Abstract
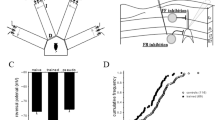
Na+, K+-ATPase and Mg2+-ATPase activities were studied in neurons and glial cells of the olfactory cortex of the rat by quantitative cytophotometry in conditions of long-term potentiation (LTP), and significant changes in direction and extent were found. Na+, K+-ATPase activity decreased in neurons in the first 15 min after LTP, with subsequent elevation by 30 min. Mg2+-ATPase activity remained unchanged in these conditions. Glial cells showed significant increases in Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the initial period after LTP, with return to control by 30 min. Again, there were no significant changes in Mg2+-ATPase activity. The formation and persistence of LTP in neurons and glial cells was accompanied by significant changes in Na+, K+-ATPase activity, which were reciprocal in nature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. A. Boldyrev, “Na+,K+-ATPase,” in: Science and Technology [in Russian], Vol. 17 (1985), pp. 5–120.
I. A. Gerasimova, T. S. Glushchenko, A. A. Mokrushin, and N. A. Emel'yanov, “Number of neurochemical correlates of the development of long-term potentiation in rat brain sections,” Biol. Membrany,9, No. 10-11, 1089–1091 (1992).
V. A. Klenikova and N. P. Taranova, “ATPase activity in neurons and glial cells in rat brain during deprivation of paradoxical sleep (a cytochemical study),” Fiziol. Zh. SSSR,74, No. 4, 490–496 (1988).
M. I. Mityushov, N. A. Emel'yanov, and A. A. Mokrushin, The Living Brain Slice as an Object of Neurophysiological and Neurochemical Study [in Russian], Leningrad (1986).
N. S. Nilova and L. N. Polezhaeva, “Lipid peroxidation in sections of the olfactory cortex of the rat brain during long-term potentiation,” Fiziol. Zh. im. I. M. Sechenova,80, 43–47 (1994).
L. I. Pavlinova and A. A. Mokrushin, “The effects of long-term potentiation on phosphoinositide metabolism in sections of the olfactory cortex,” Biol. Membrany,9, No. 10-11, 1111–1112 (1992).
L. Z. Pevzner, The Functional Biochemistry of Neuroglial Cells [in Russian], Leningrad (1972).
A. I. Roitbak, “A glial hypothesis for the formation of temporary connections,” in: Proceedings of the All-Union Symposium Celebrating the Hundredth Anniversary of the I. P. Pavlov Department of Physiology, Science Research Institute of Experimental Medicine, Academy of Medical Sciences of the USSR [in Russian], Leningrad (1991), pp. 93–95.
L. G. Tsakadze and Z. P. Kometiani, “Regulation of the Na+,K+-ATPase system by neurotransmitters,” Biol. Nauki, No.6, 16–20 (1990).
B. A. Barres, “New roles of glia,” J. Neurosci.,11, No. 12, 3685–3694 (1991).
A. A. Boldyrev, E. G. Kurella, and T. N. Fedorova, “Lipid control of brain synaptosomal membrane Na+,K+-ATPase,” in: Physiological and Biochemical Basis of Brain Activity, Abstracts of International Symposium, St. Petersburg (1994), p. 71.
G. Christoli, A. V. Nowisky, and L. J. Bindman, “The postsynaptic induction of long-term depression (LRD) of synaptic transmission in isolated rat hippocampal slices requires extracellular calcium,” J. Physiology (Lond.),428, No. 1, 257–265 (1991).
A. B. Farooqui and L. A. Horrocks, “Excitatory amino acid receptors, neural membrane phospholipid metabolism and neurological disorders,” Brain. Res. Rev.,16, No. 2, 171–191 (1991).
R. D. Fields, C. Yu, and P. C. Nelson, “Calcium, network activity, and the role of NMDA channels in synaptic plasticityin vivo,” J. Neurosci.,11, No. 1, 143–146 (1991).
K. M. McGrail, Y. M. Philips, and K. J. Sweadner, “Immunofluorescent localization of three Na+,K+-ATPase isozymes in the rat central nervous system: both neurons and glia can express more than one Na+,K+-ATPase,” J. Neurosci.,11, No. 2, 381–391 (1991).
T. Grisar, G. Franck, and E. Schoffeniels, “Glial control of neuronal excitability in mammals. Enzymatic evidence: two molecular forms of the Na+,K+-ATPase in brain,” Neurochem. Internat.,2, No. 2, 311–320 (1980).
N. L. Izvarina, T. S. Glushchenko, A. V. Tokarev, and N. A. Emelyanov, “Some neurochemical mechanisms of long-term potentiation in olfactory cortex slice,” J. Neurosci. Methods, No. 34, A1-A28 (1994).
P. R. Laming, “Do glia contribute to behavior?,” Functions in Neurology [English article in Russian-language book], Proceedings of Symposium, Tbilisi (1989), p 32.
G. Lynch and M. Baudry, “The biochemistry of memory: a new and specific hypothesis,” Science,224, No. A653, 1057–1063 (1984).
P. Rossi and D. Andgelo, “Synaptic mechanisms in long-term potentiation,” Funct. Neurol.,7, No. 1, 57–70 (1992).
Additional information
Functional Neurochemistry Laboratory (Director N. A. Emel'yanov), I. P. Pavlov Institute of Physiology, Russian Academy of Sciences, St. Petersburg. Translated from Fiziologicheskii Zhurnal im. I. M. Sechenova, Vol. 81, No. 3, pp. 16–20, March, 1995.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glushchenko, T.S., Izvarina, N.L. Na+, K+-ATPase activity in neurons and glial cells of the olfactory cortex of the rat brain during the development of long-term potentiation. Neurosci Behav Physiol 27, 49–52 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02463045
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02463045