Abstract
The effect of atropine on discharge pattern of phrenic motoneurons was investigated in rats after vagotomy. The following results were obtained:
-
1.
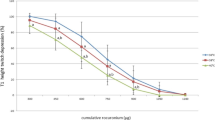
Atropine increased the distance of impulses, while the number of spikes was reduced. This effect was dose dependent for 0.6, 1.2, 2.4, and 4.8 mg/kg atropine injected intravenously. At the same time the frequency of respiration increased after administration of atropine.
-
2.
Following atropine the effect of O2-deficiency (12 Vol.-%O2) or CO2-excess (5 Vol.-% CO2 on frequency of impulses and number of spikes was absolutely reduced, but both reactions were relatively unchanged.
-
3.
N-Methylatropine did not influence the discharge pattern in phrenic motoneurons.
-
4.
The effect of atropine on frequency of impulses was also demonstrable after denervation of carotid sinus.
The different effect of atropine on depth of respiration (increase in the distance of impulses, reduction of spike number) and respiratory frequency is not elicited by alteration of chemoreception. The results indicate that atropine effects the discharge pattern of phrenic motoneurons by direct action on central respiratory regulation.
Zusammenfassung
An 78 narkotisierten, bivagotomierten Ratten wurde die Entladungsfrequenz inspirationsaktiver Einzelfasern vom N. phrenicus unter der Einwirkung von Atropin untersucht. Dabei ergab sich:
-
1.
Atropin führte in Dosen von 0,6; 1,2; 2,4 und 4,8 mg/kg i.v. zu einer dosisabhängigen Verlängerung der Impulsabstände und zu einer Abnahme der Spikezahlen in inspirationsaktiven Phrenicus-Motoneuronen. Die Atmungsfrequenz war demgegenüber nach Atropin gesteigert.
-
2.
Bei Stimulation der Atmung durch Anoxie (12 Vol.- % O2) oder Hypercapnie (5 Vol.- % CO2) war die erreichbare Steigerung der Entladungsfrequenz und die Erhöhung der Spikezahlen nach Atropin (1,0 mg/kg) absolut eingeschränkt, die relativen Änderungen waren iedoch in beiden Fällen vor und nach Atropinbehandlung gleich.
-
3.
N-Methylatropin(1,0 mg/kg)zeigte keine Wirkung auf die Entladungsfrequenz im N. phrenicus.
-
4.
Nach Denervation des Carotissinus war die Reaktion auf Atropin unverändert.
Die unterschiedliche Wirkung von Atropin auf die Atmungstiefe (Zunahme der Impulsabstände, Abnahme der Spikezahlen) und auf die Atmungsfrequenz (Steigerung der Atmungscyclen pro Zeiteinheit) scheint nicht durch eine Beeinflussung der Chemoreception, sondern durch eine direkte Wirkung an der zentralen Atmungsteuerung zustandezukommen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Ahmed, A., Marshall, P. B.: Relationship between antiacetyleholine and antitremorine activity in antiparkinsonian and related drugs. Brit. J. Pharmacol.18, 247–254 (1962).
Biscoe, T. J.: Carotid body. Structure and function. Physiol. Rev.51, 437–495 (1971).
Bovet, D., Bovet-Nitti, F.: Structure et activité pharmacodynamique des médicaments du système nerveux végétatif. Basel: Karger 1948.
Comroe, J. H., Forster, R. E., Dubois, A. B., Briscoe, W. A., Carlsen, E.: Die Lunge Stuttgart: Schattauer 1964.
Conway, C. M., Payne, J. P., Tomlin, P. J.: Blood gases after atropine administration. Lancet1969 II, 906.
Curtis, D. R., Ryall, R. W.: Nicotinic and muscarinic receptors of Renshaw cells. Nature (Lond.)203, 652–653 (1964).
Eccles, J. C.: The physiology of synapses, pp 66–68. Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1964.
Eccles, R. M., Sears, T. A., Shealy, C. N.: Intracellular recording from respiratory motoneurones of the thoracic spinal cord of the cat. Nature (Lond.)193, 844–846 (1962).
Finch, J. S., Zsigmond, E. K., de Kronfeld, T. J.: Arterial blood gases after atropine sulphate in healthy volunteers. Lancet1969 11, 773–774.
Fink, L. D., Cervoni, P.: Ganglionic blocking action of atropine and methylatropine. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther.109, 372–376 (1953).
Funderburk, W. H., Case, T. J.: The effect of atropine on cortical potentials. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.3, 213–223 (1951).
Gill, P. K., Kuno, M.: Properties of phrenic motoneurones. J. Physiol. (Lond.)168, 258–273 (1963).
Higuchi, H., Lendle, L.: Zur Frage der zentralnervösen Wirkungen von toxischen Atropindosen. Arch. Toxikol.22, 92–97 (1966).
Keszler, H.: Wichtige und weniger bekannte Nebenwirkungen von Atropin. Anaesthesist17, 262–267 (1968).
Miller, J. J., Schwarz, H. H., Forrer, G. R.: Atropine coma therapy. J. clin. exp. Psychopath.19, 312–318 (1958).
Nilwises, N., Schmidt, G.: Wirkungen von Atropinverbindungen auf die synaptische Übertragung im isolierten Cervicalganglion der Ratte. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmakol.251, 335–343 (1965).
Nishi, K., Eyzaguirre, C.: Effects of atropine on chemoreceptor discharges in the carotid body of the cat. Brain Res.23, 292–297 (1970).
Nishi, K., Eyzaguirre, C.: The action of some cholinergic blockers on carotid body chemoreceptors in vivo. Brain Res.33, 37–56 (1971).
Sakai, Y., dal Ri, H., Schmidt, G.: (1) Unterschiedliche Wirkungen der Organophosphate Paraoxon und Soman auf die Entladungsfrequenz in Einzelfasern des N. phrenicus der Ratte. Arch. Toxikol.30, 147–159 (1972).
Sakai, Y., dal Ri, H., Schmidt, G.: (2) The influence of atropine on the respiration of the rat in different types of intracollicular decerebration. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol.274, R 95 (1972).
Tomlin, P. J., Conway, C. M., Payne, J. P.: Hypoxaemia due to atropine. Lancet1964 I, 14–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Über einen Teil der Versuche wurde auf der 12. Frühjahrstagung der Deutschen Pharmakologischen Gesellschaft in Mainz 1971 berichtet [vgl. Schmidt, G., Sakai, Y., dal Ri, H.: Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmak.270, R 125 (1971)].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakai, Y., dal Ri, H. & Schmidt, G. Über die Wirkung von Atropin auf die Entladungsfrequenz in Phrenicus-Einzelfasern der Ratte. Arch Toxicol 30, 161–174 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02425933
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02425933