Abstract
In the present investigation a method of quantifying electromyograms (EMG's) from different muscle groups of the body to evaluate total muscular activity is described.
A unipolar pickup, i.e., one standard silver cup surface electrode over each active muscle, was used because the EMG outputs with this electrode configuration during the same muscular activity were found to be greater than those with a bipolar pickup, i.e., two electrodes over each muscle.
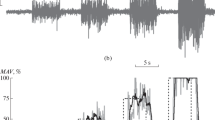
It was observed that for the purpose of quantification the root mean square (r.m.s.) value of a ‘steady’ level or the average r.m.s. value of a varying level of EMG is related in a linear fashion to the absolute mean value of the wave obtained by integrating the EMG for a specified time interval after making the waveform unidirectional. A similar relationship was observed with different voltage levels from a noise generator which was used for calibration purposes.
EMG's from different muscle groups during isometric as well as isotonic voluntary contractions were found to summate together outside the body in a manner similar to noise voltages, i.e., the r.m.s. value of the combined voltages is equal to the square root of the sum of the mean square values of the individual waves.
A method of passing EMG's through a summing amplifier and then quantifying the output for the evaluation of total muscular activity was developed, which greatly reduces the system components normally necessary for such studies.
The results obtained from a series of experiments are discussed in detail.
Sommaire
Les auteurs décrivent une méthode de quantification des électromyogrammes (E.M.G.) de différents groupes de muscles du corps utilisée pour évaluer l'activité musculaire totale.
Ils ont employé un capteur unipolaire, en l'occurrence une électrode standard de surface à coupelle d'argent appliquée à chaque muscle actif, parce que les rendements d'E.M.G. obtenus avec cette disposition d'électrodes ont été reconnus plus élevés, pour une même activité musculaire, que ceux obtenus avec un capteur bipolaire, c. -à-d. à deux électrodes par muscle.
Les auteurs ont constaté qu'aux fins de quantification la valeur efficace d'un niveau “stable” ou la valeur efficace d'un niveau variable de l'E.M.G. présente une relation linéaire avec la valeur moyenne absolue de l'onde obtenue en intégrant l'E.M.G. pour un intervalle de temps spécifié après avoir rendu la forme d'onde unidirectionnelle. Une relation similaire a été observée à différents niveaux de voltage fournis par un générateur de bruit utilisé pour le calibrage.
Les auteurs ont découvert que des E.M.G. de différents groupes de muscles établis autant pendant des contractions isométriques que pendant des contractions isotoniques volontaires s'additionnent hors du corps d'une manière similaire à celle des voltages de bruit, c. -à-d. que la valeur efficace des voltages combinés est égale à la racine carrée de la somme des valeurs carrées moyennes des ondes individuelles.
Une méthode de passage des E.M.G. par un amplificateur intégrateur, suivi de quantification du résultat en vue de l'évaluation de l'activité musculaire totale, élaborée par les auteurs, réduit considérablement les composantes de système normalement nécessaires aux travaux de ce genre.
Les résultats d'une série d'expériences sont analysés en détail.
Zusammenfassung
In der vorliegenden Untersuchung wird eine Methode zur Quantifizierung von Elektromyogrammen (EMG'e) von verschiedenen Muskelgruppen des Körpers zur Wertbestimmung von Gesamtmuskelaktivität beschrieben.
Ein einpoliges Aufnahmsgerät, das ist eine Standardoberflächenelektrode aus einer Silberschale über jedem tätigen Muskel, wurde verwendet, weil gefunden wurde, daß die EMG-Ausgänge mit dieser Elektrodenkonfiguration während der selben Muskelaktivität größer waren als jene mit einem zweipoligen Aufnahmsgerät, das ist zwei Elektroden über jedem Muskel.
Es wurde beobachtet, daß zum Zweck der Quantifizierung der quadratische Mittelwert eines stetigen Pegels, oder der durchschnittliche quadratische Mittelwert eines schwankenden Pegels des EMG in linearer Weise zum absoluten Mittelwert der Welle in Beziehung steht, der durch Integration des EMG für ein bestimmtes Zeitintervall erhalten wird, nachdem die Wellenform gleichgerichtet wurde. Eine ähnliche Beziehung wurde mit verschiedenen Spannungspegeln von einem Geräuscherzeuger beobachtet, der für Kalibrierungszwecke verwendet wurde.
Es wurde gefunden, daß EMG'e von verschiedenen Muskelgruppen sowohl während isometrischer als auch isotoner freiwilliger Zusammenziehungen außerhalb des Körpers mit einander in einer Art summieren, die Geräuschspannungen ähnlich ist, das ist der quadratische Mittelwert der vereinigten Spannungen ist gleich der Quadratwurzel der Summe der Quadratmittelwerte der individuellen Wellen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basmajian, J. V. (1962)Muscles Alive, Their Functions Revealed by Electromyography, pp. 421. Williams & Wilkins, sBaltimore.
Bayer, H. andFlechtenmacher, C. (1950) Ermüdung und Aktionsstrospannung bei der isometrischen Muskelkontracktion des Menschen.Arbeitsphysiol. 14, 261.
Bigland, B. andLippold, O. C. J. (1954) The relation between force, velocity, and integrated electrical activity in human muscles.J. Physiol. 123, 214–224.
Davis, R. C. (1943) The genetic development of patterns of voluntary activity.J. exp. Psychol. 33, 340–365.
de Vries, H. A. (1965) Muscle tonus in postural muscles.Am. J. phys. Med. 44, 275–291.
Harding, R. H. andSen, R. N. (1969a) A simple continuous pedalling rate indicator for use with a bicycle ergometer.J. Physiol. 201, 14–15P.
Harding, R. H. andSen, R. N. (1969b) A new simple method of quantifying the electromyogram to evaluate total muscular activity.J. Physiol. 204, 66–68P.
Inman, V. T., Ralston, H. J., Saunders, J. B. de C. M., Feinstein, B. andWrigh, E. W., Jr. (1952) Relation of human electromyogram to muscular tension.Electroencephy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 4, 187–194.
Lippold, O. C. J. (1952) The relation between integrated action potentials in a human muscle and its isometric tension.J. Physiol. 117, 492–499.
Lippold, O. C. J. (1964) Integration.Bull.Br. psychol. Soc. 17, 39–45.
Moore, A. D. (1967) Synthesized EMG waves and their implications.Am. J. phys. Med. 40, 1302–1316.
Müller, E. A. andOlech, K. H. (1964) Eich-Kontrolle für das permanentmagnetisch gebremste Fahrrad-Ergometer nach E. A. Müller.Arbeitswissenschaft. Nr. 6.
Ralston, H. J., Inman, V. T., Strait, L. A. andShaffrath, M. D. (1947) Mechanics of human isolated muscle.Am. J. Physiol. 151, 612–620.
Scherrer, J. andBourguignon, A. (1959) Changes in electromyogram produced by fatigue in man.Am. J. phys. Med. 38, 148–157.
Shaw, J. C. (1967) In:A Manual of Psycho-Physiological Methods (Eds.Venables, P. H. andMartin, I. I.), pp. 403–465. North-Holland, Amsterdam.
Wilcott, R. C. andBeenken, H. G. (1957) Relation of integrated surface electromyography and muscle tension.Percept. mot. Skills 7, 295–298.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harding, R.H., Sen, R.N. Evaluation of total muscular activity by quantification of electromyograms through a summing amplifier. Med. & biol. Engng. 8, 343–356 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02477662
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02477662