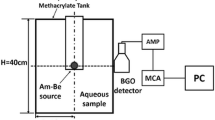
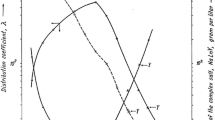
Abstract
Using an aniline sulfur resin for the selective enrichment of mercurials from surface waters it is possible to determine ppb amounts of mercury by INAA within less than three days after irradiation. Interferences from other elements, especially Na, Se, U and Au, can be avoided by following defined preconcentration and elution conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. J. KRÄMER, Thesis, Darmstadt 1975.
H. J. KRÄMER, Deutsches Patent Nr. P 2608336,6.
H. J. KRÄMER, B. NEIDHART, Radiochem. Radioanal. Letters, 22 (1975) 209.
H. J. KRÄMER, B. NEIDHART, Radiochem. Radioanal. Letters 23 (1975) 295.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krämer, H.J., Neidhart, B. Determination of trace amounts of dissolved mercury compounds by instrumental neutron activation analysis following a selective preconcentration. J. Radioanal. Chem. 37, 835–838 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02519394
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02519394