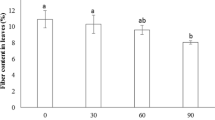
Summary
Effects of soil salinity and soil water regime on growth and chemical composition ofSorghum halepense L. was studied with a view to evaluating its potential as a forage crop in saline soils. The experiment was conducted under controlled conditions using pot-culture with three levels of soil salinity (ECe 0.5, 5.0, 10.0 ds/m) and three soil water regimes (60%, 40% and 20% of water holding capacity of the soil). High soil salinity and low soil water combiningly had an adverse effect on plant growth but the biomass production was appreciably high (57 to 75% of control) even under high soil salinity (ECe 10 ds/m) when sufficient water was available. Belowground plant parts were relatively more salt-tolerant than shoots. There occurred an increase in the concentration of certain nutrients (N, Ca, Mg, TNC) in the plants in response to salinity, which along with increased root: shoot ratios was inferred as an adaptive feature of the plant for persistence under saline conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert R and Popp M 1978 The role of soluble carbohydrates in halophytes of the area of the Neusiedler Lake (Austria). Oecol. Plant. 13, 27–42.
Allen S E, Grimshaw H M, Parkinson J A and Quarmby C 1974 Chemical analysis of Ecological Materials. John Wiley and Son, New York.
Bernstein L 1975 Effect of salinity and sodicity on plant growth. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 13, 295–312.
Bernstein L and Hayward H E 1958 Physiology of salt tolerance. Ann. Rev. Pl. Physiol. 9, 25–46.
Bogdan A V 1977 Tropical pasture and fodder plants. Longman, London and New York.
Eck H V and Musick J T 1979 Plant water stress effects on irrigated grain Sorghum II. Effects on nutrients in plant tissues. Crop. Sci. 19, 592–598.
Gerakis P A, Guerrero F P and Williams W A 1975. Growth, water relations and nutrition of three grassland annuals as affected by drought. J. Appl. Ecol. 12, 125–135.
Greenway H and Munns R 1980 Mechanism of salt tolerance in non-halophytes. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 31, 149–150.
Heikal M M D 1977 Physiological studies on salinity VI changes in water content and mineral composition of some plants over a range of salinity stress. Plant and Soil 48, 223–232.
Rains D W 1972 Salt transport by plants in relation to salinity. Ann. Rev. Plant. Physiol. 23, 367–388.
Rana R S 1977 Plant adaptation to soil salinity and alkalinity. Proc. Indo-Hungarian Sem. Management of Salt Affected Soils. CSSRI, Karnal pp 177–191.
Rana R S, Singh K N, Parkash V and Ahuja P S 1980 Growing forage in barren alkali soils. Seeds Farms 6, 37–39.
Sinha A, Gupta S R and Rana R S 1982 Effects of osmotic tension and salt stress on germination of three grass species. Plant and Soil 69, 13–19.
Smith D 1969 Removing and analyzing total non-structural carbohydrates from plant tissues. Res. Rep. No. 41, Res. Div., Univ. of Wisconsin, Madison.
Strogonov B P 1964 Physiological basis of salt tolerance of plants Jerusalem: Isr. Program for Sci. Transl
Turner N C and Begg J E 1981 Plant water relations and adaptation to stress. Plant and Soil 58, 97–132.
United States Salinity Laboratory Staff 1954 Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. USDA Handbook 60.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, A., Gupta, S.R. & Rana, R.S. Effect of soil salinity and soil water availability on growth and chemical composition ofSorghum halepense L.. Plant Soil 95, 411–418 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374621
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374621