Abstract
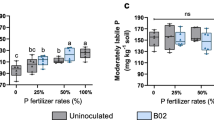
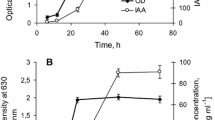
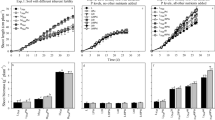
The influence of inoculation with phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (Enterobacter agglomerans) on maize growth, P uptake and root exudation was studied. Plants were grown in an axenic culture device where P was supplied as soluble phosphate at different contents (0, 5, 15 or 25 ppm) in the nutrient solution and as insoluble rock phosphate added to the culture sand. Experimental device was successfully used to obtain axenic root systems or good establishment of the inoculated strain in the rhizosphere of maize (109 bact. g−1 dry rhizospheric material). Plant growth was promoted by inoculation only for 5 or 15 ppm of soluble P in the nutrient medium without any significant effect on P uptake by the plant, suggesting that the quantities of P released by bacterial rhizospheric activity were very small. Amounts of organic compounds (total C and water-soluble C) exuded were relatively low (3.0 to 6.4% of the total plant biomass) and were reduced by bacterial inoculation when plant growth was largely promoted.
Carbon balance modification and plant growth hormone production by the inoculated strain were suspected and discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azcon R, Barea J M and Hayman D S 1976 Utilization of rock phosphate in alkaline soils by plants inoculated with mycorrhizal fungi and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria. Soil Biol. Biochem. 8, 135–138.
Bajpai P D and Sundara Rao W V B 1972 Phosphate solubilizing Bacteria. Part I. Solubilization of phosphate in liquid culture by selected bacteria as affected by different pH values. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 17, 41–53.
Banik S and Dey B K 1981 Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms of a lateritic soil. I. Solubilization of inorganic phosphates and production of organic acids by microorganisms, isolated in sucrose calcium phosphate agar plates. Zbl. Bakt II, 478–486.
Barber D A and Martin J K 1976 The release of organic substances by cereal roots into soil. New Phytol. 76, 69–80.
Barber D A and Lynch J M 1977 Microbial growth in the rhizosphere. Soil Biol. Biochem. 9, 305–308.
Barea J M, Azcon R and Hayman D S 1975 Possible synergistic interactions between endogone and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in low-phosphate soils.In Endomycorrhizas. Eds. F E Sanders, B Mosse and P B Tinker. pp 409–417. Academic Press, London.
Berthelin J and Leyval C 1982 Ability of symbiotic and nonsymbiotic rhizospheric microflora of maize (Zea mays) to weather micas and to promote plant growth and plant nutrition. Plant and Soil 68, 369–377.
Brown M E 1972 Plant growth substances produced by microorganisms of soil and rhizosphere. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 35, 443–451.
Datta H, Banik S and Gypta K K 1982 Studies of the efficacity of a phytohormone producing solubilizingBacillus firmus in augmenting paddy yield in acid soils of Nageland. Plant and Soil 69, 365–375.
El Gibaly M H, El Reweiny F A, Abdel Nasser M and El Dahtory T A 1977 Studies on phosphate-solubilizing bacteria in soil and rhizosphere of different plants. III. Inoculation with phosphate-dissolving microorganisms. Zbl. Bakt. II, 245–250.
Gerretsen F C 1948 The influence of microorganisms on the phosphate intake by the plant. Plant and Soil 1, 51–81.
Jacquinot L 1969 La nutrition minérale du mil. I. Effets de la nature de l'alimentation azotée sur l'absorption de l'azote et sur la croissance. Interaction de l'alimentation en fer Agron. Trop. 24, 1129–1138.
Kabesh M O, Saber M S M and Yoursy M 1975 Effect of phosphate dissolving bacteria and phosphate fertilization on the P uptake by pea plants cultivated in a calcareous soil. Z. Pflanzenernachr. Bodenkd. 6, 605–611.
Kraffczyk I, Trolldenier G and Beringer H 1984 Soluble root exudates of maize: Influence of potassium supply and rhizosphere microorganisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 16, 315–322.
Leyval C and Berthelin J 1983 Effets rhizosphériques de plantes indicatrices de grands types de pédogenèse sur quelques groupes bactériens modifiant l'état des minéraux. Rev. Ecol. Biol. Sol 20, 191–206.
Louw H A and Webley D M 1958 A plate method for estimating the numbers of phosphate dissolving and acid producing bacteria in soil. Nature. London 182, 1317–1318.
Ocampo J A, Barea J M and Montoya E 1975 Interactions between Azotobacter and ‘phosphobacteria’ and their establishment in the rhizosphere as affected by soil fertility. Can. J. Soil Sci. 21, 1160–1165.
Prikryl Z and Vancura V 1980 Root exudates of plants. VI. Wheat root exudation as dependent on growth, concentration gradient of exudates and the presence of bacteria. Plant and Soil 57, 69–83.
Raghu K and MacRae I C 1966 Occurrence of phosphate dissolving microorganisms in the rhizosphere of rice plants and in submerged soils. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 29, 582–586.
Raj J, Bagyaraj D J and Manjunath A 1980 Influence of soil inoculation with vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza and a phosphate dissolving bacterium on plant growth and32P-uptake. Soil Biol. Biochem. 13, 105–108.
Ralston D B and McBride R P 1976 Interaction of mineral phosphate-dissolving microbes with red pine seedlings. Plant and Soil 45, 493–507.
Ratnayake M, Leonard R T and Menge J A 1978 Root exudation in relation to supply of phosphorus and its possible relevance to mycorrhizal formation. New Phytol. 81, 543–552.
Sperber J I 1958 The incidence of apatite solubilizing organisms in the rhizosphere and soil. Austr. J. Agric. Res. 9, 778–781.
Swaby R J and Sperber J 1958 Phosphate dissolving microorganisms in the rhizosphere of legumes—Nutrition of the legumes. Proc. Univ. Nottingham 5th Easter Sch. Agric. Sci., 289–294.
Tardieux-Roche A 1966 Contribution à l'étude des interactions entre phosphates naturels et microflore du sol. Ann. Agron. 4 and 5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laheurte, F., Berthelin, J. Effect of a phosphate solubilizing bacteria on maize growth and root exudation over four levels of labile phosphorus. Plant Soil 105, 11–17 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02371137
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02371137