Abstract
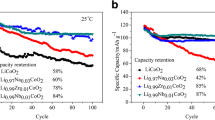
A series of divalent non-transition metal, especially Mg doped LiCoO2 solid solutions with the general formula LiMgxCo1−xO2 (x=0.00–0.20) was synthesized by the solid state fusion method trying to reduce the cost and toxicity, and to improve the overall electrochemical cell performance. All synthesized cathodes were characterized by XRD, TG/DTA, FTIR, SEM, particle size analysis and charge-discharge performances at constant current of 0.05 mA. All compounds were found to possess phase purity, have better crystallinity, preferred surface morphology and size-reduced particles of uniform distribution. The incorporation of the larger Mg2+ ion compared to the Li+ ion up to 0.20 mol-% leads to an increase in the unit cell volume, which restricts the concentration of the Co-O bond upon delithiation. Mg2+, commonly known for its structure stabilizing effect, has been found to have only a small effect on the crystal lattice of LiCoO2, especially at higher substituent levels, mainly due to the migration of Mg2+ ions from slab to inter-slab structure. The effect of Mg2+ on the modification of the capacity and structural stability compared to the unmodified LiCoO2 cathode is discussed in detail.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Mizushima, P.C. Jones, P.J. Wiseman and J.B. Goodenough, Mater. Res. Bull.17, 783 (1980).
Sony Lithium-Ion Battery performance Summary, EC,2, 31 (1994).
C. Delmas, I, Saadoune, Solid State Ionics53–56, 370 (1992).
C. Delmas, I. Saadoune, A.Rougier, J. Power Sources43–44, 595 (1993).
I. Saadoune, C. Delmas, J. Mater. Chem.6, 193 (1996).
J. Cho, G. Kim, H.S. Lim, J. Electrochem Soc.146, 3571 (1999).
J. Cho, H. Jung, Y. Park, G. Kim, H.S. Lim, J. Electrochem Soc.147, 15 (2000).
P. Periasamy, B. Ramesh Babu, R. Thirunakaran, N. Kalaiselvi, T. Premkumar, N.G. Renganathan, M. Raghavan, N. Muniyandi, Bull. Mater. Sci.23, 345 (2000).
G. Ceder, M.K. Aydinol, A.F. Kohan, Comput. Mater. Sci.8, 61 (1997).
G. Ceder, Y.M. Chiang, D.R. Sadoway, M.K. Aydinol, Y.I. Jang, B. Huang, Nature392, 694 (1998).
Y.I. Jang, B. Huang, H. Wang, D.R. Sadoway, G. Ceder, Y.M. Chiang, H. Liu, H.J. Tamura, J. Electrochem. Soc.146, 862 (1999).
Y.I. Jang, B. Huang, H. Wang, D.R. Sadoway, G. Ceder, Y.M. Chiang, H. Liu, H.J. Tamura, J. Power Sources81–82, 589 (1999).
C. Poullerie, L. Croguennec, Ph. Biensan, P. Willmann, and C. Delmas, J. Electrochem. Soc.147, 2061 (2000).
H. Hirano, R. Kanno, Y. Kawamoto, Y. Takeda, K. Yamamura, M. Takano, K. Ohyama, M. Ohashi and Y. Yamaguchi, Solid State Ionics78, 123 (1995).
C.C. Chang, J.Y. Kim, P.N. Kumta, J. Power Sources89, 56 (2000).
H. Tukamoto and A.R. West, J. Electrochem. Soc.144, 3164 (1977).
A. Lundbald and Bergman, Solid State Ionics96, 173 (1997).
A. Lundbald, S.A. EI-Hakam, S.E. Samra, Indian J. Chem. Sec. A29, 470 (1990).
D.R. Lide (Ed.), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 74th Ed., The Chemical Rubber Company, Ohio (1993–1994).
W.U. Malik, D.R. Gupta, I. Masood, R.S. Gupta, J. Mater. Sci. Lett.4, 532 (1985).
A. Reisman, J. Amer. Chem. Soc.80, 3558 (1958).
UIImann’s Encyclopaedia of Industrial Chemistry, A 16, 5th Ed., Verlagsgessellschaft mbH, VCH Publishers, Weinheim, 1990, p.131.
C. Julien, S.S. Michael, S. Ziolkiewcz, Int. J. Inorg. Mater.1, 29 (1999).
T. Ohuzuku, U. Ueda, N. Nagayama, Y. Iwakoshi, H. Homori, Electrochim. Acta38, 1159 (1993).
T. Ohzuku, A. Ueda, N. Yamamoto, J. Electrochem. Soc.142, 1431 (1995).
A.R. Naghash, J.Y. Lee, Electrochem. Acta46, 941 (2001).
A.R. Naghash, J.Y. Lee, Electrochem. Acta46, 2293 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thirunakaran, R., Kalaiselvi, N., Periasamy, P. et al. Mg substituted LiCoO2 for reversible lithium intercalation. Ionics 9, 388–394 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02376591
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02376591