Summary
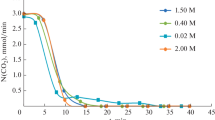
The present study was carried out to determine the influence of carbon dioxide and oxygen tension on the respiratory activity of bone cells in mouse calvaria in vitro. Five-day-old mouse calvaria were removed aseptically and incubated individually for 1 h at 37° C in a closed reaction chamber containing 1.5 ml of tissue culture medium made up of 60% horse serum in Gey's solution containing 100 unit/ml penicillin and 100µg/ml streptomycin. Before the calvaria were added, the medium in the incubation chamber was equilibrated with 10%, 20%, 30%, or 50% oxygen balanced with nitrogen. The effect of CO2 on oxygen utilization by the calvaria was determined by incubating the calvaria in a medium previously equilibrated with either 50% O2 balanced with N2 or 50% O2 and 5% CO2 balanced with N2. At each oxygen tension, the rate of oxygen utilization by the calvaria was measured polarographically by a Clark oxygen electrode. The results showed that the rate of oxygen uptake of bone increased as the oxygen tension increased and carbon dioxide stimulated significantly the rate of oxygen utilization by the bone cells. In view of the previous reports that both carbon dioxide and oxygen tension are implicated in the process of bone resorption, it is suggested that these two factors may affect bone resorption by influencing the oxygen utilization by bone cells and ultimately controlling their energy metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldhaber, P.: The effect of hyperoxia on bone resorption in tissue culture, Arch. Pathol.66:635–641, 1958
Goldhaber, P.: Behavior of bone in tissue culture. In R.F. Sognnaes (ed.): in Calcification in Biological Systems, pp. 349–372. American Association for the Advancement of Science, Washington, D.C., 1960
Stern, B., Glimcher, M.J., Goldhaber, P.: The effect of various oxygen tensions on the syntehsis and degradation of bone collagen in tissue culture, Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.121:869–872, 1966
Mahgoub, A., Stern, P.: Carbon dioxide and the effect of parathyroid hormone on bone in vitro, Am. J. Physiol.226:1272–1275, 1974
Ceriotti, G.: A microchemical determination of deoxyribonucleic acid, J. Biol. Chem.198:297–303, 1952
Ceriotti, G.: Determination of nucleic acid in animal tissues, J. Biol. Chem.214:56–70, 1955
Kenny, A.D., Draskoczy, P.R., Goldhaber, P.: Citric acid production by resorbing bone in tissue culture, Am. J. Physiol.226:502–504, 1959
Mundy, G.R., Shapiro, J.L., Bandelin, J.G., Canalis, E.M., Raisz, L.G.: Direct stimulation of bone resorption by thyroid hormones, J. Clin. Invest.58:529–534, 1976
Komaromi, I.: The effect of thyroxine derivatives on oxygen consumption and adrenal weight in the rat, Acta. Physiol. Acad. Sci. Hung.27:213–219, 1965
Hassinen, I.E., Ylikahri, R.H., Kahonen, M.I.: Regulation of cellular respiration by thyroid hormone, Arch. Biochem. Biophys.93:147; 255–261, 1971
Cohn, D.V., Griffith, F.D.: The influence of parathyroid extract on oxidative and decarboxylative pathways in bone. In P.J. Gaillard, R.V. Talmage, and A. M. Budy (eds.): The Parathyroid Glands: Ultrastructure, Secretion and Function, pp. 231–242. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1965
Gesinski, R.M., Morrison, J.H., Toepfer, J.R.: Measurement of oxygen consumption of rat bone marrow cells by a polarographic method, J. Appl. Physiol.24:751–754, 1968
Minkin, C., Jennings, J.M.: Carbonic anhydrase and bone remodeling: sulfonamide inhibition of bone resorption, Science176:1031–1033, 1972
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korayem, M.R., Goldhaber, P. Effect of carbon dioxide and various oxygen tensions on the respiratory activity of bone. Calcif Tissue Int 27, 165–169 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441180
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02441180