Abstract
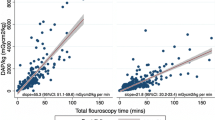
Exposure area product (EAP) and center field entrance exposure (free-in-air) were measured in seventeen pediatric patients undergoing cardiac catheterization. Exposures were recorded separately for biplane fluoroscopy and cine angiocardiography using flat-plate ionization chambers. In the posterior-anterior (PA) projections, median EAP was 425 Roentgen-square centimeter (R-cm2), with a range of 90.5–3,882 R-cm2; 29–35% of this exposure occurred during cine filming. In the lateral projection, median EAP was 276 R-cm2 (range 117–1,173); 52–59% of this exposure was due to cine filming. Median center field entrance exposure in the PA view was 7.86 Roentgens (R) with a range 2.16–73.9 of and in the lateral projection 7.39 R (range 2.64–24.6). As much as 25% of the exposure from the entire examination was contributed by manual “test” exposures to set cine radiographic kVp.
We recommend use of testing circuits, which determine cine radiographic factors automatically and thus should lower levels of exposure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams FH, Norman AD, Bass D, Oko G (1978) Chromosome damage in infants and children after cardiac catheterization and angiocardiography. Pediatrics 62:312–316
Gustaffson M, Mortensson W (1976) Irradiation to the thyroid gland at cardiac catheterization and angiocardiography in children. Br J Radiol 49:686–689
Rowley KA (1974) Patient exposure in cardiac catherization and cinefluorography, using the eclair 16 mm camera at speeds up to 200 frames per second. Br J Radiol 47:169–178
Reuter FG (1978) Physician and patient exposure during cardiac catheterization. Circulation 58:134–139
Waldman JD, Rummerfield PA, Gilpin EA, Kirkpatrick SE (1981) Radiation exposure to the child during cardiac catheterization. Circulation 64:158–163
Wochos JF, Cameron JR (1977) Patient exposure from diagnostic X-rays. An analysis of 1972–1974. NEXT (Nation-wide Evaluation of X-ray Trends) Data, US, Dept. of HEW Publication (FDA), 77-8020
Leibovic SJ, Caldicott WJH Gastrointestinal fluoroscopy: Patient dose and methods for reduction. (in press) Br J Radiol
Leibovic SJ, Lebowitz RL (1980) Reducing patient dose in voiding cystourethrography. Urol Radiol 2:103–107
Webster LW, Alpert NM, Brownell GL (1974) In James AE, Wagner MN, Cooke RL, eds, Pediatric nuclear medicine. Saunders, Philadelphia, PA
Falicov RE (1978) Radiation exposure during cardiac catheterization (Letter). Circulation 58:1213
Reuter FG (1978) (Letter). Circulation 58:1214
Woodrow TW, King D, Harrison E, Sbar S (1978) (Letter). Circulation 58:1213–1214
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leibovic, S.J., Fellows, K.E. Patient radiation exposure during pediatric cardiac catheterization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 6, 150–153 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02552767
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02552767