Abstract
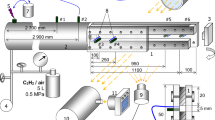
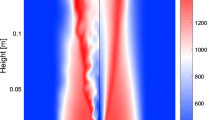
The influence of an inhibitor (CF3Br or Halon 1301) on the propagation of high-speed turbulent flames, quasi-detonations and the transition to detonation has been investigated for methane-air, propane-air and acetylene-air mixtures. The experiments are carried out in a 13 m tube (15 cm diameter) filled with regularly spaced orifice plates (blockage ratio of 0.39) to ensure rapid flame acceleration. In all cases, the addition of the inhibitor reduces the turbulent flame velocity and extinguishes the flame with sufficient inhibitor concentration (2.7% and 7.5% for methane-air and propane-air, respectively). For acetylene-air mixtures, the quasi-detonation speed is progressively reduced with increasing inhibitor concentration and eventually causes the failure of the quasi-detonation and transition back to a fast turbulent flame. The inhibitor also narrows the propagation limits in all cases. To elucidate the inhibition mechanism, detailed modelling of both the turbulent flame structure as well as the chemical kinetics are required.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biordi JC, Lazarra CP, Papp JF (1974). Flame structure studies of CF3Br-inhibited methane flames. II. Kinetics and mechanisms. 15th Symposium (Int.) on Combustion, The Combustion Institute 917–932
Chue RS, Clarke J, Lee JHS (1993) Chapman-Jouguet deflagrations. Proc. Roy. Soc. Long. A 441:607
Knystautas K, Lee JHS, Peraldi O, Chan CK (1986) Transmission of a flame from a rough to a smooth walled tube. In: Bowen JR, Leyer JC, Soloukhin RI (eds) Dynamics of Explosions. AIAA Progress in Astronautics and Aeronautics 106, pp 37–52
Lee JH, Knystautas R, Chan CK (1984) Turbulent flame propagation in obstacle-filled tubes. 20th Symposium (Int.) on Combustion, The Combustion Institute, 1663–1672
Moen IO, Ward SA, Thibault PA, Lee JHS, Knystautas R, Dean T, Westbrook CK (1984) 20th Symposium (Int.) on Combustion, The Combustion Institute, 1717–1725
Peraldi O, Knystautas R, Lee JHS (1986) Criteria for transition to detonation in tubes. 21st Symposium (Int.) on Combustion, The Combustion Institute, 1629–1637
Safieh HY, Vandooren J, Van Tiggelen PJ (1982) Experimental study of inhibition induced by CF3Br in a CO−H2−O2−Ar flame. 19th Symposium (Int.) on Combustion, The Combustion Institute, 117–126
Vandooren J, da Gruz FN, Van Tiggelen PJ (1988) The inhibiting effect of CF3H on the structure of a stoichiometric H2/CO/O2/Ar flame. 22th Symposium (Int.) on Combustion, The Combustion Institute, 1587–1595
Westbrook CK (1982) Inhibition of hydrocarbon oxidation in laminar flames and detonations by halogenated compounds. 19th Symposium (Int.) on Combustion, The Combustion Institute, 127–141
Wilson WE (1965) Structure, kinetics, and mechanism of a methane-oxygen flame inhibited with methyl bromide. 10th Symposium (Int.) on Combustion, The Combustion Institute, 47–54
Wilson WE, O'Donovan JT, Fristrom RM (1969) Flame inhibition by halogen compounds. 12th Symposium (Int.) on Combustion, The Combustion Institute, 929–942
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnston, M.H., Zhang, F., Frost, D.L. et al. Effect of an inhibitor on high-speed turbulent flames and the transition to detonation. Shock Waves 5, 305–309 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02425223
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02425223