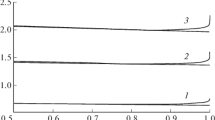
Abstract
Networks of the hydrogen bonds and those consisting of lines connecting nearby molecules were constructed using configurations of water molecules obtained by the Monte-Carlo method. The concentrations of closed cycles of hydrogen bonds were established to be determined only by the probability of hydrogen bond formation. Characteristics of a model ideal water network were determined. Topological properties of the Polk model and those of the network of nearest neighbors substantially differ from the properties of the ideal network. The totality of the hydrogen bonds in pure water was proposed to be considered as a hierarchical system. Three topologically different structures of water associates were determined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. G. Malenkov, inFizicheskaya khimiya. Sovremennye problemy [Physical Chemistry. Modern Problems], Khimiya, Moscow, 1984, 41 (in Russian).
V. V. Sinyukov,Struktura odnoatomnykh zhidkostei, vody and rastvorov elektrolitov [Structure of Monatomic Liquids, Water, and Electrolyte Solutions], Nauka, Moscow, 1976, 256 pp. (in Russian).
Water: A Comprehensive Treatise, 7: Water and Aqueous Solutions at Subzero Temperatures Ed. F. Franks, Plenum, New York, 1982.
D. Eizenberg and W. Kauzmann,The Structure and Properties of Water, Clarendon, Oxford, 1969.
H. E. Stanley and J. TeixeraJ. Chem. Phys., 1980,73, 3404.
H. E. Stanley, R. L. Blumberg, and A. Geiger,Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter, 1983,28, 1626.
M. P. Fontana and B. Rosi,J. Mol. Liq., 1989,41, 347.
Yu. G. Bushuev and A. K. Lyashchenko,Zh. Fiz. Khim., 1996,70, 416 [Russ. J. Phys. Chem., 1996,70, 380 (Engl. Transl.)].
Yu. G. Bushuev and A. K. Lyashchenko,Zh. Fiz. Khim., 1994,68, 525 [Russ. J. Phys. Chem., 1994,68, 470 (Engl. Transl.)].
Yu. G. Bushuev and A. K. Lyashchenko,Zh. Fiz. Khim., 1995,69, 38 [Russ. J. Phys. Chem., 1995,69, 33 (Engl. Transl.)].
Yu. G. Bushuev, T. A. Dubinkina, and V. P. Korolev,Zh. Fiz. Khim, 1997,71, 105 [Russ. J. Phys. Chem., 1997,71 (Engl. Transl.)].
D. E. Polk,J. Non Cryst. Solids, 1971,5, 365.
A. Gaiger, N. N. Medvedev, and Yu. I. Naberukhin,Zh. Strukt. Khim., 1992,33, No. 2, 79 [Russ. J. Struct. Chem., 1992,33, No. 2 (Engl. Transl.)].
Primenenie teorii grafov v khimii [Application of Graph Theory to Chemistry], Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1988, 306 pp. (in Russian).
B. G. Ozol-Kalnin and A. Ya. Travitis,Vysokomol. Soedin. B, 1982,24, 329 [Polym. Sci. USSR, Ser. B, 1982,24 (Engl. Transl.)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated fromIzvestiya Akademii Nauk. Seriya Khimicheskaya, No. 5, pp. 928–931, May, 1997.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bushuev, Y.G. Properties of the network of the hydrogen bonds of water. Russ Chem Bull 46, 888–891 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02496112
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02496112