Summary
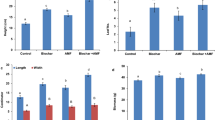
The effects of mineral phosphate-dissolving microbes on the growth of Pinus resinosa Ait. has been investigated. Seedlings were grown in a soil deficient in soluble phosphate but enriched with insoluble calcium phosphate. Treatments were designed to compare the effect of soluble phosphate fertilizer and inoculation of calcium phosphate-dissolving bacteria on seedling growth. Results indicate that the inoculation enhanced seedling growth as well or better than the soluble phosphate fertilizer. re]19750605
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnihotri, V. P., Solubilizations of insoluble phosphates by some soil fungi isolated from nursery seedbeds. Can. J. Microbiol. 16, 877–880 (1970).
Bajpai, P. D., Influence of seed inoculation with phosphorus-solubilizing organisms on availability of phosphorus as estimated by Neubauer's technique using P32 as tracer. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 38, 696–700 (1967).
Bjorkman, E., Forest tree mycorrhiza; the conditions for its formation and the significance for tree growth and afforestation. Plant and Soil. 32, 589–610 (1970).
Breed, R. S., Murray, E. G. D. and Smith, N. R. (Eds.). In Bergey's Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, 7th ed. The Williams and Wilkins Co., Baltimore (1957).
Broadfoot, W. M. and Ike, A. F.Jr., Research progress in fertilizing southern hardwoods. In Forest Fertilization, Tennessee Valley Authority, Muscle Shoals, Ala. (1968).
Cann, D. B., MacDougall, J. I. and Hilchey, J. D., Soil Survey of Kings County, N.S., N. S. Dep. Agric. Market. Report 15 (1965).
Casida, L. E.Jr., Phosphatase activity of some common soil fungi. Soil Sci. 87, 305–310 (1959).
Chang, S. C. and Jackson, M. L., Fractionation of soil phosphorus. Soil Sci. 84, 133–144 (1957).
Chhonkar, P. K. and Subba-Rao, N. S., Phosphate solubilization by fungi associated with legume root nodules. Can. J. Microbiol. 13, 749–753 (1967).
Cooper, R., Bacterial fertilizers in the Soviet Union. Soils and Fert. 22, 327–333 (1959).
Gerretsen, F. C., The influence of micro-organisms on the phosphate intake by the plant. Plant and Soil 1, 51–81 (1948).
Harrison, M. J., Pacha, R. E. and Morita, R. Y., Solubilization of inorganic phosphates by bacteria isolated for Upper Klamath Lake sediment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17, 50–57 (1972).
Hocking, D., Preparation and use of a nutrient solution for culturing seedlings of lodgepole pine and white spruce. Northern Forest Research Centre. Info. Rep. NOR-X-1, Edmonton, Alberta (1971).
James, N., Soil extract in soil microbiology. Can. J. Microbiol. 4, 363–370 (1958).
Katznelson, H. and Bose, B., Metabolic activity and phosphate dissolving capability of bacterial isolates from wheat roots, rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil. Can. J. Microbiol. 5, 79–85 (1959).
Katznelson, H., Rouatt, J. W. and Peterson, E. A., The rhizosphere effect of mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal roots of yellow birch seedlings. Can. J. Bot. 40, 377–382 (1962).
Metson, A. J., Conductivity method. In Methods of Chemical Analysis for Soil Survey Samples. N.Z. Dept. Sci. and Indust. Res. Publ. Bull. 12. pp. 142–145 (1961).
Peech, M., Hydrogen ion activity. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part II. C. A.Black, D. D.Evans, J. L.White, L. E.Ensminger, and F. E.Clark (eds.). Am. Soc. Agron. Inc., Madison, Wisconsin. pp. 914–927. (1965).
Pritchett, W. L. and Smith, W. H., Fertilizer responses in young pine plantations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 36, 660–663 (1972).
Ralston, D. B., M. Sc. Thesis. (1974).
Rouatt, J. W. and Katznelson, H., A study of the bacteria on the root surface and in the rhizosphere soil of crop plants. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 24, 164–171 (1961).
Rose, R. E., Techniques for determining the effect of microorganisms on insoluble inorganic phosphates. N.Z. J. Sci. Technol. 38B, 773–780 (1956).
Rosendahl, R. O., The effect of mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal fungi on the availability of difficultly-soluble potash and phosphate minerals. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 7, 477–479 (1942).
Snedecor, G. W. and Cochran, W. G., One-way classifications. Analysis of variance. In Statistical Methods. The Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa. pp. 258–298 (1967).
Sperber, J. I., Solution of apatite by soil microorganisms producing organic acids. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 9, 782–787 (1958).
Sperber, J. I., The incidence of apatite-solubilizing organisms in the rhizosphere and soil. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 9, 778–781 (1958).
Sperber, J. I., Release of phosphate from soil minerals by hydrogen sulphide. Nature 181, 934 (1958).
Spurr, S. H. and Barnes, B. V., Fertilization of Forest Soils. In Forest Ecology, 2nd Ed. The Ronald Press Co., New York. pp. 179–180 (1973).
Waksman, S. A., Principles of Soil Microbiology, 2nd Ed. Bailliere, Tindall and Cox, London, pp. 566–587 (1932).
Wilde, S. A., Chemical properties of forest soils. In Forest Soils and Forest Growth, Chronica Botanica Co., Waltham, Mass. (1946).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dalhousie University, Biology Department, Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ralston, D., McBride, R. Interaction of mineral phosphate-dissolving microbes with red pine seedlings. Plant Soil 45, 493–507 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011709
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011709