Abstract
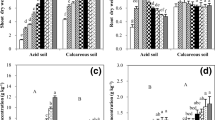
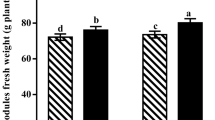
A green house study was conducted on the effect of P and Zn on nodulation and N fixation in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) in a loamy sand (Typic Torripsamments) using treatment combinations of five levels of P (0, 25, 50, 100 and 250 ppm), and six levels of Zn (0, 5, 10, 20, 40 and 100 ppm). The number, dry matter and leghaemoglobin content of nodules, and amount of N fixed generally increased with Zn alone upto 19 ppm and P alone upto 50 ppm, and decreased with their higher levels. Application of 25 to 50 ppm P and 5 to 10 ppm Zn counteracted to a greater extent the adverse effect of 40 and 100 ppm Zn, and 250 ppm P, resp. Maximum nodulation and N fixation (91 to 145% over zero P and Zn, at maturity) was recorded with 25 to 50 ppm P applied along with 5 to 10 ppm Zn. At 64 days, depletion in soil-N was noted, particularly when P was applied, whereas at maturity there was a gain in soil-N, ranging from 10.5 to 44.5 kg/2×106 kg soil depending upon P and Zn treatments. The increase in nodulation and N fixation with balanced P and Zn nutrition might be attributed to an increase in leghaemoglobin, and K and Fe concentration in nodules, and increased plant growth, resulting into enhanced activity of N fixing organisms. The results showed that balanced P and Zn nutrition is essential not only for plant growth but also for maximum activity of Rhizobium for N fixation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Bremner J M 1960 Determination of nitrogen in soil by Kjeldahl method. J. Agric. Sci. 55, 11–33.
Brown A L, Krantz B A and Eddings J L 1970 Zinc-phosphorus interaction as measured by plant response and soil analysis. Soil Sci. 110, 415–421.
Burstorm S M 1951In Plant Growth Substances. 340 p. Univ. Wisconsin. Madison, USA.
Christensen N W 1972 A new hypothesis to explain phosphorus induced zinc deficiency. Diss. Abstr. Int. 32(B), 4348.
Demeterio J L, Roscoe E Jr and Poulsen G M 1972 Nodulation and nitrogen fixation by two soybean varieties as affected by phosphorus and zinc nutrition. Agron. J. 64, 566–568.
Gromeman A T 1974 Effect of deep placement of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers on dry matter production, nodulation and chemical composition of soybean. Diss. Abstr. Int. 34 (B) 4787.
Hartree E F 1957In Haematin Compounds in Modern Methods 245. Springer Verlag, W. Germany.
Jackson M L 1958In Soil Chemical Analysis. pp 134–204. Prentice Hall, New Delhi
Kanwar J S and Chopra S L 1967In Practical Agricultural Chemistry. pp 29–107. S. Chand and Co., Delhi.
Kapoor D C, Gangwar M S and Tilak K V B R 1975 Influence of zinc on symbiotic nitrogen fixation by soybean (Glycine max. L.) in silt loam soil. Indian J. Agric. Res. 9, 51–56.
Khare N K and Rai M M 1968 The effect of phosphorus on symbiotic nitrogen fixation by leguminous crops. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 16, 111–114.
Lindsay W L and Norvell W A 1978 Development of DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. J. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 42, 421–428.
McIlveen W, Spoots R A and Davis D D 1975 Influence of soil zinc on nodulation, mycorrhizae and ozone sensitivity of Pinto-bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Phytopathology 65, 645–647.
Pandey S N 1969 Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and molybdenum on nodule formation. Indian J. Agron. 14, 205–207.
Shukla U C 1972 Effect of various phosphatic fertilizers on zinc availability in soils of southern United States, Agrochimica 16, 435–442.
Singh R, Singh N and Sidhu G S 1968 Symbiotic nitrogen fixation by summer (Kharif) legumes of Panjab. J. Res. P.A.U. Ludhiana 5, 88–94.
Takkar P N, Mann M S, Bansal R L, Randhawa N S and Singh H 1976 Yield and uptake response of corn to zinc as influenced by phosphorus fertilization. Agron. J. 68, 942–946.
Yadav O P 1979 Effect of phosphorus and zinc on yield, nutrients uptake, nodulation and nitrogen fixation in gram (Cicer arietinum L.). Ph.D. Diss. Haryana Agric. Univ. Library. Hissar, India.
Yie S T 1969 A study on the relationship of zinc concentration to nitrogen fixation in soybean. J. Sci. Engin. Taiwan 6, 1–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Work done at Harvana Agricultural University, Hissar, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, U.C., Yadav, O.P. Effect of phosphorus and zinc on nodulation and nitrogen fixation in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Plant Soil 65, 239–248 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374654
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374654