Summary
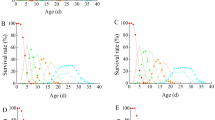
The parasitoid waspPteromalus puparum was reared for many generations under controlled laboratory conditions: larval development in diapausing pupae ofPieris brassicae, 14 hours photoperiod, temperature of 21 °C or 25 °C. The fluctuations in the density of population appear to be the main source of variation for larval development.
An increase in the number of larvae living in the same host pupa results in a decrease of adult size, a reduction of developmental time and a diminution of incidence of larval diapause.
According to these results, it appears that a high population density hastens the occurrence of metamorphosis and makes it easier. It is suggested that various nervous stimulations, such as food shortage and interactions between larvae, may induce the onset of neurosecretion by the brain.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliographie
Bakken, K. — 1954. Feeding period, growth and pupation in larvae ofDrosophila melanogaster. —Ent. exp. appl.,2, 171–186.
Bodenstein, F. W. — 1953. Postembryonic development. — InRoeder, K. D., Insect physiology. —J. Wiley and Sons, N.Y., 822–865.
Cousin, G. — 1932. Étude expérimentale de la diapause chez les Insectes. —Bull. Biol. suppl.,15, 341 pp.
David, J. — 1953. Étude expérimentale des variations de l'aile vestigiale deDrosophila melanogaster Meigen. —Bull. Biol.,87, 431–460.
Faure, J. C. — 1926. Contribution à l'étude d'un complexe biologique: la Piéride du chou et ses parasites Hyménoptères. —Thèse Fac. Sci. Lyon, 221 pp.
Fourche, J. — 1965. La respiration larvaire chezDrosophila melanogaster. Consommation d'oxygène au cours du jeûne. —C. R. Acad. Sci.,261, 3478–3481.
Fuzeau-Braesch, S. — 1961. Les déterminismes de la diapause chez les Insectes. —Ann. Biol.,37, 43–69.
Grassé, P. P. — 1958. L'ellet de groupe sur l'animal et sur l'homme. —J. Psych. norm. path.,55, 129–150.
Iwao, S. — 1959. Comparisons of the manifestations of density-dependant variability inLeucania unipunctata, L. loreyi andL. placida [Lep. Noctuidae]. —Jap. J. Ecol.,9, 32–38.
Jackson, D. J. — 1963. Diapause inCaraphractus cinctus Walk. [Hym. Mymaridae], a parasitoid of the egg ofDytiscidae. —Parasitol.,53, 225–251.
Klomp, H. — 1964. Intraspecific competition and the regulation of insect numbers. —Ann. Rev. Ent.,9, 17–40.
Lees, A. D. — 1955. The physiology of diapause in arthropods. —Univ. Press, Cambridge, 151 pp.
Legay, J. M. — 1962. Caractère des processus métaboliques au cours de la diapause des Insectes. —Ann. Nutr. Alim.,16, 65–89.
Robertson, F. W. — 1963. The ecological geneties of growth inDrosophila. VI. The genetic correlation between the duration of the larval period and body size in relation to larval diet. —Genet. Res.,4, 74–92.
Sang, J. H. — 1949. The ecological determinants of population growth inDrosophila culture. III. Larval and pupal survival. —Physiol. Zool.,22, 183–202.
Saunders, D. S. — 1962. The effect of the age of femaleNasonia vitripennis upon the incidence of larval diapause. —J. Insect. Physiol.,8, 309–318.
—— — 1965. Larval diapause of maternal origin: induction of diapause inNasonia vitripennis Walk. —J. exp. Biol.,42, 495–508.
—— — 1966a. Larval diapause of maternal origin: II. The effect of photoperiod and temperature onNasonia vitripennis. —J. Ins. Physiol.,12, 569–581.
—— — 1966b. Larval diapause of maternal origin. III. The effect of host shortage onNasonia vitripennis. —J. Ins. Physiol.,12, 899–908.
Sokoloff, A. — 1955. Competition between sibling species of the pseudoobscura subgroup ofDrosophila. —Ecol. Monograph.,25, 387–409.
Velthuis, H. H. W., Velthuis-Kluppel, F. M. &Bossink, G. A. H. — 1965. Some aspects of the biology and population dynamics ofNasonia vitripennis Walker [Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae]. —Ent. exp. appl.,8, 205–227.
Wylie, H. G., — 1965. Effects of superparasitism onNasonia vitripennis (Walk.) [Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae]. —Canad. Ent.,97, 326–331.
Zaher, M. A. &Long, D. B. — 1959. Some effects of larval population density on the biology ofPieris brassicae L. andPlusia gamma L. —Proc. R. ent. Soc. Lond. A,34, 97–109.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouletreau, M., David, J. Influence de la densité de population larvaire sur la taille des adultes, la durée de développement et la fréquence de la diapause chezPteromalus puparum L. [Hym., Chalcidien]. Entomophaga 12, 187–197 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370616
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02370616