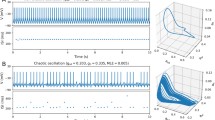
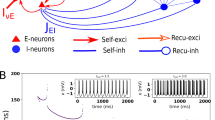
Abstract
In this paper, we study nonlinear spatio-temporal dynamics in synchronous and asynchronous chaotic neural networks from the viewpoint of the modeling and complexity of the dynamic brain. First, the possible roles and functions of spatio-temporal neurochaos are considered with a model of synchronous chaotic neural networks composed of a neuron model with a chaotic map. Second, deterministic point-process dynamics with spikes of action potentials is demonstrated with a biologically more plausible model of asynchronous chaotic neural networks. Last, the possibilities of inventing a new brain-type of computing system are discussed on the basis of these models of chaotic neural networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aihara K (ed) (1994) Applied chaos and applicable chaos (in Japanese) Science-sha, Tokyo
Aihara K, Katayama R (1995) Chaos engineering in Japan. Commun ACM 38(11):103–107.
Aihara K, Katayama R (eds) (1997) A special issue on chaos engineering. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 5(1)
Grebogi C, Yorke JA (eds) (1997) The impact of chaos on science and society United Nations University Press, Tokyo
M. Yamaguti (ed) (1994) Towards the harnessing of chaos, Elsevier Amsterdam
McCulloch WS, Pitts WH (1943) A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in neural nets. Bull Math Biophys 5:115–133
Hodgkin AL, Huxley AF (1952) A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol (London) 117:500–544
Aihara K (1988) Neural computers (in Japanese). Tokyo Denki University Press, Tokyo
Aihara K (1990) Chaotic neural networks. In: Kawakami H (ed) Bifurcation phenomena in nonlinear systems and theory of dynamical systems, World Scientific, Singapore, pp 143–161
Aihara K (ed) (1993) Chaos in neural systems (in Japanese). Tokyo Denki University Press, Tokyo
Aihara K, Matsumoto G, Ikegaya Y (1984) Periodic and nonperiodic responses of a periodically forced Hodgkin-Huxley oscillator. J Theor Biol 109:249–269
Aihara K, Matsumoto G (1986) Chaotic oscillations and bifurcations in squid giant axons. In: Holden AV (ed) Chaos, Manchester University Press, Manchester, and Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp 257–269.
Aihara K, Numajiri T, Matsumoto G et al. (1986) Structures of attractors in periodically forced neural oscillators. Phys Lett A 116:313–317
Matsumoto G, Aihara K, Hanyu Y et al. (1987) Chaos and phase locking in normal squid axons. Phys Lett A 123:162–166
Matsumoto G, Aihara K, Ichikawa M et al. (1984) Periodic and nonperiodic responses of membrane potentials in squid giant axons during sinusoidal current stimulation. J Theor Neurobiol 3:1–14
Aihara K (ed) (1993) Neural, fuzzy and chaotic computing-introduction to a new generation of analog computing (in Japanese). Ohm-sha, Tokyo
Aihara K, Takabe T, Toyoda M (1990) Chaotic neural networks. Phys Lett A 144 6(7):333–340
Rumelhart DE, McClelland JL, the PDP Research Group (1986) Parallel Distributed Processing, MIT Press, Cambridge
Hopfield JJ, Tank DW (1985) ‘Neural” computation of decisions in optimization problems, Biol Cybern 52:141–152
Adachi M, Aihara K (1997) Associative dynamics in a chaotic neural network, Neural Networks 10(1):83–98
Chen L, Aihara K (1995) Chaotic simulated annealing by a neural network model with transient chaos. Neural Networks 8(6):915–930
Chen L, Aihara K (1997) Chaos and asymptotical stability in discrete-time neural networks, Physica D 104:286–325.
Tokuda I, Aihara K, Nagashima T (1997) Global bifurcation structure of chaotic neural networks and its application to traveling salesman problems, Neural Networks 10(9):1673–1690
Yamada T, Aihara K (1997) Nonlinear neurodynamics and combinatorial optimization in chaotic neural networks. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 5(1):53–68
Watanabe M, Aihara K, Kondo S (1995) Automatic learning in chaotic neural networks. Trans IEICE J78-A(6):686–691
Watanabe M, Aihara K, Kondo S (1997) Self-organization dynamics in chaotic neural networks. In: Judd K et al. (eds) control and chaos. Birkhäuser, Boston, pp 320–333
Freeman WJ (1992) Tutorial on neurobiology-from single neurons to brain chaos. Int J Bifurcation Chaos 2(3):451–481
Skarda CA, Freeman WJ (1987) How brains make chaos in order to make sense of the world. Behav Brain Sci 10:161–195
Ichinose N, Aihara K (1994) Asynchronous chaotic neural networks. In: Yamaguti M (ed) Towards the harnessing of chaos. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 353–356
Ichinose N, Aihara K (1995) An analysis on pulse propagation dynamics in asynchronous chaotic neural networks. Trans IEICE J78-A(3):373–380 (in Japanese); English-language translation, Electronics and communications in Japan, Part 3, 78(11):52–59, Scripta Technical, John Wiley, New York
Judd K, Aihara K (1993) Pulse propagation networks: a neural network model that uses temporal coding by action potentials. Neural Networks 6(2):203–215
Maass W (1995) On the computational complexity of networks of spiking neurons. In: Tesauro G, Tourctzky D, Leens T (eds) Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 7:185–190
Abeles M (1982) Role of the cortical neuron: integrator or coincidence detector? Israel J Med Sci 18:83–92
Softky WR, Koch C (1993) The highly irregular firing of cortical cells is inconsistent with temporal integration of random ESPS. J Neurosci 13:334–350
Diez-Martinez O, Segundo JP (1983) Behavior of a single neuron in a recurrent excitatory loop. Biol Cybern 47:33–41
Pakdaman K, Vibert JF, Boussard E et al. (1996) Single neuron with recurrent excitation: effect of the transmission delay. Neural Networks 9(5):797–818
Fujii H, Ito H, Aihara K et al. (1996) Dynamical cell assembly hypothesis-theoretical possibility of spatio-temporal coding in the cortex. Neural Networks 9(8):1303–1350
Watanabe M, Aihara K (1997) Chaos in neural networks composed of coincidence detector neurons. Neural Networks 10(8):1353–1359
Watanabe M, Aihara K, Kondo S (1998) A dynamical neural network with temporal coding and functional connectivity. Biol Cybern 78:87–93
Aihara K (1998) Forced chaos in nerve membranes and its modeling and application to chaotic parallel distributed processing. Proceedings on Chaos Memorial Symposium in Asuka, in press
Shimizu K, Aihara K, Kotani M (1991) An electronics circuit model of chaotic neural networks. Electronics and Communications in Japan, Part 3, 74(1):51–64 Scripta Technica, John Wiley, New York
Kanou N, Horio Y, Aihara K et al. (1993) A current-mode circuit of a chaotic neuron model. Trans IEICE E76-A (4):642–644
Horio Y, Suyama K, Dec A et al. (1994) Switched-capacitor chaotic neural networks for traveling salesman problem. Proc WCNN94 4, pp 690–696
Horio Y, Suyama K (1995) Experimental observations of 2- and 3-neuron chaotic neural networks using switched-chapacitor chaotic neuron IC chip. Trans IEICE E78-A(4):529–535
Horio Y, Aihara K (1997) Chaotic neural network integrated circuit (in Japanese) Seitai no kagaku 48(1):67–71
Nanya T (1995) Survey on asynchronous VLSI system design techniques (in Japanese). Future Electron Devices J 6(3):11–16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Aihara, K., Ichinose, N. Modeling and complexity in neural networks. Artif Life Robotics 3, 148–154 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481131
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481131