Summary
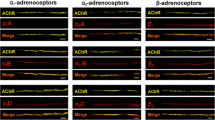
By studying the in vitro effects of three sympathomimetic amines (l-epinephrine, l-norepinephrine and l-isoproterenol) and of four adrenergic blocking agents (dichloroisoproterenol, alderline, tolazoline and phenoxybenzamine) under identical experimental conditions, the presence of adrenotropic receptors of the extraocular muscles of three species is demonstrated and their nature is determined. No difference of the receptor-pattern is revealed within the extrinsic muscles of the same, however, between the three species: a dual adrenotropic receptor mechanism is found in the extraocular muscles of the rabbit (predominance of the adrenotropic α-receptor type) and of the cat (predominance of the adrenotropic β-receptor type). Only the β-type receptors are detected in the extraocular muscles of the rhesus monkey.
Responses of isolated Felderstruktur and Fibrillenstruktur fibers of the rabbit's superior rectus muscle to sympathomimetic agents clearly indicate, that the adrenotropic receptors are located in the Felderstruktur fibers. It is reasonable to assume, that the Felderstruktur fibers of the cat and the rhesus monkey carry the adrenotropic receptors too.
Zusammenfassung
Durch Untersuchen der in vitro-Wirkung von 3 Catecholaminen (l-Epinephrin, l-Norepinephrin und l-Isoproterenol) und 4 adrenergischen Blockern (Dichloroisoproterenol, Alderlin, Tolazolin, Phenoxybenzamin) auf die extraoculären Muskeln des Kaninchens, der Katze und des Rhesusaffen werden unter identischen Versuchsbedingungen adrenotrope Receptoren in den äußeren Augenmuskeln dieser Säugetiere nachgewiesen und in α- und β-Typen eingeteilt. Innerhalb derselben Species ist das Verteilungsmuster der α- und β-Typen konstant, nicht jedoch zwischen den 3 Species: in den äußeren Augenmuskeln des Kaninchens und der Katze finden sich α- und β-adrenotrope Receptoren, wobei beim Kaninchen die adrenotropen Receptoren vom α-Typ, bei der Katze diejenigen vom β-Typ überwiegen. In den extraoculären Muskeln des Rhesusaffen werden ausschließlich adrenergische Receptoren vom β-Typ gefunden.
Die Reaktion isolierter Felder- und Fibrillenstrukturfasern aus dem M. rectus superior des Kaninchens auf Sympathomimetica zeigt, daß die adrenotropen Receptoren auf den Felderstrukturfasern sitzen. Es darf angenommen werden, daß auch bei der Katze und dem Rhesusaffen die Felderstrukturfasern Träger der adrenergischen Receptoren sind.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Ahlquist, R. P.: A study of the adrenotropic receptors. Amer. J. Physiol.153, 586–600 (1948).
—: The adrenotropic receptor-detector. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn.139, 38–41 (1962).
Alphen, G. W. H. M. van, R. Kern, andS. L. Robinette: Comparison of adrenergic receptors of the intraocular muscles in cat, rabbit and monkey. Arch. Ophthal.74, 253–259 (1965).
Brand, D. E., andC. R. Leeson: Structural differences of fast and slow fibers in human extraocular muscle. Amer. J. Ophthal.62, 478–487 (1966).
Cheng, K., andG. M. Breinin: Fine structure of nerve endings in extraocular muscle. Arch. Ophthal.74, 822–834 (1965).
Dietert, S. E.: The demonstration of different types of muscle fibers in human extraocular muscle by electron microscopy and cholinesterase staining. Invest. Ophthal.4, 51–63 (1965).
Hess, A., andG. Pilar: Slow fibres in the extraocular muscles of the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.)169, 780–798 (1963).
Kern, R.: A comparative pharmacologic-histologic study of slow and twitch fibers in the superior rectus muscle of the rabbit. Invest. Ophthal.4, 901–910 (1965).
—: Über die adrenergischen Receptoren der extraokulären Muskeln des Rhesusaffen. Eine in vitro Studie. Albrecht v. Graefes Arch. klin. exp. Ophthal.174, 278–286 (1968).
Krnjevic, K., andR. Miledi: Some effects produced by adrenaline upon neuromuscular propagation in rats. J. Physiol. (Lond.)141, 291–304 (1958).
Krüger, P.: Die Innervation phasisch bzw. tonisch reagierender Muskeln von Säugetieren und des Menschen. Acta anat. (Basel)40, 186–210 (1960).
Mayr, R., L. Stockinger u.W. Zenker: Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen an unterschiedlich innervierten Muskelfasern der äußeren Augenmuskulatur des Rhesusaffen. Z. Zellforsch.75, 434–452 (1966).
Oppel, O.: Über die motorischen, sensorischen und sensiblen Nerveneinrichtungen im menschlichen Augenmuskelapparat und ihre sinnesphysiologische Bedeutung. Albrecht v. Graefes Arch. klin. exp. Ophthal.171, 337–366 (1967).
Zenker, W., andH. Anzenbacher: On the different forms of myoneural junction in two types of muscle fiber from the external ocular muscles of the rhesus monkey. J. cell. comp. Physiol.63, 273–285 (1964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kern, R. Die adrenergischen Receptoren der extraoculären Muskeln des Kaninchens, der Katze und des Rhesusaffen. II. Albrecht v Graefes Arch. klin. exp. Ophthal. 175, 359–374 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02440011
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02440011