Abstract
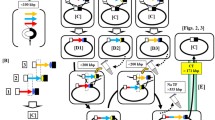
A novel approach to the cloning large DNAs in theBacillus subtilis chromosome was examined. AnEscherichia coli prophage lambda DNA (48.5 kb) was assembled in the chromosome ofB. subtilis. The lambda DNA was first subcloned in four segments, having partially overlapping regions. Assembly of the complete prophage was achieved by successive transformation using three discrete DNA integration modes: overlap-elongation, Campbell-type integration, and gap-filling. In theB. subtilis chromosome, DNA was elongated, using contiguous DNA segments, via overlap-elongation. Jumping from one end of a contiguous DNA stretch to another segment was achieved by Campbell-type integration. The remaining gap was sealed by gap-filling. The incorporated lambda DNA thus assembled was stably replicated as part of the 4188 kbB. subtilis chromosome under non-selective conditions. The present method can be used to accommodate larger DNAs in theB. subtilis chromosome and possible applications of this technique are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anagnostopoulos C (1990) Genetic rearrangements inBacillus subtilis 168. In: Drlica K, Riley M (eds) The bacterial chromosome. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 361–367
Arber W (1983) A beginners guide to lambda biology. In: Hendrix RW, Roberts JW, Stahl FW, Weisberg RA (eds) Lambda II. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York pp 381–394
Breitling R, Sorokin AV, Behnke D (1990) Temperature-inducible gene expression inBacillus subtilis mediated by thecI857-encoded repressor of bacteriophage lambda. Gene 93:35–40
Burke DT, Carle GF, Olson MV (1987) Cloning of large segments of exogenous DNA into yeast by means of artificial chromosome vectors. Science 236:806–812
Campbell AM (1993) Thirty years ago in genetics: prophage insertion into bacterial chromosome. Genetics 133:433–438
Dose K, Bieger-Dose A, Kerz O, Gill M (1991) DNA strand breaks limit survival in extreme dryness. Orig Life 21:177–187
Dubnau DA (1982) Genetic transformation inBacillus subtilis. In: Dubnau D (ed) The molecular biology of the bacilli, vol 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 147–178
Errington J (1990) Gene cloning techniques. In: Harwood CR, Cutting S (eds) Molecular biological methods for Bacillus. John Wiley and Sons, UK, pp 175–220
Heinemann JA (1991) Genetics of gene transfer between species. Trends Genet 7:181–185
Holloway BW (1993) Genetics for all bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 47:659–684
Itaya M (1993a) Physical map of theBacillus subtilis 168 chromosome. In: Sonenshein AL, Hoch JA, Losick R (eds)Bacillus subtilis and other gram-positive bacteria. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 463–471
Itaya M (1993b) Stability and asymmetric replication of theBacillus subtilis 168 chromosome. J Bacteriol 175:741–749
Itaya M (1993c) Integration of repeated sequences (pBR322) in theBacillus subtilis 168 chromosome without affecting the genome structure. Mol Gen Genet 241:287–297
Itaya M (1994) First evidence for homologous recombination mediated large DNA inversion on theBacillus subtilis chromosome. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:1836–1841
Itaya M, Tanaka T (1990) Gene-directed mutagenesis on the chromosome ofBacillus subtilis 168. Mol Gen Genet 223:268–272
Itaya M, Tanaka T (1991) Complete physical map of theBacillus subtilis 168 chromosome constructed by a gene-directed mutagenesis method. J Mol Biol 220:631–648
Itaya M, Laffan JJ, Sueoka N (1992) Physical distance between the site of type II DNA binding to the membrane andoriC on theBacillus subtilis 168 chromosome. J Bacteriol 174:5466–5470
Kohara Y, Akiyama K, Isono K (1987) The physical map of the wholeEscherichia coli chromosome: Application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell 50:495–509
Mandel M, Higa A (1970) Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol 53:159–162
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Ogura M, Kawata-Mukai M, Itaya M, Takio K, Tanaka T (1994) Multiple copies of theproB gene enhance degS-dependent extracellular protease production inBacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 176:5673–5680
Petit M-A, Mesas JM, Noirot P, Morel-Deville F, Ehrlich SD (1992) Induction of DNA amplification in theBacillus subtilis chromosome. EMBO J 11:1317–1326
Saito H, Miura K (1963) Preparation of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid by phenol treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta 72:619–629
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sanger F, Coulson AR, Hong GF, Hill DF, Petersen GB (1982) Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol 162:729–773
Shepherd NS, Pfrogner BD, Coulby JN, Ackerman SL, Vaidyanathan G, Sauer RH, Balkenhol TC, Sternberg N (1994) Preparation and screening of an arrayed human genomic library generated with the P1 cloning system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2629–2633
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–519
Spizizen J (1958) Transformation of biochemically deficient strains ofBacillus subtilis by deoxyribonucleate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 44:1072–1078
Trautner AT, Noyer-Weidner M (1993) Restriction/modification and methylation systems inBacillus subtilis, related species, and their phages. In: Sonenshein AL, Hoch JA, Losick R (eds)Bacillus subtilis and other gram-positive bacteria. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 539–552
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. Böhme
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Itaya, M. Toward a bacterial genome technology: integration of theEscherichia coli prophage lambda genome into theBacillus subtilis 168 chromosome. Molec. Gen. Genet. 248, 9–16 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02456608
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02456608