Abstract
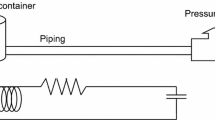
The electrolytic pressure transducer is basically an old device that has not received much attention in recent years. However, it is shown in this paper that a properly designed electrolytic catheter-tip transducer may have favourable characteristics compared with existing types. A description of a prototype transducer is given, including data concerning sensitivity, linearity, dynamic response, temperature stability and long-term stability. Some patient-hazard aspects connected with the introduction of catheter-tip transducers close to the heart are also discussed.
Sommaire
Le capteur de pression électrolytique n'a pas attiré beaucoup d'attention ces dernières années. Cependant, ce rapport montre qu'un capteur électrolytique de bout de cathéter de conception appropriée peut avoir des caractéristiques favorables par rapport aux modèles existants à l'heure actuelle. Il s'ensuit une description d'un capteur prototype y compris les données de sensibilité, linéarité, réponse dynamique, stabilité de température et stabilité à longue échéance. Egalement, discussion de certains aspects dangereux pour le patient eu égard à l'introduction des capteurs de bout de cathéter à proximité du coeur.
Zusammenfassung
Der elektrolytische Druckwandler hat in den vergangenen Jahren keine große Beachtug erlangt. In dieser Abhandlung wird jedoch aufgezeigt, deß ein entsprechend konstruierter elektrolytischer Katheterspitzen-Wandler im Vergleich mit gegenwärtig existierenden Typen günstige Eigenschaften aufweisen kann. Ein Prototyp-Wandler wird beschrieben—einschließlich technischer Daten über Empfindlichkeit, Linearität, dynamisches Ansprechverhalten, Temperatur- und Dauerstabilität. Einige Gesichtspunkte in bezug auf das Risiko, das sich für die durch Patienten Einführung des Katheterspitzenwandlers nahe dem Harzen ergibt, werden ebenfalls behandelt.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garten, S. (1916) Beiträge zur Lehre vom Kreislauf.Z. Biol. 66, 23–82.
Geddes, L. A. (1970)The direct and indirect measurement of blood pressure. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago.
Gruenbaum, O. F. F. (1897–98) On a new method of recording alterations of pressure.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 22, xlix-li.
Hök, B. andGroth, Ö. (1972) An electrolytic pressure sensor for bio-medical applications. 3rd Int. Conf. Med. Phys. Med. Engng., Göteborg, Sweden, 30.5.
Schuetz, E. (1931) Konstruktion einer manometrischen Sonde mit elektrischer Transmission.Z. Biol. 91, 515–521.
Wiederhielm, C. A. andRushmer, R. F. (1964) Pre- and post-arteriolar resistance changes in the blood vessels of the frog's mesentery.Bibl. Anat. 4, 234–243.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hök, B. Electrolytic catheter-tip pressure transducer. Med. & biol. Engng. 12, 355–359 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02477805
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02477805