Abstract
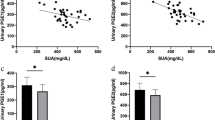
The concentrations of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), sodium, potassium and creatinine were determined in the blood and urine of 50 renal transplant recipients treated with cyclosporine A or azathioprine, as immunosuppressive agents, for at least one year post transplantation. Fourteen healthy subjects served as control group. The urinary PGE2 excretion was significantly decreased in all treated renal transplant recipients and this reduction was associated with significant decrease in urinary excretion of sodium and potassium. On the other hand, a high elevation in blood PGE2 concentration was observed while no significant changes were seen in sodium and potassium levels in the blood of these renal transplant recipients. The observations suggest an association between urinary PGE2 reduction and immunosuppressive treatments in renal transplant recipients; also, PGE2 may regulate intra-renal haemodynamics and influence the renal tubular electrolyte excretion. Moreover, urinary PGE2 can be used as an indicator of successful renal transplantation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campbell, P. N., Smith, A. D.: Biochemistry Illustrated. Churchill-Livingstone, New York 1982, pp. 206–208.
Frolich, J. C., Rosenkranz, B., Kitajima, W., Fischer, C., Walker, L.: Prostacyclin as a renal hormone. In: P. J. Lewis, J. O'Grady (eds): Clinical Pharmacology of Prostacyclin. 1981, Ch. 8, pp. 53–58.
Thompson, D., Rowe, D. J., Briggs, J. D.: Measurement of urine prostaglandin E2 as a predictor of acute renal transplant rejection: Preliminary findings.Ann. Clin. Biochem., 22, 161 (1985).
Ladefoged, J.: Urinary prostaglandin E2 excretion in renal allotransplantation in man.Prostaglandins, 34, 611 (1987).
Jaffa, B. M., Parker, C. W.: Radioimmunoassay for prostaglandins.Radioassay Clin. Med., 33 (1974).
Willis, J. B.: Analysis of biochemical material by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. In: Glick, D. (ed.): Methods of Biochemical Analysis. Interscience Publishers, New York 1963, pp. 1–67.
Van Pilsum, J. F., Bovis, M.: Effects of various protein precipitants on recoveries of creatinine added to plasma.Clin. Chem., 3, 90 (1957).
Snedecor, G. W.: Statistical Methods Applied to Experiments in Agriculture and Biology. 5th ed., Aems. College Press 1956, p. 132.
Buck, A. C., Sampson, W. F., Lote, C. J., Blacklock, N. J.: The influence of renal prostaglandins on glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and calcium excretion in urolithiasis.J. Urol., 53, 485 (1981).
Haylor, J., Lote, C. J.: Renal function in conscious rats after indomethacin. Evidence for a tubular action of endogenous prostaglandin.J. Physiol., 298, 371 (1980).
Lote, C. J., Rider, J. B., Thomas, S.: The effect of prostaglandin E on the short circuit current and sodium, potassium chloride and calcium movements across isolated frog (Rana temproria) skin.Pflügers Arch. Ges. Physiol., 352, 145 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Sharabasy, M.M.H., El-Naggar, M.M. Prostaglandin E2 in renal transplant recipients. International Urology and Nephrology 24, 447–451 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02550640
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02550640