Abstract
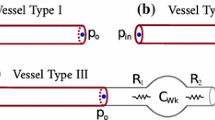
The paper presents a theoretical model which can be used to simulate a vascular network which includes loops and bypass grafts, a feature not possible with previous models. Using the linearised Navier-Stokes equations, the linearised equation of a uniform thick-walled viscoelastic tube, and the equation of continuity, the model is applied to a vascular network which includes a bypass graft. This method represents each segment of an artery or graft by a four-terminal-network whose A, B, C, D parameters are functions of the frequency and physical characteristics of the segment. The model predicts the flow and pressure waveforms at any point in the human arterial network very accurately when compared with data obtained from normal patients, patients with arterial stenoses and for hypertensive patients. The model also gives results which are in close agreement with hydraulic experimental data for the input impedance of systems with bypass loops.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aatre, V. K. (1986)Network theory and filter design. John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York.
Avolio, A. P. (1980) Multi-branched model of the human arterial system.Med. & Biol. Eng. & Comput.,18, 709–718.
Billet, A., Queral, L., Polito, W. andDagher, F. (1984) The vascular steal phenomenon: an experimental model.Surg.,96, 923–927.
Cox, R. H. (1969) Comparison of linearized wave propagation models for arterial blood flow analysis.J. Biomech.,2, 251–265.
Gabe, I. T., Karnell, J., Porje, I. G. andRudewald, B. (1964) The measurement of input impedance and apparent phase velocity in the human aorta.Acta. Physiol. Scand.,61, 73–84.
How, T. V. andCampbell, H. (1985) Arterial steal phenomenon in femoro-tibial bypass with arterio-venous shunt.J. Biomech.,18, 463–465.
Hyman, W. A. andBrewer, M. A. (1980) The hemodynamics of arterial steal.,13, 469–675.
Jager, G. N. (1965) Electrical model of the human systemic arterial tree. Ph. D. Thesis. Univ. of Utrecht.
Jager, G. N., Westerhof, N. andNoordergraaf, A. (1965) Oscillatory flow impedance in electrical analog of arterial system.Circ. Res.,16, 121–133.
Latham, R. D., Westerhof, N., Sipkema, P., Rubal, B. J., Reuderink, P. andMurgo, J. P. (1985) Regional wave travel and reflections along the human aorta: a study with six simultaneous micromanometric pressures.Circ.,72, 1257–1269.
Li, J. K.-J. (1987)Arterial system dynamics. New York University Press, New York.
Lightner, M. R. andDirector, S. W. (1982) Computer-aided design of electronic circuits. InElectronics engineers' handbook.Fink, D. G. andChristiansen, D. (Eds.), Sec.27, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Luchsinger, P. C., Snell, R. E., Patel, D. J. andFry, D. L. (1964) Instantaneous pressure distribution along the human aorta.Circ. Res.,15, 503–510.
McDonald, D. A. (1974)Blood flow in arteries. Arnold, London.
McHale, P. A., Rembert, J. C. andGreenfield, J. C. (1980) Measurement and significance of aortic pressure-flow relationships in man. InBasic haemodynamics and its role in disease processes.Patel, D. J. andVaishnav, R. N. (Ed.), University Park Press, Baltimore, 363–406.
Merillon, J. P., Fontenier, G. J., Lerallut, M. Y., Jaffrin, M. Y., Motte, G. A., Genain, C. P., Gourgon, R. R. (1982) Aortic input impedance in normal man and arterial hypertension: its modification during change in aortic pressure.Cardiovasc. Res.,16, 646–656.
Mills, C. J., Gabe, I. T., Gault, J. H., Mason, D. T., Ross, J., Braunwald, E. andShillingford, J. P. (1970) Pressure-flow relationships and vascular impedance in man.,4, 405–417.
Milnor, W. R. (1982)Hemodynamics. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore.
Nichols, W. W., Conti, C. R., Walker, W. E. andMilnor, W. R. (1977) Input impedance of the systematic circulation in man.Circ. Res.,40, 451–458.
Noordergraff, A. (1969) Hemodynamics. InBiological engineering.Schwan, H. P. (Ed.), McGraw-Hill, New York, 391–545.
Noordergraff, A. (1978)Circulatory system dynamics. Academic Press, New York.
O'Rourke, M. F., Blazek, J. V., Morreels C. L. Jr. andKrovetz, L. G. (1968) Pressure wave transmission along the human aorta.Circ. Res.,23, 567–579.
O'Rourke, M. F. (1970) Arterial hemodynamics in hypertension., Suppl. II,16 and17, 123–133.
O'Rourke, M. F. (1976) Pulsatile arterial hemodynamics in hypertension.Austr. N. Z. J. Med., Suppl.II,6, 40–48.
Patel, D. J., Greenfield, J. C., Austen, W. G., Morrow, A. G. andFry, D. L. (1965) Pressure-flow relationships in the ascending aorta and femoral artery of man.J. Appl. Physiol.,20, 459–463.
Rittgers, S. E., Karayannacos, P. E., Guy, J. F., Nerem, R. M., Shaw, G. M., Hostetler, J. R. andVasko, J. S. (1978) Velocity distribution and intimal proliferation in autologous vein grafts in dogs.Circ. Res.,42, 792–801.
Roller, M. L. andClark, M. E. (1969) Precursor cerebral circulation models.J. Biomech.,2, 241–250.
Sunagawa, K., Maughan, W. L. andSagawa, K. (1985) Stroke volume effect of changing arterial input impedance over selected frequency ranges.Am. J. Physiol.,17, H477-H484.
Taylor, M. G. (1966a) The input impedance of an assembly of randomly branching elastic tubes.Biophys. J.,6, 29–51.
Taylor, M. G. (1966b) Wave transmission through an assembly of randomly branching elastic tubes.,6, 697–716.
Ting, C. T., Brin, K. P., Lin, S. J., Wang, S. P., Chang, M. S., Chiang, B. N. andYin, F. C. P. (1985) Arterial hemodynamics in human hypertension.J. Clin. Invest.,78, 1462–1471.
Tukmachi, E. S. A. andTaylor, D. E. M. (1985) Method of assessing the contribution of components of an anastomosing vascular network to total vascular impedance.J. Biomed. Eng.,7, 105–112.
Westerhof, N., Elzinga, G. andVan den Bos, G. C. (1973) Influence of central and peripheral changes on the hydraulic input impedance of the systemic arterial tree.Med. & Biol. Eng.,11, 710–723.
Westerhof, N., Murgo, J. P., Sipkema, P., Giolma, J. P. andElzinga, G. (1979) Arterial impedance. InQuantitative cardiovascular studies.Hwang, N. H. C., Gross, D. R. andPatel, D. J. (Eds.), University Park Press, Balitmore, 111.
Wiener, F., Morkin, E., Skalak, R. andFishman, A. P. (1966) Wave propagation in the pulmonary circulation.Circ. Res.,19, 834–850.
Womersley, J. R. (1957a) The mathematical analysis of the arterial circulation in a state of oscillatory motion. Wright Air Development Center, Technical Report WADC-TR56-614.
Womersley, J. R. (1957b) Oscillatory flow in arteries: the constrained elastic tube as a model of arterial flow and pulse transmission.Phys. Med. Biol.,2, 178–187.
Wylie, B. E. andStreeter, V. (1977)Fluid transients. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Helai, M.A., Watts, K.C., Marble, A.E. et al. Theoretical model for assessing haemodynamics in arterial networks which include bypass grafts. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 28, 465–473 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441970
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441970