Abstract
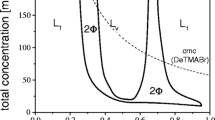
While the aqueous solubility for bilayer phospholipids is less than 10−10 M—keeping lipid membranes at essentially constant mass, single chain surfactants can have a significant aqueous solubility. Thus, in surfactant solutions, both monomer and micelles can interact with a lipid bilayer, and the mass and composition of the bilayer can be changed in seconds. These changes in composition are expected to have direct consequences on bilayer structure and material properties. We have found that the exchange of surfactants like lysolecithin can be described in terms of a kinetic model in which monomer and micelles are transported to the membrane from bulk solution. Molecular transport is considered at the membrane interfaces and across the midplane between the two monolayers of the bilayer. Using micropipet manipulation, single vesicles were transferred into lysolecithin solutions, and the measurement of vesicle area change gave a direct measure of lysolecithin uptake. Transfer back to lysolecithin-free media resulted in desorption. The rates of uptake and desorption could therefore be measured at controlled levels of membrane stress. With increasing lysolecithin concentration in the bulk phase, the amount of lysolecithin in the membrane reached saturation at ∼3 mol% for concentrations below the critical micelle concentration (CMC) and at >30 mol% for concentrations above the CMC. When convective transport was used to deliver lysolecithin, uptake occurred via a double exponential: initial uptake into the outer monolayer was fast (∼0.2 sec−1); transfer across the bilayer midplane was much slower (0.0019 sec−1).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aniansson, E.A., S. N. Wall, M. Almgen, H. Hoffmann, I. Kielmann, W. Ulbricht, R. Zana, J. Lang, and C. Tondre. Theory of the kinetics of micellar equilibria and quantitative interpretation of chemical relaxation studies of micellar solutions of ionic surfactants.J. Phys. Chem. 80:905–922, 1976.
Arakawa, Y., and O. Wada. Inhibition of neutrophil chemotaxis by organotin compounds.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 123:543–548, 1984.
Banerjji, R., C. Arroyo, C. Cordon-Cardo, and E. Gilboa. The role of IL-2 secreted from genetically modified tumor cells in the establishment of antitumor immunity.J. Immunol. 152:2324–2332, 1994.
Bedell, C. R. The Design of Drugs to Macromolecular Targets. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1992, p. 287.
Bell, R. M. Protein kinase C activation by diacylglycerol second messengers.Cell 45:631–632, 1986.
Berridge, M. J. Inositol triphosphate and diacylglycerol. Two interacting second messengers.Annu. Rev. Biochem. 56:159–193, 1987.
Brown, R. E. Spontaneous transfer between organized lipid assemblies.Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1113:375–389, 1992.
Brugge, J., T. Curran, E. Harlow, and F. McCormick. Origins of Human Cancer. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1991, p. 904.
Cuyper, M. D., M. Joniau, and H. Dangreau. Intervesicular phospholipid transfer. A free-flow electrophoresis study.Biochemistry 22:415–420, 1983.
Devaux, P. F. Static and dynamic lipid assymetry in cell membranes.Biochemistry 30:1163–1173, 1991.
Doms, R. W., and A. Helenius. Properties of a viral fusion protein. In: Molecular Mechanisms of Membrance Fusion, edited by S. Ohki, D. Doyle, T. D. Flanagan, S. W. Hui, and E. Mayhew. New York: Plenum Press, 1988, pp. 385–398.
Doody, M. C., H. J. Pownall, Y. J. Kao, and L. C. Smith. Mechanism and kinetics of transfer of a fluorescent fatty acid between single-walled phosphatidylcholine vesicles.Biochemistry 19:108–116, 1980.
Duckwitz-Peterlein, G., G. Eilenberger, and P. Overath. Phospholipid exchange between bilayer membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 469:311–325, 1977.
Elamrani, K., and A. Blume. Incorporation of lysolecithin into lecithin vesicles. Kinetics of lysolecithin induced vesicle fusion.Biochemistry 21:521–526, 1982.
Elliott, J. R., D. A. Haydon, B. M. Bendry, and D. Needham. Inactivation of the sodium current in squid giant axons by hydrocarbons.Biophys. J. 48:617–622, 1985.
Evans, E. Mechanics of cell deformation and cell-surface adhesion. In: Physical Basis of Cell-Cell Adhesion, edited by P. Bongrand. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1988, pp. 91–123.
Evans, E. Micromethods for measurement of deformability and adhesivity properties of blood cells and synthetic membrane vesicles. In: Physical Basis of Cell-Cell Adhesion, edited by P. Bongrand, Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1988, pp. 173–189.
Evans, E. Structure and deformation properties of red blood cells. In: Methods in Enzymology, edited by S. P. Colowick,et al. San Diego: Academic Press, 1989, pp. 3–35.
Evans, E., and D. Needham. Physical properties of surfactant bilayer membranes: thermal transitions, elasticity, rigidity, cohesion, and colloidal interactions.J. Phys. Chem. 91:4219–4228, 1987.
Evans, E., W. Rawicz, and A. Hoffman. Lipid bilayer expansion and mechanical degradation in solutions of water-soluble bile-acids. Bile Acids in Gastroenterology: Basic & Clinical Advances, Falk Symposium. XIII International Bile Salt Meeting. San Diego: 1994.
Franks, N. P., and W. R. Lieb. The structure of lipid bilayers and the effects of general anaesthetics.J. Mol. Biol. 133:469–500, 1979.
Homan, R., and H. J. Pownall. Transbilayer diffusion of phospholipids: dependence on headgroup structure and acyl chain length.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 938:155–166, 1988.
Hui, S. W., and C. Huang. X-ray diffraction evidence for fully interdigitated bilayers of 1-stearoyllysophosphatidylcholine.Biochemistry 25:1330–1335, 1986.
Kan, C. C., J. Yan, and R. Buttman. Rates of spontaneous exchange of synthetic radiolabeled sterols between lipid vesicles.Biochemistry 31:1866–1874, 1992.
Kleinfeld, A. M. Fatty acid transport across membranes. In: Permeability and Stability of Lipid Bilayers, edited by E. A. Disalvo and S. A. Simon. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1995, pp. 241–258.
Kwok, R., and E. Evans. Thermoelasticity of large lecithin bilayer vesicles.Biophys. J. 35:637–652, 1981.
Lubin, B., and D. Chiu. Properties of vitamin E-deficient erythrocytes following peroxident injury.Pediatr. Res. 16: 928–932, 1982.
Marsh, D. Handbook of Lipid Bilayers. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1990, pp. 387.
Massey, J. B., A. M. Gotto, and H. J. Pownall. Kinetics and mechanism of the spontaneous transfer of fluorescent phosphatidylcholines between apolipoprotein-phospholipid recombinants.Biochemistry 21:3630–3636, 1982.
Mattai, J., and G. C. Shipley. The kinetics of formation and structure of the low-temperature phase of 1-stearoyl-lysophosphatidylcholine.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 859:257–265, 1986.
McIntosh, T. J., A. D. Magid, and S. A. Simon. Range of solvation pressure between lipid membranes: dependence on the packing density of solvent molecules.Biochemistry 28: 7904–7912, 1989.
McLean, L. R., and M. C. Phillips. Mechanism of cholesterol and phosphatidilcholine exchange or transfer between unilamelar vesicles.Biochemistry 20:2893–2900, 1981.
McLean, L. R., and M. C. Phillips. Kinetics of phosphatidilcholine and lysophosphatidilcholine exchange between unilamelar vesicles.Biochemistry 23:4624–4630, 1984.
Needham, D. Micropipet manipulation of lipid membranes: direct measurements of the material properties of a cohesive structure that is only two molecules thick.J. Mat. Educ. 14:217–238, 1992.
Needham, D. Cohesion and permeability of lipid bilayer membranes: In: Permeability and Stability of Lipid Bilayers, edited by E. A. Disalvo and S. A. Simon. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1995, pp. 49–79.
Needham, D., and E. Evans. Structure and mechanical properties of giant lipid (DMPC) vesicle bilayers from 20°C below to 10°C above the liquid crystal-crystalline phase transition at 24°C.Biochemistry 27:8261–8269, 1988.
Needham, D., T. J. McIntosh, and E. Evans. Thermomechanical and transition properties of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine/cholesterol bilayers.Biochemistry 27:4668–4673, 1988.
Needham, D., and R. S. Nunn. Elastic deformation and failure of lipid bilayer membranes containing cholesterol.Biophys. J. 58:997–1009, 1990.
Nichols, J. W. Thermodynamics and kinetics of phospholipid monomer-vesicle interaction.Biochemistry 24:6390–6398, 1985.
Nichols, J. W. Low concentrations of bile salts increase the rate of spontaneous phospholipid transfer between vesicles.Biochemistry 25:4596–4601, 1986.
Nichols, J. W. Phospholipid transfer between phosphatidylcholine-taurocholate mixed micelles.Biochemistry 27: 3925–3931, 1988.
Nichols, W. J., and R. E. Pagano. Kinetics of soluble lipid monomer diffusion between vesicles.Biochemistry 20: 2783–2789, 1981.
Nichols, W. J., and R. E. Pagano. Use of resonance energy transfer to study the kinetics of amphiphile transfer between vesicles.Biochemistry 21:1720–1726, 1982.
Potter, H. Electroporation in biology: methods, applications and instrumentation.Anal. Biochem. 174:361–373, 1988.
Redelmeier, T. E., M. J. Hope, and P. R. Cullis. On the mechanism of transbilayer transport of phosphatidylglycerol in response to transmembrane pH gradients. 29:3046–3053, 1990.
Roseman, M. A., and T. E. Thompson. Mechanism of the spontaneous transfer of phospholipids between bilayers.Biochemistry 19:439–444, 1980.
Ruden, T., and E. Gilboa. Use of antisense RNA inhibition to protect cells from HTLV-1 mediated oncogenic transformation of cultured human lymphoid cells.J. Virol. 63:677–682, 1989.
Shoemaker, D. G., and J. W. Nichols. Hydrophobic interaction of lysophospholipids and bile salts at submicellar concentrations.Biochemistry 29:5837–5842, 1990.
Simon, S. A., E. A. Disalvo, K. Gawrisch, V. Borovyagin, E. Toon, S. S. Schiffman, D. Needham, and T. J. McIntosh. Increased adhesion between neutral bilayers. Interbilayer bridges formes by tannic acid.Biophys. J. 66: 1943–1958, 1994.
Soltesz, S. A., and D. A. Hammer. Micropipette manipulation techniques for the monitoring of pH-dependent membrane lysis as induced by the fusion peptide of influenza virus.Biophys. J. 68:315–325, 1995.
Teissié, J., and M.-P. Rols. Interfacial membrane alteration associated with electropermeabilization and electrofusion. In: Guide to Electroporation and Electrofusion, edited by D. C. Chang, B. M. Chassy, J. A. Saunders, and A. E. Sowers. San Diego: Academic Press, 1992, pp. 139–153.
Valentine, W. M., D. G. Graham, and D. C. Anthony. Covalent cross-linking of erythrocyte spectrin by carbon disulfide.Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 121:71–77, 1993.
VanEchteld, C. J. A., B. DeKruijff, J. G. Mandersloot, and J. DeGier. Effects of lysophosphatidylcholines on phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol liposome systems as revealed by 31P-NMR, electron microscopy and permeability studies.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 649: 211–220, 1981.
Wimley, W. C., and T. E. Thompson. Exchange and flip-flop of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine in liquid-crystalline, gel, and two-component, two-phase large unilamellar vesicles.Biochemistry 29:1296–1303, 1990.
Wimley, W. C., and T. E. Thompson. Transbilayer and interbilayer phospholipid exchange in dimyristoylphosphatidilcholine/dymiristoylphosphatidylethanolamine large unilamelar vesicles.Biochemistry 30:1702–1709, 1991.
Wolf, D. E., A. P. Winiski, A. E. Thing, K. M. Bocian, and R. E. Pagano. Determination of the transbilayer distribution of fluorescent lipid analogues by nonradiative fluorescence resonance energy transfer.Biochemistry 31:2865–2873, 1992.
Zhelev, D. V., and D. Needham. Influence of electric fields on biological and model membranes. In: Biological Effects of Electric and Magnetic Fields, edited by D. O. Carpenter. Orlando: Academic Press 1993, pp. 105–142.
Zhelev, D. V., and D. Needham. The use of chemical agents that reversibly modify cell and lipid vesicle membranes, to improve yields and cell viability in electroporation and transfection. Duke University, Invention disclosure, 1993.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Needham, D., Zhelev, D.V. Lysolipid exchange with lipid vesicle membranes. Ann Biomed Eng 23, 287–298 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02584429
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02584429