Summary
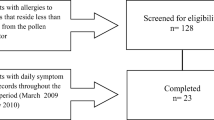
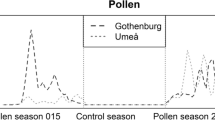
We conducted this study during the early spring to demonstrate direct response between increases in atmospheric pollen concentrations and symptom prevalence in a general population. We examined pollen concentrations indoors, outdoors and regionally in 31 households with similar background vegetation, pollen concentration, TSP and pollulant gas levels. Indoor pollen concentrations were low but persistent (X=16 grains/m3 air); local outdoor concentrations were 3 times greater. Regional daily mean pollen values of grasses, ragweed, mulberry and total pollen were compared with symptom scores using X2 contingency tests. We obtained daily symptom scores and measures of peak expiratory flow from 121 individuals characterized as «normal», «atopic» or «peak flow responsive». In atopic individuals, prevalence of nasal symptoms increased with pollen concentration increases for ragweed, mulberry and total pollen exposure. No significant response was found with spring grasses whose atmospheric pollen concentration was limited in the selected cluster. Decrease of lung function in the peak flow responsive population was found associated with mulberry pollen only. The small pollen grain size may result in greater tracheo-bronchial deposition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbee R.A., Lebowitz M.D., Thompson H.C., Burrows B., (1976) —Immediate skin-test reactivity in a general population sample. Ann. Intern. Med.84:129–133.
Frasani F., Gorini M., (1987) —Airborne pollens and symptoms score in allergic patients undergoing immunotherapy. G. Boehm, Leuschner R.M. (eds), Advances in Aerobiology, Experientia Supplementum,51:89–92.
Horak F., Jäger S., (1980) —Der biologische Expositionstest: Eine Testmethode bei Pollinose unter Ausnutzung der naturlichen Exposition. Federal Environmental Agency (eds), «First International Conference on Aerobiology-Proceeding», Erich Schmidt Verlag, Berlin, p. 355–359.
Holberg C.J., O'Rourke M.K., Lebowitz M.D., (1987) —Multivariate analysis of ambient environmental factors and respiratory effects. Int. J. of Epidemiol.16:399–410.
Käpylä M., Penttinen A., (1981) —An evaluation of the microscopical counting methods of the tape in Hirst-Burkard pollen and spore trap. Grana20:131–141.
Kneist W., Düngemann H., Gehrken H., Borelli S., (1987)Relationship of airborne pollens and spores to symptoms on the skin and mucous membranes of patients in the high altitude climate in Davos. In: G. Boehm and R.M. Leuschner (eds)), Advances in Aerobiology, Experientia Supplementum51:81–85.
Kumer E., Mandrioli P., Tampieri F., (1980) —A comparison between the concentration of airborne pollens and the clinical symptomatology in allergic subjects under treatment with hyposensitizing agents. In: Federal Environmental Agency (eds), First International Conference on Aerobiology-Proceeding. Erich Schmidt Verlag, Berlin, p. 348–354.
Lebowitz M.D., Quackenboss J.J., (1988) —Identification of sensitivity and susceptibility in subjects and evaluation of their empirical responses to air pollution. APCA Symposium Volume Paper 88-124-2.
Lebowitz M.D., Collins L., Holberg C.J., (1987) —Time series analysis of respiratory responses to indoor and outdoor environmental phenomena. Env't. Res.43:332–341.
Lebowitz M.D., Quackenboss J.J., Camilli A.E., Bronnimann D., Holberg C.J., Boyer B., (1987) —The epidemiological importance of intraindividual changes in pulmonary responses. Euro. J. Epidemiol.3:390–398.
Lucking J.C., Benjamin A.C., Everson D.A., Monroe N.L., (1988) —Arizona Statistical Review, 44th Annual Edition, Valley National Bank of Arizona, pp. 89.
O'Rourke M.K., (1982) —Composition and distribution of urban vegetation. J. Arid Envir.5:235–248.
O'Rourke M.K., (1986) —The implications of atmospheric pollen rain for fossil pollen profiles in the arid southwest. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Arizona, Tucson, 169 pp.
O'Rourke M.K., Lebowitz M.D., (1984) —A comparison of regional atmospheric pollen types at and near homes. Grana23:55–64.
Quackenboss J.J., Lebowitz M.D., Boyer-Pfersdorf P., Lanand S., Monroe S., Sells M., Winburn J., (1988) —An update on the Tucson community study of indoor/outdoor air pollution and respiratory responses. APCA Symposium Volume, Paper 88-124-2.
Quackenboss J.J., Lebowitz M.D., Michaud J.P., Bronnimann D., (1989a) —Formaldehyde exposure and acute health effects study. In press, Envir. Int.15:169–176.
Quackenboss J.J., Lebowitz M.D., Crutchfield C.D., (1989b).Indoor-outdoor relationships for particulate matter: exposure classifications and health effects. In press, Envir. Int.15:353–360.
Quackenboss J.J., Lebowitz M.D., Hayes C., (1989c) —Epidemiological study of respiratory responses to indoor/outdoor air quality. In press, Envir. Int.15:493–502.
Spieksma F.Th., (1983) —Airborne pollen concentration in Leiden, The Netherlands, 1977–1981, I. Trees and shrubs flowering in the spring. Grana 22:119–128.
Spieksma F.Th., Van Den Assem A., Collette B.J., (1985) —Airborne pollen concentration in Leiden, The Netherlands, 1977–1981, II. Poaceae (grasses), variations and relation to hay fever. Grana24:99–108.
SPSSInc. (1988) — SPSS/PC V. 2.0Base Manual, SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois.
Solomon W.R., (1988) —Aerobiology and inhalant allergens. Allergy Principles and Practice. E. Middleton, C.E. Reed, E.F. Ellis, N.F. Adkinson Jr., J.W. Yunginger (eds). C.F. Mosby Company, Washington, D.C. Chapter 16, p. 312–372.
WHOReport, (1988) —Biological contaminants in indoor air. EURO Reports and Studies, 42 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O'Rourke, M.K., Quackenboss, J.J. & Lebowitz, M.D. An epidemiological approach investigating respiratory disease response in sensitive individuals to indoor and outdoor pollen exposure in Tucson, Arizona. Aerobiologia 5, 104–110 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02486508
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02486508