Abstract
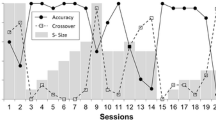
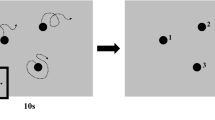
Behavioral shaping procedures and adapted devices were used to establish controlled hand movements in two severely disabled adults with profound mental retardation. Both individuals made arm/hand movements that were arbitrary or under partial voluntary control. Switches were adapted and positioned bilaterally on or near these hand movements to avoid shaping a complex response topography. Contact resulted in contingent music or beverages. Both subjects acquired controlled hand movements on each switch. As the number of switch operations increased, the response requirement needed to access the music or beverages was increased. For Subject 1, the schedule for music was abruptly changed to a conjugate schedule. For Subject 2, the value of the fixed ratio schedule for the automated delivery of beverages was gradually increased over values to a maximum of FR 40. Increases in the schedule response requirements were accompanied by increases in rate of responding, providing evidence that controlled hand movements had been acquired. During schedule conditions with high response requirements, responding was not only susstained by both subjects, but cumulative records show a high rate of responding controlled by the scheduled delivery of reinforcement. The conditioning of two responses simultaneously on separate switches and the schedule conditions with high response requirements demonstrate behavioral shaping procedures not investigated in previous studies. The adapted switches and the automated beverage dispensing device show the sucessful use of technology in training programs in adults with profound multiple handicaps. Applications for the shaping procedures and adapted devices in assessment and applied situations are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dewson, M., and Whiteley, J. H. (1987). Sensory reinforcement of head turning with non-ambulatory, profoundly mentally retarded persons.Res. Dev. Dis. 8: 413–426.
Fehr, M. A., Wacker, D., Trezise, J., Lennon, R., and Meyerson, L. (1979). Visual, auditory, and vibratory stimulation as reinforcers for profoundly retarded children.Rehabil. Psychol. 26: 4, 201–209.
Haskett, J., and Hollar, W. D. (1978). Sensory reinforcement and contingency awareness in profoundly retarded children.Am. J. Ment. Def. 83: 1, 60–68.
Murphy, R. J., and Doughty, N. R. (1977). Establishment of controlled arm movements in profoundly retarded students using response contingent vibratory stimulation.Am. J. Ment. Def. 82: 2, 212–216.
Realon, R. E., Favell, J. E., and Dayvault, K. A. (1988). Evaluating the use of adapted leisure materials on the engagement of persons who are profoundly, multiply handicapped.Ed. Train. Ment. Retard. 23: 228–237.
Reese, H. W., and Lipsitt, L. P. (1970).Experimental Child Psychology. Academic Press, New York, pp. 105.
Reid, D. H., Philips, J. F., and Green, C. W. (1991). Teaching persons with profound multiple handicaps: A review of the effects of behavioral research.J. Appl. Behav. Anal. 24: 319–336.
Rice, H. K., McDaniel, M. W., Stallings, V. D., and Gatz, M. J. (1967). Operant behavior in vegetative patients II.Psychological Rec. 17: 449–460.
Spradlin, J. E., Girardeau, F. L., and Corte, E. (1965). Fixed ratio and fixed interval behavior of severely and profoundly retarded subjects.J. Exp. Child Psychol. 2: 340–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutowski, S.J. Response acquisition for music or beverages in adults with profound multiple handicaps. J Dev Phys Disabil 8, 221–231 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02578391
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02578391