Abstract
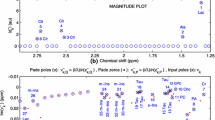
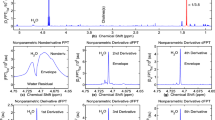
Proton MR spectra of a healthy human prostatic gland show a major signal for citrate appearing as an AB-type multiplet. After application of multipulse localization sequences, the outer lines of this multiplet often appear with dispersion line shapes disturbing the baseline and interfering with proper quantification of citrate itself and other nearby resonances. Based upon analytical descriptions of the time evaluation of an AB spin system during a point resolved spectroscopy (PRESS) pulse sequence (90x-τ1,-180y-τ2-180y-t), equations were derived representing the intensity of the absorption and dispersion line shape of the outer lines of the citrate multiplet at the top of echo t=τ2-τ1. From these equations, it was calculated that the outer lines of citrate can be removed almost completely using a PRESS pulse sequence with τ1=11 ms and τ2=60 ms. The theoretical description was confirmed by the almost complete disappearance of the two outer citrate resonances inin vitro andin vivo proton MR spectra acquired with this pulse sequence timing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heerschap A, Jager G, de Koster A, Barentsz J, de la Rosette J, Debruyne F, Ruijs J (1993) 1H MRS of prostate pathology.Proceedings of the 12th Annual Meeting of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, p. 213.
Kurhanewicz J, Vigneron DB, Nelson SJ, Hricak H, MacDonald JM, Konety B, Narayan P (1995) Citrate as anin vivo marker to discriminate prostate cancer from benign hyperplasia and normal prostate peripheral zone: detection via localized proton spectroscopy.Urology 45: 459–466.
Kurhanewicz J, Vigneron DB, Hricak H, Narayan P, Carroll P, Nelson SJ (1996) Three-dimensional H-1 MR spectroscopic imaging of thein situ human prostate with high (0.24–0.7-cm3) spatial resolution.Radiology 198: 795–805.
Heerschap A, Jager GJ, van der Graaf M, Barentsz JO, de la Rosette JJMCH, Oosterhof GON, Ruijs SHJ (1997)In-vivo proton MR spectroscopy reveals altered metabolite content in malignant prostate tissue.Anticancer Res (in press).
Mulkern RV, Bowers JL (1993) Calculating spectral modulations of AB systems during PRESS acquisitions.Magn Reson Mad 30: 518–519.
Mulkern R, Bowers J (1994) Density matrix calculations of AB spectra from multipulse sequences: quantum mechanics meetsin vivo spectroscopy.Concepts Magn Reson 6: 1–23.
Straubinger K, Schick F, Lutz O (1995) Computeralgebra calculations and measurements on AB spin systems for double-spin-echo sequences.MAGMA 3: 109–118.
Wilman AH, Allen PS (1995) The response of the strongly coupled AB system of citrate to typical1H MRS localization sequences.J Magn Reson B 107: 25–33.
van der Graaf M, Heerschap A (1996) Effect of cation binding on the proton chemical shifts and the spin-spin coupling constant of citrate.J Magn Reson B 112: 58–62.
Kavanagh JP (1985) Sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, zinc, citrate and chloride content of human prostatic and seminal fluid.J Reprod Fertil 75: 35–41.
Haase A, Frahm, J, Hänicke W, Matthaei D (1985)1H NMR chemical shift selective (CHESS) imaging.Phys Med Biol 30: 341–344.
Klose U (1990)In vivo proton spectroscopy in the presence of eddy currents.Magn Reson Med 14: 26–30.
Heerschap A, Jager GJ, van der Graaf M, Barentsz JO, Ruijs SHJ (1997) Proton MR spectroscopy of the normal human prostate with an endorectal coil and a double spin-echo pulse sequence.Magn Reson Med 37: 204–213.
van der Graaf M, van den Boogaart A, Bovée WMMJ, Heerschap A (1997) Fitting of the AB-type multiplet of citrate using prior knowledge of phase and amplitude modulation.Proceedings of the 5th Scientific Meeting of the International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, p 1419.
Knijn A, de Beer R, van Ormondt D (1992) Frequency-selective quantification in the time domain.J Magn Reson 97: 444–450.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Graaf, M., Jager, G.J. & Heerschap, A. Removal of the outer lines of the citrate multiplet in proton magnetic resonance spectra of the prostatic gland by accurate timing of a point-resolved spectroscopy pulse sequence. MAGMA 5, 65–69 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02592268
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02592268