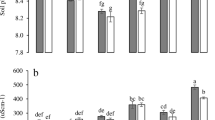
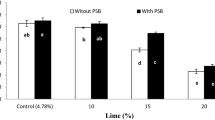
Abstract
Poor availability of phosphorus (P) in calcareous soil is one of the main reasons for low chickpea productivity. The high pH and calcium in calcareous soil fix the P making it unavailable to the crop. Furthermore, if the availability of P is increased from a comparatively cheaper source of P, the farmers’ cost of production could be decreased. We hypothesized that proper management of P sources like rock phosphate (RP) and single superphosphate (SSP), phosphate solubilizing bacteria (PSB), and rhizobium could improve the solubility and availability of P for higher chickpea yield. Therefore, a two-year field experiment was conducted in a randomized complete block design with a split-plot arrangement, using four replications. P sources in different ratios (RP:SSP; 0:100, 25:75, 50:50, 75:25, 100:0) were assigned to the main plot, while combinations of PSB and rhizobium into a subplot. The results revealed that among P source ratios (RP:SSP), 0:100 and 25:75 exerted a significant effect on chickpea phenology, nodulation, yield contributing traits, total P uptake, and increased seed yield by 63% and 53% as compared to 100:0 across the years, respectively. Early development, higher nodule biomass, yield contributing traits, and P uptake along with an increase of 16% in seed yield were obtained in PSB applied plots than without PSB. Seed inoculation with rhizobium improved all the studied traits, delayed flowering and maturity, and increased seed yield by 17% than without rhizobium. The findings suggested that PSB solubilized the poor available P from RP in combination with SSP which could improve the efficiency of rhizobium in nodulation, seed yield, and P uptake of chickpea. Thus, phosphorus source ratio (RP:SSP) of 25:75 along with PSB and rhizobium are recommended for higher productivity of chickpea in calcareous soils of Pakistan.









Similar content being viewed by others

References
Afzal A, Bano A (2008) Rhizobium and phosphate solubilizing bacteria improve the yield and phosphorus uptake in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Int J Agric Biol 10:85–88
Ahmed M, Badr EA (2009) Effect of bio- and mineral phosphorus fertilizer on the growth, productivity and nutritional value of some chickpea cultivars (Cicer arietinum, L.) in newly cultivated land. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 3:4656–4664
Ali MA, Khalid L (2015) Comparative performance of wheat in response to different phosphatic fertilizers. Int J Res 1:2394–5907
Ali A, Ishtiaq M, Jan NE (2003) Effect of rhizobium Leguminosarum inoculum on the growth and yield of different pea cultivars. Sarhad J Agric 19(1):55–59
Amanullah, Iqbal A, Khan A, Khalid S, Shah A, Parmar B, Khalid S, Muhammad A (2019) Integrated management of phosphorus, organic sources, and beneficial microbes improve dry matter partitioning of maize. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 50:2544–2569
Amanullah SA, Iqbal A, Fahad S (2016) Foliar phosphorus and zinc application improve growth and productivity of maize (Zea mays L.) under moisture stress conditions in semi-arid climates. J Microb Biochem Technol 8:433–439
Anwar S, Faraz M, Iqbal A, Islam M, Iqbal M, Alamzeb M, Parmar B (2017) Phosphorus management improve productivity of wheat varieties under semiarid climates. J Pharmacogn Phytochem SP1:259–263
Asif I, Khan A, Mazhar I, Ikram U (2017) Integrated use of phosphorus and organic matter improve fodder yield of moth bean (Vigna aconitifolia Jacq.) under irrigated and dryland conditions of Pakistan. J AgriSearch 4:10–15
Aziz T, Gill M, Rahmatullah DS, Schubert S (2005) Rock phosphate acquisition by four Brassica cultivars. In: Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of German Society of Plant Nutrition September 27–28
Badini SA, Khan M, Baloch SU, Baloch SK, Baloch HN, Bashir W, Badini AR, Badini MA (2015) Effect of phosphorus levels on growth and yield of chickpea (Cicer aretinum L.) varieties. J Nat Sci Res 5:169–176
Barea J‑M, Pozo MJ, Azcon R, Azcon-Aguilar C (2005) Microbial co-operation in the rhizosphere. J Exp Bot 56:1761–1778
Bray RH, Kurtz LT (1945) Determination of total, organic, and available forms of phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci 59:39–46
Bremner J, Mulvaney C (1982) Nitrogentotal. In: Page AL, Keeney DR (eds) Method of soil analysis, Part II, 2nd edn. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Inc., Madison, pp 595–624
Chabot R, Antoun H, Cescas MP (1996) Growth promotion of maize and lettuce by phosphate-solubilizing Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar. phaseoli. Plant Soil 184:311–321
Chaves MM, Pereira JS, Maroco J, Rodrigues ML, Ricardo CPP, Osório ML, Carvalho I, Faria T, Pinheiro C (2002) How plants cope with water stress in the field? Photosynthesis and growth. Ann Bot 89:907–916
Chen Y, Rekha P, Arun A, Shen F, Lai W‑A, Young CC (2006) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria from subtropical soil and their tricalcium phosphate solubilizing abilities. Appl Soil Ecol 34:33–41
Chhonkar P, Tilak K (1997) Bio-fertilizers for sustainable agriculture: research gaps and future needs. Plant Nutr Needs Supply Effic Policy 1:52–66
Dai J, Becquer T, Rouiller JH, Reversat G, Bernhard-Reversat F, Lavelle P (2004) Influence of heavy metals on C and N mineralisation and microbial biomass in Zn‑, Pb‑, Cu-, and Cd-contaminated soils. Appl Soil Ecol 25:99–109
Dalal L, Nandkar P (2011) Effect of NPK fertilizers in relation to seed yield in Brassica juncea (L.) var. Pusa bold. Bioscan 6:59–60
Dey R, Pal K, Bhatt D, Chauhan S (2004) Growth promotion and yield enhancement of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) by application of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Microbiol Res 159:371–394
Dutta D, Bandyopadhyay P (2009) Performance of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) to application of phosphorus and bio-fertilizer in laterite soil. Arch Agron Soil Sci 55:147–155
Egamberdiyeva D, Juraeva D, Poberejskaya S, Myachina O, Teryuhova P, Seydalieva L, Aliev A (2004) Improvement of wheat and cotton growth and nutrient uptake by phosphate solubilizing bacteria. In: Proceeding of 26th annual conservation tillage conference for sustainable agriculture Auburn, pp 58–65
Ekin Z (2010) Performance of phosphate solubilizing bacteria for improving growth and yield of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) in the presence of phosphorus fertilizer. Afr J Biotechnol 9:3794–3800
El Hadi EA, Elsheikh E (1999) Effect of Rhizobium inoculation and nitrogen fertilization on yield and protein content of six chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars in marginal soils under irrigation. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 54:57–63
Erman M, Demir S, Ocak E, Tüfenkçi Ş, Oğuz F, Akköprü A (2011) Effects of rhizobium, arbuscular mycorrhiza and whey applications on some properties in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under irrigated and rainfed conditions 1—Yield, yield components, nodulation and AMF colonization. Field Crop Res 122:14–24
Fairhurst T, Witt C, Buresh R, Dobermann A, Fairhurst T (2007) Rice: a practical guide to nutrient management. Int. Rice Res. Inst.
Frossard E, Condron LM, Oberson A, Sinaj S, Fardeau J (2000) Processes governing phosphorus availability in temperate soils. J Environ Qual 29:15–23
Garg S, Bahl G (2008) Phosphorus availability to maize as influenced by organic manures and fertilizer P associated phosphatase activity in soils. Bioresour Technol 99:5773–5777
Gaur A (1990) Phosphate solubilizing micro-organisms as biofertilizer. Omega scientific
Geneva M, Zehirov G, Djonova E, Kaloyanova N, Georgiev G, Stancheva I (2006) The effect of inoculation of pea plants with mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobium on nitrogen and phosphorus assimilation. Plant Soil Environ 52:435–440
Gholami A, Shahsavani S, Nezarat S (2009) The effect of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on germination, seedling growth and yield of maize. World Acad Sci Eng Technol 49:19–24
GOP, G.J.F.D. (2019) Pakistan Economic Survey 2019–20. Economic Advisor’s Wing, Islamabad
Gruhn P, Goletti F, Yudelman M (2000) Integrated nutrient management, soil fertility, and sustainable agriculture: current issues and future challenges. Intl Food Policy Res Inst
Gulati A, Rahi P, Vyas P (2008) Characterization of phosphate-solubilizing fluorescent pseudomonads from the rhizosphere of seabuckthorn growing in the cold deserts of Himalayas. Curr Microbiol 56:73–79
Gupta S, Namdeo S (2000) Fertilizer economy through composts and bio-fertilizer in chickpea. Ann Plant Soil Res 2:244–246
Halvorson JJ, Smith JL (2009) Carbon and nitrogen accumulation and microbial activity in Mount St. Helens pyroclastic substrates after 25 years. Plant Soil 315:211–228
Hameeda B, Rupela O, Reddy G, Satyavani K (2006) Application of plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with composts and macrofauna for growth promotion of Pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum L.). Biol Fertil Soils 43:221–227
Hussain N, Khan AZ, Akbar H, Akhtar S (2006) Growth factors and yield of maize as influenced by phosphorus and potash fertilization. SJA 22:579–581
Hussain N, Khan MB, Ahmad R (2008) Influence of phosphorus application and sowing time on performance of wheat in calcareous soils. Int J Agric Biol 10:399–404
Iqbal A, Gui H, Zhang H, Wang X, Pang N, Dong Q, Song M (2019a) Genotypic variation in cotton genotypes for phosphorus-use efficiency. Agronomy 9:689
Iqbal A, Song M, Shah Z, Alamzeb M, Iqbal M (2019b) Integrated use of plant residues, phosphorus and beneficial microbes improve hybrid maize productivity in semiarid climates. Acta Ecol Sinica 39:348–355
Iqbal A, Dong Q, Wang X, Gui H, Zhang H, Zhang X, Song M (2020a) High nitrogen enhance drought tolerance in cotton through antioxidant enzymatic activities, nitrogen metabolism and osmotic adjustment. Plants 9:178
Iqbal A, Dong Q, Wang X, Gui H, Zhang H, Zhang X, Song M (2020b) Variations in nitrogen metabolism are closely linked with nitrogen uptake and utilization efficiency in cotton genotypes under various nitrogen supplies. Plants 9:250
Iqbal A, Qiang D, Zhun W, Xiangru W, Huiping G, Hengheng Z, Nianchang P, Xiling Z, Meizhen S (2020c) Growth and nitrogen metabolism are associated with nitrogen-use efficiency in cotton genotypes. Plant Physiol Biochem 149:61–74
Islam M (2011) Growth, nitrogen fixation and nutrient uptake by chickpea (Cicer arietinum) in response to phosphorus and sulfur application under rainfed conditions in Pakistan. Int J Agric Biol 13:725–730
Jackson G, Berg R, Kushnak G, Carlson G, Lund E (1993) Phosphorus relationships in no-till small grains. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 24:1319–1331
Jamwal J, Bhagat K (2004) Reponse of wheat (Triticum aestivum) to top-dressing of diammonium phosphate in rainfed areas of Shivalik foothills. Indian J Agron 49:251–253
Jat R, Ahlawat I (2004) Effect of vermicompost, biofertilizer and phosphorus on growth, yield and nutrient uptake by gram (Cicer arietinum) and their residual effect on fodder maize (Zea mays). Indian J Agric Sci 74(7):359–361
Jiang D, Hengsdijk H, Ting-Bo D, Qi J, Wei-Xing C (2006) Long-term effects of manure and inorganic fertilizers on yield and soil fertility for a winter wheat-maize system in Jiangsu, China. Pedosphere 16:25–32
Kennedy I, Islam N (2001) The current and potential contribution of asymbiotic nitrogen fixation to nitrogen requirements on farms: a review. Aust J Exp Agric 41:447–457
Khan FU, Khan AA, Iqbal A, Ali A, Iqbal M, Alamzeb M, Jan MF, Parmar B (2017) Effеct of phosphorus and rhizobium inoculation on yield and yield components of mungbеan. J Pharmacogn Phytochem SP1:252–258
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Wani PA (2007) Role of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms in sustainable agriculture—a review. Agron Sustain Dev 27:29–43
Khan MS, Zaidi A, Ahemad M, Oves M, Wani PA (2010) Plant growth promotion by phosphate solubilizing fungi–current perspective. Arch Agron Soil Sci 56:73–98
Khan ST, Iqbal A, Fahad S (2016) Growth and productivity response of hybrid rice to application of animal manures, plant residues and phosphorus. Front Plant Sci 7:1440
Kyei-Boahen S, Slinkard AE, Walley FL (2002) Evaluation of rhizobial inoculation methods for chickpea. Agron J 94:851–859
Madurapperumage A, Tang L, Thavarajah P, Bridges W, Shipe E, Vandemark G, Thavarajah D (2021) Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) as a source of essential fatty acids—A biofortification approach. Front Plant Sci 12:734980
Maliha R, Samina K, Najma A, Sadia A, Farooq L (2004) Organic acids production and phosphate solubilization by phosphate solubilizing microorganisms under in vitro conditions. Pak J Biol Sci 7:187–196
Mclean EO (1982) Soil pH and lime requirement. In: Albert LP, Keeney DR (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part II. Chemical and microbiological properties, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Inc., Madison, pp 209–223
Meena K, Pareek R, Jat R (2001) Effect of phosphorus and biofertilizers on yield and quality of chickpea. Ann Agric Res 22:388–390
Muhammad A, Ahmad H, Muhammad A, Ejaz A, Sagoo A, Inayat U, Amir H, Muhammad M (2010) Nodulation, grain yield and grain protein contents as affected by rhizobium inoculation and fertilizer placement in chickpea cultivar bittle-98. Sarhad J Agric 26:467–474
Mukherjee P, Rai R (2000) Effect of vesicular arbuscular mycorrhizae and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria on growth, yield and phosphorus uptake by wheat (Triticum aestivum) and chickpea (Cicer arietinum). Indian J Agron 45:602–607
Namvar A, Sharifi RS (2011) Phenological and morphological response of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) to symbiotic and mineral nitrogen fertilization. Žemdirbystė 98:121–130
Namvar A, Sharifi RS, Sedghi M, Zakaria RA, Khandan T, Eskandarpour B (2011) Study on the effects of organic and inorganic nitrogen fertilizer on yield, yield components, and nodulation state of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 42:1097–1109
Nawab K, Iqbal A, Fahad S, Khan MJ, Akbar H, Hussain I, Ali A (2017) Response of summer pulses (mung bean vs. mash bean) to integrated use of organic carbon sources and phosphorus in dry lands. Afr J Agric Res 12:3470–3490
Neenu S, Ramesh K, Ramana S, Biswas A, Rao AS (2014) Growth and yield of different varieties of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) as influenced by the phosphorus nutrition under rainfed conditions on Vertisols. Int J Bio Resour Stress Manag 5:53–57
Pattanayak S, Mishra K, Jena M, Nayak R (2001) Evaluation of green manure crops fertilized with various phosphorus sources and their effect on subsequent rice crop. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 49:285–291
Pawar K, Bendre N, Deshmuhk R, Perance R (1998) Field response of chickpea seed inoculation of Rhizobium strains to nodulation and grain yield. J Maharashtra Agric Univ 22:370–371
Pierre MJ, Bhople BS, Kumar A, Erneste H, Emmanuel B, Singh YN (2014) Contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AM fungi) and rhizobium inoculation on crop growth and chemical properties of rhizospheric soils in high plants. IOSR-JAVS 7:45–55
Pradhan N, Sukla L (2006) Solubilization of inorganic phosphates by fungi isolated from agriculture soil. Afr J Biotechnol 5(10):850–854
Prajapati B, Gudadhe N, Gamit V, Chhaganiya H (2017) Effect of integrated phosphorus management on growth, yield attributes and yield of chickpea. Farming Manag 2:36–40
Pramanik K, Bera A (2012) Response of biofertilizers and phytohormone on growth and yield of chickpea (Cicer arietinium L.). J Crop Weed 8:45–49
Prasad S, Singh M, Jay S (2014) Response of Rhizobium inoculation and phosphorus levels on mungbean (Vigna radiata) under guava-based agri-horti system. Bioscan 9:557–560
Qhorchiany M, Gh A, Alikhani H, Allahdadi A, Zarei M (2011) Effects of mycorrhizal fungi and bacteria, Pseudomonas fluorescence Rbskvlar ear characteristics, chlorophyll content and yield of corn in drought conditions. J Soil Water 21:97–114
Rao NSS (1995) Soil microorganisms and plant growth. Science Publishers
Rehan W, Jan A, Liaqat W, Jan MF, Ahmadzai MD, Ahmad H, Haroon J, Anjum MM, Ali N (2018) Effect of phosphorous, rhizobium inoculation and residue types on chickpea productivity. Pure Appl Biol 7:1203–1213
Rhoades J (1996) Salinity: electrical conductivity and total dissolved solids. In: Methods of soil analysis: Part 3 Chemical methods, pp 417–435
Richardson AE, Simpson RJ (2011) Soil microorganisms mediating phosphorus availability update on microbial phosphorus. Plant Physiol 156:989–996
Rokhzadi A, Toashih V (2011) Nutrient uptake and yield of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) inoculated with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Aust J Crop Sci 5:44–48
Rooge R, Patil V, Ravikishan P (1998) Effect of phosphorus application with phosphate solubilizing organisms on the yield, quality and P‑uptake of soybean. Legum Res 21:85–90
Rudresh D, Shivaprakash M, Prasad R (2005) Effect of combined application of Rhizobium, phosphate solubilizing bacterium and Trichoderma spp. on growth, nutrient uptake and yield of chickpea (Cicer aritenium L.). Appl Soil Ecol 28:139–146
Salami AO, Oyetunji OJ, Igwe NJ (2005) An investigation of the impact of Glomus clarum (mycorrhiza) on the growth of tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum mill.) on both sterilized and non-sterilized soils. Arch Agron Soil Sci 51:579–588
Saxena J, Chandra S, Nain L (2013) Synergistic effect of phosphate solubilizing rhizobacteria and arbuscular mycorrhiza on growth and yield of wheat plants. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 13:511–525
Singaram P, Kothandaraman G (1994) Studies on residual, direct and cumulative effect of phosphorus sources on the availability, content and uptake of phosphorus and yield of maize. Madras Agric J 81:425–429
Singh R, Soni SK, Kalra A (2013) Synergy between Glomus fasciculatum and a beneficial Pseudomonas in reducing root diseases and improving yield and forskolin content in Coleus forskohlii Briq. under organic field conditions. Mycorrhiza 23:35–44
Soltanpour P, Schwab A (1977) A new soil test for simultaneous extraction of macro-and micro-nutrients in alkaline soils. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 8:195–207
Tagore G, Namdeo S, Sharma S, Kumar N (2014) Effect of Rhizobium and phosphate solubilizing bacterial inoculants on symbiotic traits, nodule leghemoglobin, and yield of chickpea genotypes. Int J Agron 581627:1–8
Togay N, Togay Y, Cimrin KM, Turan M (2008) Effects of Rhizobium inoculation, sulfur and phosphorus applications on yield, yield components and nutrient uptakes in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Afr J Biotechnol 7:776–782
Trolove S, Hedley M, Kirk G, Bolan N, Loganathan P (2003) Progress in selected areas of rhizosphere research on P acquisition. Soil Res 41:471–499
Venkatesh M, Majumdar B, Kumar K (2003) Effect of rock phosphate, single super phosphate and their mixtures with FYMon yield, quality and nutrient uptake by turmeric (Curcuma longa 1.) in acid alfisol of Meghalaya. J Spices Aromat Crop 12:47–51
Verma JP, Yadav J, Tiwari KN, Kumar A (2013) Effect of indigenous Mesorhizobium spp. and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on yields and nutrients uptake of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under sustainable agriculture. Ecol Eng 51:282–286
Vessey JK (2003) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria as biofertilizers. Plant Soil 255:571–586
Viruel E, Erazzú LE, Martínez Calsina L, Ferrero MA, Lucca ME, Siñeriz F (2014) Inoculation of maize with phosphate solubilizing bacteria: effect on plant growth and yield. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 14:819–831
Vyas P, Gulati A (2009) Organic acid production in vitro and plant growth promotion in maize under controlled environment by phosphate-solubilizing fluorescent Pseudomonas. BMC Microbiol 9:1–15
Wahid F, Fahad S, Danish S, Adnan M, Yue Z, Saud S, Siddiqui MH, Brtnicky M, Hammerschmiedt T, Datta R (2020) Sustainable management with mycorrhizae and phosphate solubilizing bacteria for enhanced phosphorus uptake in calcareous soils. Agriculture 10:334–340
Yadav S, Verma A, Nepalia V (2016) Effect of phosphorus, sulphur and seaweed sap on growth, yield and nutrient uptake of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Res Crop 17:496–502
Yazdani M, Bahmanyar MA, Pirdashti H, Esmaili MA (2009) Effect of phosphate solubilization microorganisms (PSM) and plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on yield and yield components of corn (Zea mays L.). World Acad Sci Eng Technol 49:90–92
Yoseph T (2011) Effects of Rhizobium inoculants and P fertilization on growth, yield and yield components of haricot bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) at Umbullo Wacho watershed, Southern Ethiopia. Southern Ethiopia, School of plant and Horticultural Sciences, Hawassa University, Hawassa
Zafar N, Munir MK, Ahmed S, Zafar M (2020) Phosphorus Solubilizing Bacteria (PSB) in combination with different Fertilizer sources to enhance yield performance of chickpea. Life Sci J 17:84–88
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Contributions
Madeeha Alamzeb conducted the experiment, collected and analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. Inamullah conceived the idea, designed the experiment, and edited the manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
M. Alamzeb and Inamullah declare that they have no competing interests.
Supplementary Information
10343_2022_722_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Figure S1. Mean monthly rainfall (above), minimum and maximum temperatures (below) at the Agronomy Research Farm of the University of Agriculture, Peshawar during the crop growing seasons (2017–18 & 2018–19).
Table S1. List of source and target traits used for correlation network based on correlation coefficient.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alamzeb, M., Inamullah. Management of Phosphorus Sources in Combination with Rhizobium and Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria Improve Nodulation, Yield and Phosphorus Uptake in Chickpea. Gesunde Pflanzen 75, 549–564 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00722-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00722-2