Abstract
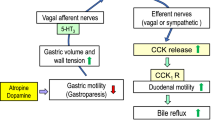
We evaluated the effect of the specific cholecystokinin (CCK) receptor antagonist, loxiglumide, on gallbladder contractile function in guinea pigs. Five mg/kg body weight (BW) of loxiglumide was administered orally to guinea pigs once a day for 3 days. We then investigated gallbladder contractile function and plasma CCK concentrations in the guinea pigs. Maximal gallbladder pressure induced by cerulein was significantly depressed on the 1st and 3rd days following loxiglumide administration. On the 1st day, the plasma CCK concentration was significantly increased compared with that of the control group during fasting and 15 min after the administration of an intraduodenal test meal. These results suggest that the disturbed gallbladder contraction is due to the competitive inhibition of CCK by loxiglumide. Gallbladder contractile function in guinea pigs is depressed by loxiglumide; however, this effect is reversible after short-term loxiglumide administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tani S, Ito H, Koide M, et al. Involvement of endogenous cholecystokinin in the development of acute pancreatitis induced by closed duodenal loop. Pancreas 1993;8:109–115.
Tani S, Okabayashi Y, Nakamura T, et al. Effect of a new cholecystokinin receptor antagonist, loxiglumide, on acute pancreatitis in two experimental animal models. Pancreas 1990;5:284–290.
Chang RSL, Lotti VJ. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of an extremely potent and selective nonpeptide cholecystokinin antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1986;83:4923–4926.
Niederau M, Niederau C, Strohmeyer G, et al. In vivo effects of new CCK receptor-antagonists on rat pancreatic secretion: Potency in vivo is lower than in vitro (abstract). Gastroenterology 1987;92:1553.
Otsuki M, Fujii M, Nakamura T, et al. Loxiglumide. A new proglumide analog with potent cholecystokinin antagonistic activity in the rat pancreas. Dig Dis Sci 1989;34:857–864.
Adler G, Reinshagen M, Koop I, et al. Differential effect of atropine and a cholecystokinin receptor antagonist on pancreatic secretion. Gastroenterology 1989;96:1158–1164.
Hildebrand P, Beglinger C, Gyr K, et al. Effects of a cholecystokinin receptor antagonist on intestinal phase of pancreatic and biliary responses in man. J Clin Invest 1990;85:640–646.
Schwarzendrube J, Niederau M, Luthen R, et al. Effect of cholecystokinin-recept or blockade on pancreatic and biliary function in healthy volunteers. Gastroenterology 1991;100:1683–1690.
Setnikar I, Bani M, Cereda R, et al. Anticholecystokinin activities of loxiglumide. Arzneim-Forsch/Drug Res 1987;37(11):1168–1171.
Makovec F, Bani M, Cereda R, et al. Pharmacological properties of lorglumide as a member of a new class of cholecystokinin antagonists. Arzneim-Forsch/Drug Res 1987;37(11):1265–1268.
Setnikar I, Chiste R, Makovec F, et al. Pharmacokinetics of loxiglumide after single intravenous or oral doses in man. Arzneim-Forsch/Drug Res 1988;38(1):716–720.
Hashimura E, Shimizu F, Nishino T, et al. Production of rabbit antibody specific for amino-terminal residues of cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8) by selective suppression of cross-reactive antibody response. J Immunol Methods 1982;55:375–387.
Himeno S, Tarui S, Nakayama S, et al. Plasma cholecystokinin responses after ingestion of liquid meal and intraduodenal infusion of fat, amino acids, or hydrochloric acid in man: Analysis with region-specific radioimmunoassay. Am J Gastroenterol 1983;78:703–707.
Niederau C, Heintges T, Rovati L, et al. Effects of loxiglumide on gallbladder emptying in healthy volunteers. Gastroenterology 1989;97:1331–1336.
Corazziari E, Ricci R, Biliotti D, et al. Oral administration of loxiglumide (CCK antagonist) inhibits postprandial gallbladder contraction without affecting gastric emptying. Dig Dis Sci 1990;35:50–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsubo, K., Arai, M., Omachi, H. et al. Effect of a cholecystokinin receptor antagonist (loxiglumide) on gallbladder contractile function in guinea pigs. J Gastroenterol 31, 578–581 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02355060
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02355060