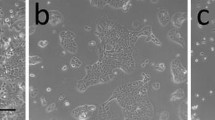
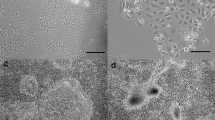
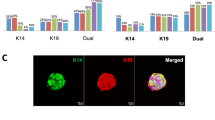
The growth and differentiation of normal human mammary epithelial cells (HMEC) were studied after propagation of serial cultures from breast tissue biopsies from 42 mammoplasty patients. Cells were grown for up to 7 mo. in low calcium medium. HMEC cultures displayed heterogeneous growth patterns, according to the average doubling time of 44 ± 6 h for 32 generations. Proliferation peaked at Day 30. HMEC maintained a normal karyotype and were organized in ductlike structures when cultured in collagen gel matrix. The cultures retained several phenotype traits of the epithelial lineage, including the expression of cytokeratins 18 and 19, specific mammary gland antigens, as shown by indirect HMEC immunostaining by the monoclonal antibodies DF3, EMA, 7B10, and 1BE12. Estrogen receptors were undetectable, whereas progesterone receptors were present at very low density. High-affinity cell surface receptors for epidermal growth factor (EGF) (Kd=1.1×10−10 M) were observed at a density of 50 000 to 100 000 sites per cell. Accordingly, [3H]thymidine incorporation in HMEC was optimally stimulated by EGF at concentrations of 10−11 to 10−10 M. HMEC were also seen to possess functional VIP receptors linked to the adenylate cyclase system, as we previously observed in seven human breast cancer cell lines. These results show that long-term cultures of HMEC provide useful models for studying the growth and differentiation of the normal human mammary gland, and the role of growth factors and hormones in these functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ances, I. G. Serum concentrations of epidermal growth factor in human pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 115:357–362; 1973.
Band, V.; Sager, R. Distinctive traits of normal and tumor-derived human mammary epithelial cells expressed in a medium that supports long-term growth of both cell types. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:1249–1253; 1989.
Bandyopaadhyay, G. K.; Imagawa, W.; Wallace, D. R., et al. Proliferative effects of insulin and epidermal growth factor on mouse mammary epithelial cells in primary culture. J. Biol. Chem. 263:7567–7573; 1988.
Berthon, P.; Delbourg, V.; Taillemite, J-L., et al. Functional VIP receptors in normal, spontaneously immortalized and cancerous mammary epithelial cells. Regul. Peptides 26:141a; 1989.
Blose, S. H.; Meltzer, D. I.; Feramisco, J. R. 10 nm filament induced to collapse in cell microinjection with antibodies against tubulin. J. Cell Biol. 95:229a; 1982.
Boynton, A. L.; Whitfield, J. F.; Isaacs, R. J., et al. Control of 3T3 cell proliferation by calcium. In Vitro 10:12–17; 1974.
Boynton, A. L.; Whitfield, J. F.; Isaacs, R. J., et al. The control of human WI-38 proliferation by extracellular calcium and its elimination by SV40 virus-induced proliferative transformation. J. Cell. Physiol. 92:241–248; 1977.
Brennan, J. K.; Mansky, J.; Roberts, G., et al. Improved methods for reducing calcium and magnesium concentrations in tissue culture medium: application to studies of lymphoblast proliferation in vitro. In Vitro 11:354–360; 1975.
Brown, C. F.; Teng, C. T.; Pentecost, B. T., et al. Epidermal growth factor precursor in mouse lactating mammary gland alveolar cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 3:1077–1083; 1989.
Carpenter, G.; Cohen, S. Epidermal growth factor. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 48:193–216; 1979.
Chaproniere, D. M.; McKeehan, W. L. Serial culture of single adult human prostatic epithelial cells in serum-free medium containing low calcium and a new growth factor from bovine brain. Cancer Res. 46:819–824; 1986.
Chastre, E.; Emami, S.; Gespach, C. Expression of membrane receptors and (proto)oncogenes during the ontogenic development and neoplastic transformation of the intestinal mucosa. A review article. Life Sci. 44:1721–1742; 1989.
Colomb, E.; Berthon, P.; Dussert, C., et al. Estradiol and EGF requirement for cell cycle progression of normal human mammary epithelial cells in culture. Int. J. Cancer 49:932–937; 1991.
Cussenot, O.; Berthon, P.; Faille, A., et al. Immortalization of human adult normal prostatic epithelial cells by liposomes containing SV40. J. Urol. 143:881–886; 1991.
Fitzpatrick, S. L.; Brightwell, J.; Wittliff, J. L., et al. Epidermal growth factor binding by breast tumor biopsies and relationship to estrogen receptor and progestin receptor levels. Cancer Res. 44:3448–3453; 1984.
Fitzpatrick, S. L.; Lachance, M. P.; Schultz, G. S. Characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor and action on human breast cancer cells in culture. Cancer Res. 44:3442–3447; 1984.
Gespach, C.; Bawab, W.; De Cremoux, P., et al. Pharmacology, molecular identification and functional characteristics of vasoactive intestinal peptide receptors in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 48:5079–5083; 1988.
Gespach, C.; Hui Bon Hoa, D.; Rosselin, G. Regulation by vasoactive intestinal peptide, histamine, somatostatin-14 and -28 of cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels in gastric glands isolated from the guinea pig fundus and antrum. Endocrinology 112:1597–1606; 1983.
Gown, A. M.; Vogel, A. M. Monoclonal antibodies to intermediate filament proteins of human cells: unique and cross-reacting antibodies. J. Cell Biol. 95:414–424; 1982.
Greaves, M. F.; Hariri, G.; Newman, R. A., et al. Selective expression of the common acute lymphoblastic leukemia (gp100) antigen on immature lymphoid cells and their malignant counterpart. Blood 61:628–639; 1983.
Hammond, S. L.; Ham, G. H.; Stampfer, M. R. Serum free growth of human mammary epithelial cells: a rapid clonal growth in defined medium and extended serial passage with pituitary extract. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:5435–5439; 1984.
Haslam, S. Z. Cell to cell interactions and normal mammary gland function. J. Dairy Sci. 71:2843–2854; 1988.
Hennings, H.; Michael, D.; Cheng, C., et al. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell 19:245–254; 1980.
Imai, Y.; Leung, C. K.; Friesen, H. G., et al. Epidermal growth factor receptors and effect of epidermal growth factor on growth of human breast cancer cells in long-term tissue culture. Cancer Res. 42:4394–4398; 1982.
Kufe, D.; Inghirami, G.; Abe, M., et al. Differential reactivity of a novel monoclonal antibody (DF3) with human malignantversus benign breast tumors. Hybridoma 3:223–232; 1984.
Lechner, J.; Haugen, A.; Autrup, H., et al. Clonal growth of epithelial cells from normal human bronchus. Cancer Res. 41:2294–2304; 1981.
Le Meuth, V.; Farjaudon, N.; Bawab, W., et al. Characterization of binding sites for VIP-related peptides and activation of adenylate cyclase in developing pancreas. Am. J. Physiol. 260:G265-G274; 1991.
Lin, J. J. Monoclonal antibodies against myofibrillar components of rat skeletal muscle decorate the intermediate filaments of cultured cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78:2335–2339; 1981.
Malet, C.; Gompel, A.; Spritzer, P., et al. Tamoxifen and hydroxytamoxifen isomersversus estradiol effects on normal human breast cells in culture. Cancer Res. 48:7193–7199; 1988.
Marie, J-C.; Hui Bon Hoa, D.; Jackson, R., et al. The biological relevance of HPLC-purified vasoactive intestinal polypeptide monoiodinated at tyrosine 10 or tyrosine 22. Regul. Pept. 12:113–123; 1985.
McGrath, C. M.; Soule, H. D. Calcium regulation of normal human mammary epithelial cell growth in culture. In Vitro 20:652–662; 1984.
McGrath, C. M.; Soule, H. D. Renewal inhibition of human mammary cell growthin vitro: cortisol and the recruitment of cells to terminal differentiation. J. Cell. Physiol. 116:385–396; 1983.
Medina, D.; Oborn, C. J. Growth of preneoplastic mammary epithelial cells in serum-free medium. Cancer Res. 40:3982–3987; 1980.
Miyata, A.; Arimura, A.; Dahl, R. R., et al. Isolation of a novel 38 residue-hypothalamic polypeptide which stimulates adenylate cyclase in pituitary cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 164:567–574; 1989.
Moll, R.; Achtstatter, T.; Becht, E., et al. Cytokeratins in normal and transitional epithelium. Am. J. Pathol. 132:123–144; 1988.
Murphy, L. C.; Murphy, L. J.; Dubik, D., et al. Epidermal growth factor gene expression in human breast cancer cells: regulation of expression by progestins. Cancer Res. 48:4555–4560; 1988.
Murphy, L. J.; Sutherland, R. L.; Stead, B., et al. Progestin regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor in human mammary carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 46:728–734; 1986.
Nunez, A. M.; Jakowlew, S.; Briand, J. P., et al. Characterization of the estrogen-induced pS2 protein secreted by the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Endocrinology 121:1759–1765; 1987.
Ormerod, M. G.; Steele, K.; Westwood, J. H., et al. Epithelial membrane antigen: partial purification, assay and property. Br. J. Cancer 48:533–541; 1983.
Osborne, C. K.; Hamilton, B.; Nover, M. Receptor binding and processing of epidermal growth factor by human breast cancer cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 55:86–93; 1982.
Pancino, G-F.; Charpin, C.; Calvo, F., et al. A novel monoclonal antibody (7B10) with differential reactivity between human mammary carcinoma and normal breast. Cancer Res. 47:4444–4452; 1987.
Pancino, G-F.; Charpin, C.; Osinaga, E., et al. Characterization and distribution in human tissues of a glycoproteic antigen defined by monoclonal antibody 1BE12 raised against the human breast cancer cell line T47D. Cancer Res. 50:7333–7342; 1990.
Pekonen, F.; Partanen, S.; Makinen, T., et al. Progestin regulation of epidermal growth factor in human mammary carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 46:728–734; 1986.
Petersen, O. W.; Hoyer, P. E.; Van Deurs, B. Frequency and distribution of receptor-positive cells in normal, nonlactating human breast tissue. Cancer Res. 47:5748–5751; 1987.
Petersen, O. W.; Van Deurs, B. Distinction between vascular smooth muscle cells and myoepithelial cells in primary monolayer cultures of human breast tissue. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 25:259–266; 1989.
Petersen, O. W.; Van Deurs, B. Preservation of defined phenotypic traits in short-term cultured human breast carcinoma derived epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 47:856–866; 1987.
Prud’homme, J-F.; Jolivet, A.; Pichon, M-F., et al. Monoclonal antibodies against native and denaturated forms of estrogen-induced breast cancer protein (BCEI:pS2) obtained by expression inEscherichia coli. Cancer Res. 50:2390–2396; 1990.
Richards, J.; Imagawa, W.; Balakrishnan, A., et al. The lack of effect of phenol red or estradiol on the growth response of human, rat and mouse mammary cells in primary culture. Endocrinology 123:1335–1340; 1988.
Rosselin, G. The receptors of the VIP family peptides (VIP, secretin, GRF, PHI, PHM, GIP, glucagon and oxytomodulin). Specificities and identity. Peptides 7:89–100; 1986.
Rudland, P. S.; Barraclough, R. Stem cells in mammary gland differentiation and cancer. J. Cell Sci. Suppl. 10:95–114; 1988.
Rudland, P. S.; Hugues, C. M.; Ferns, S. A., et al. Characterization of human mammary cell types in primary culture: immunofluorescent and immunocytochemical indicators of cellular heterogeneity. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 25:23–36; 1989.
Russo, J.; Mills, M. J.; Moussalli, M. J., et al. Influence of breast development on the growth properties of primary cultures. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 25:643–649; 1989.
Seabright, M. A. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet 2:971–972; 1971.
Skalli, O.; Ropraz, P.; Trzeciak, A., et al. A monoclonal antibody againstα-smooth muscle actin: a new probe for smooth muscle differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 103:2787–2796; 1986.
Smith, J. A.; Winslow, D. P.; Rudland, P. S. Different growth factors stimulate cell division of rat mammary epithelial, myoepithelial and stromal cell lines in culture. J. Cell. Physiol. 119:320–326; 1984.
Soule, H. D.; Maloney, T. M.; Wolman, S. R., et al. Isolation and characterization of a spontaneously immortalized human breast cell line, MCF-10. Cancer Res. 50:6075–6085; 1990.
Soule, H. D.; McGrath, C. M. A simplified method for passage and long-term growth of human mammary epithelial cells. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 22:6–12; 1986.
Stampfer, M. R.; Bartley, J. C. Induction of transformation and continuous cell lines from normal human mammary epithelial cells exposed to benzo-a-pyrene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:2394–2398; 1985.
Stampfer, M. R.; Hallowes, R. C.; Hackett, A. J. Growth of normal human mammary cells in culture. In Vitro 16:415–425; 1980.
Stoner, G.; Babcock, M. Influence of growth factors on proliferation of normal and chemically transformed rat esophageal epithelial cells. Proc. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 23:42; 1982.
Taketani, Y.; Oka, T. Possible physiological role of epidermal growth factor in the development of the mouse mammary gland during pregnancy. FEBS Lett. 152:256–260; 1983.
Taylor-Papadimitriou, J.; Stampfer, M.; Bartek, J., et al. Keratin expression in human mammary epithelial cells cultured from normal and malignant tissue: relation toin vivo phenotypes and influence of medium. J. Cell Sci. 94:403–413; 1989.
Valverius, E. M.; Bates, S. E.; Stampfer, M. R., et al. Transforming growth factorα production and epidermal growth factor expression in normal and oncogene transformed human mammary epithelial cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 3:203–214; 1989.
Viac, J.; Reano, A.; Brochier, J., et al. Reactivity pattern of a monoclonal anti-keratin antibody (KL1). J. Invest. Dermatol. 81:351–354; 1983.
Yang, J.; Richards, J.; Bowman, P., et al. Sustained growth and three-dimensional organization of primary mammary tumor epithelial cells embedded in collagen gels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76:3401–3405; 1979.
Yang, N-S.; Kube, D.; Park, C., et al. Growth of human mammary epithelial cells on collagen gel surfaces. Cancer Res. 41:4093–4100; 1981.
Zajchowski, D.; Band, V.; Pauzie, N., et al. Expression of growth factors and oncogenes in normal and tumor-derived human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 48:7041–7047; 1988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berthon, P., Pancino, G., de Cremoux, P. et al. Characterization of normal breast epithelial cells in primary cultures: Differentiation and growth factor receptors studies. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Animal 28, 716–724 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02631059
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02631059