Abstract
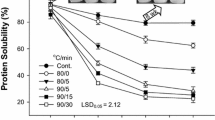
The mechanism for solubilization of alcohol-leached soy protein concentrate (ALSPC) by physical modification was studied from the standpoint of molecular interactions, which are related to the differences in protein solubility under different conditions. The low solubility of ALSPC is caused by both noncovalent and covalent forces, but the noncovalent forces do not affect the solubility of modified soy protein concentrate (MSPC). Gel filtration shows that the major constituents of soluble protein from ALSPC and MSPC are protein molecules and protein aggregates, respectively. Physical modification promotes the formation of aggregates that are readily soluble in buffer. Fluorescence spectroscopy further proved that the hydrophobic groups are located in the interior of the aggregates. The reason for the formation of soluble protein aggregates during physical modification of ALSPC is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hua, Y.F., Physical Modification of Soy Protein Concentrate Prepared by Alcohol Leaching Process, Ph.D. Dissertation of Wuxi University of Light Industry, Wuxi, 1993.
Howard, P.A., M.F. Campbell, and D.T. Zollinger, Water-Soluble Vegetable Protein Aggregates, U.S. Patent 4234620 (1980).
Voutsinas, L.P., E. Cheung, and S. Nakai, Relationships of Hydrophobicity to Emulsifying Properties of Heat-Denatured Proteins,J. Food Sci. 48:26–32 (1983).
Nakai, S., Structure-Function Relationships of Food Proteins with an Emphasis on the Importance of Protein Hydrophobicity,J. Agric. Food Chem. 31:676–683 (1983).
Kinsella, J.E., S. Damodaran, and B. German, Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Oilseed Proteins with Emphasis on Soy Protein, inNew Protein Foods, Vol. 5, edited by A.M. Altschul and H.L. Wilcke, Academic Press, Orlando, 1985, pp. 108–179.
Yamagishi, T., F. Yamauchi, and K. Shibasaki, Isolation and Partial Characterization of Heat-Denatured Products of Soybean 11S Globulin and Their Analysis by Electrophoresis,Agric. Biol. Chem. 44:1575–1582 (1980).
Nakai, S., and E. Li-Chan, Quantitative Estimation of Hydrophbicity, inHydrophobic Interaction in Food Systems, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1988, pp. 23–42.
Shimada, K., and S. Matsusita, Relationship Between Thermocoagulation of Proteins and Amino Acid Composition,J. Agric. Food Chem. 28:413–417 (1980).
Damodaran, S.J., Refolding of Thermally Unfolded Soy Proteins During the Cooling Regime of the Gelation Process: Effect on Gelation,Ibid. 36:262–269 (1988).
Yamagishi, T., A. Miyakawa, N. Noda, and F. Yamauchi, Isolation and Electrophoretic Analysis of Heat-Induced Products of Mixed Soybean 7S and 11S Globulins,Agric. Biol. Chem. 47:1229–1237 (1983).
Demchenko, A.P., inUltraviolet Spectroscopy of Proteins, Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, 1986, pp. 21–51.
T. Yamagishi, T. Tomisawa, and F. Yamauchi, Spectroscopic Studies on the Aggregates and the Dissociates Induced by Heating Soybean 11S Globulin in the Presence ofN-Ethylmaleimide,Agric. Biol. Chem. 47:2475–2481 (1983).
Damodaran, S., Interrelationship of Molecular and Functional Properties of Food Protein, inFood Protein, edited by J.E. Kinsella and W.G. Soucie, American Oil Chemists’ Society, 1989, pp. 21–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, Y.F., De Ni, P., Gu, W.Y. et al. Mechanism of physical modification of insoluble soy protein concentrate. J Am Oil Chem Soc 73, 1067–1070 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02523418
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02523418