Abstract
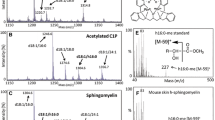
This study reports the application of modern methods of molecular species analysis in determination of the structure of both major and minor glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelins of human erythrocytes. Individual phospholipid classes were resolved from total lipid extracts by thin-layer chromatography. Diradylglycerols were released by phospholipase C and converted into trimethylsilyl ethers, which were resolved into the alkenylacyl, alkylacyl and diacylglycerol subclasses by normal phase high performance liquid chromatography. Molecular species of diradylglycerols and ceramides were quantitated according to carbon and double bond number by gas liquid chromatography using a fused silica capillary column wall-coated with bonded RTx-2330. The molecular species of ceramides were determined by GC/MS. The diradyl glycerophosphocholines contained 93.0% diacyl, 4.6% alkylacyl and 2.5% alkenylacyl, white the diradyl glycerophosphoethanolamines were made up of 48.8% diacyl, 47.8% alkenylacyl and 3.4% alkylacyl subclasses. Analysis of the molecular species showed that the long chain polyunsaturated acids were mainly combined with C16 in all diradyl GPC subclasses and in diacyl GPE, while in the alkylacyl and alkenylacyl GPE and in diacyl glycerophosphoinositol and diacyl glycerophosphoserine they were combined mainly with C18 saturated fatty chains. In addition to the C16 and C18 alkyl and alkenyl, the ether fractions also contained significant proportions of C20, C22 and C24 chains. The molecular species of the ceramide moieties of the SPH were made up largely of mono- and diunsaturated species. Over 200 molecular species were identified and quantitated in a representative sample of human red blood cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CV:
-
coefficients of variation
- FAME:
-
fatty acid methyl esters
- FID:
-
flame ionization detection
- GC:
-
gas chromatography
- GC/MS:
-
gas chromatography/mass spectroscopy
- GLC:
-
gas-liquid chromatography
- GPC:
-
glycerophosphocholines
- GPE:
-
glycerophosphoethanolamines
- GPI:
-
glycerophosphoinositol
- GPL:
-
glycerophospholipids
- GPS:
-
glycerophosphoserine
- HPLC:
-
high performance liquid chromatography
- PI:
-
phosphatidylinositol
- PS:
-
phosphatidylserine
- SPH:
-
sphingomyelins
- TLC:
-
thin-layer chromatography
- TMS:
-
trimethylsilyl
- BDMS:
-
tertiary-butyldimethylsilyl
References
Berridge, M.J. (1987)Ann. Rev. Biochem. 56, 159–193.
Sivakoff, M., Pure, E., Hsueh, W., and Needleman, P. (1979)Fed. Proc. 38, 78–82.
Aveldano, M.I., and Sprecher, H. (1987)J. Biol. Chem. 262, 1180–1186.
Spener, F. (1983) inEther Lipids (Mangold, H.K., and Paltauf, F., eds.) pp. 239–259, Academic Press, New York.
Mangold, H.K., and Weber, N. (1987)Lipids 22, 789–799.
Demopoulos, C., Pinchard, R.N., and Hanahan, D.J. (1979)J. Biol. Chem. 254, 9355–9358.
Blank, M.L., Snyder, F., Byers, L.W., Brooks, B., and Muirhead, E.E. (1979)Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 90, 1194–1200.
Low, M. (1987)Biochem. J. 244, 1–13.
Myher, J.J., Pind, S., and Kuksis, A. (1988)J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 65, 524. Abs. No. HH7.
Kuksis, A., Breckenridge, W.C., Marai, L., and Stachnyk, O. (1969)J. Lipids Res. 10, 25–32.
Folch, J., Lees, M., and Sloane Stanley, G.H. (1957)J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509.
Pind, S., and Kuksis, A. (1987)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 901, 78–87.
Myher, J.J., and Kuksis, A. (1984)Can. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 62, 352–362.
Kuksis, A., and Myher, J.J. (1986) inFat Absorption (Kuksis, A., ed.), Vol. 1, pp. 1–41, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florda.
Myher, J.J., Kuksis, A., Breckenridge W.C., and Little, J.A. (1981),Can. J. Biochem. 59, 626–636.
Myher, J.J., and Kuksis, A. (1984)J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 10, 13–23.
Myher, J.J., and Kuksis, A. (1982)Can. J. Biochem. 60, 638–650.
Dodge, J.T., and Phillips G.B. (1967)J. Lipid Res. 8, 667–675.
Van Golde, L.M.G., Tomasi, V., and Van Deenen, L.L.M. (1967)Chem. Phys. Lipids 1, 282–293.
Marai, L., and Kuksis, A. (1969)J. Lipid Res. 10, 141–152.
Rogiers, V. (1980)J. Chromatogr. 182, 27–33.
Diagne, A., Fauvel, J., Record, M., Chap, H., and Douste-Blazy, L. (1984)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 793, 221–231.
Breckenridge, W.C., and Palmer, F.B.St.C. (1982)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 712, 707–711.
Antoku, Y., Sakai, T., and Iwashita, H. (1985)J. Chromatogr. Biomed. Applic. 342, 359–362.
Child, P., Myher, J.J., Kuypers, F.A., Op den Kamp, J.A.F., Kuksis, A., and Van Deenen, L.L.M. (1985)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 812, 321–332.
Touchstone, J.C., Alvarez, J.G., Levin, S.S., and Storey, B.J. (1985)Lipids 20, 869–875.
Nelson, G.J. (1972) inBlood Lipids and Lipoproteins (Nelson, G.J., ed.), pp. 317–386, Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Van Meer, G., Poorthuis, B.J.H.M., Op den Kamp, J.A.F., and Van Deenen, L.L.M. (1980)Eur. J. Biochem. 103, 283–288.
Shohet, S.B. (1971)J. Lipid Res. 12, 139–142.
Myher, J.J., Kuksis, A., and Pind, S. (1989)Lipids 24, 408–418.
Roberts, W.L., Myher, J.J., Kuksis, A., and Rosenberry, T.L. (1987)Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 150, 271–277.
Roberts, W.L., Myher, J.J., Kuksis, A., Low, M.G., and Rosenberry, T.L. (1988)J. Biol. Chem. 263, 18766–18775.
Gaulton, G.N., Kelly, K.L., Pawlowski, J., Mato, J.M., and Jarett, L. (1988)Cell 53, 963–970.
Van Blitterswijk, W.J., Hilkmann, H., and Storme, G.A. (1987)Lipids 22, 820–823.
Op den Kamp, J.A.F. (1979)Ann. Rev. Biochem. 48, 47–71.
Op den Kamp, J.A.F., Roelofsen, B., and Van Deenen, L.L.M. (1985)Trends Biochem. Sci. 10, 320–323.
Boegheim, J.P.J. Jr., Van Linde, M., Op den Kamp, J.A.F., and Roelofsen, B. (1983)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 735, 438–442.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Myher, J.J., Kuksis, A. & Pind, S. Molecular species of glycerophospholipids and sphingomyelins of human erythrocytes: Improved method of analysis. Lipids 24, 396–407 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02535147
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02535147