Abstract
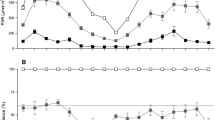
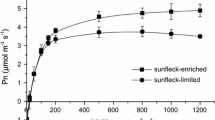
Seasonal variation in the light environment on the forest floor of a deciduous forest was investigated with special reference to sunflecks. Diurnal variations and seasonal changes in frequency and irradiation period of the sunflecks (sunfleck duration) were measured. The hourly total sunfleck duration varied seasonally; that is, 30–40 min in spring and autumn and about 15–20 min in summer. There was no large variation in the hourly sunfleck duration during daytime hours (from 9.00 to 15.00 h). The emergence frequency of sunflecks was 1.3–4.8 per h with two peaks, one in the morning and one in the afternoon. The mean duration of a sunfleck, however, showed a characteristic daily pattern with a peak around noon. Sunfleck duration was long around noon, ranging from 12 to 18 min, and short around 10.00 and 14.00 h, ranging from 6 to 10 min. Using the light photosynthesis curves of Pyrola japonica and Syneilesis palmata (Koizumi & Oshima 1985), the contribution of sunflecks to the dry matter production of these understory species was evaluated. It was shown that the sunflecks contributed 7–10% of the carbon gain in S. palmata, but only 2–3% of that in P. japonica.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson M. C. (1964) Studies on the woodland climate. II. Seasonal variation in the seasonal climate. J. Ecol. 52: 643–63
Chazdon R. I. (1986) Light variation and carbon gainin rain forest understory palms. J. Ecol. 74: 995–1012.
Evans G. C. (1956) An area survey method of investigaing the distribution of light intensity in woodlands, with particular reference to sunflecks. J. Ecol. 44: 391–428.
Fetcher N., Atrain B. R. & Oberbauer S. F. (1983) Effects of light regime on the growth, leaf morphology, and water relations of seedling of two species of tropical trees. Oecologia 58: 314–19.
Kira T. (1949) Forest Zomes of Japan. Ringyo-gizyutukyokai, tokyo (in Japanese).
Koizumi, H. (1985) Studies on the life history of an evergreen herb, Pyrola japonica, population on a forest floor in a warm temperate region. 1. Growth, net production and matter economy. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 98: 383–92.
Koizumi H. (1989) Studies on the life history of an evergreen herb, Pyrola japonica, population on a forest floor in a warm temperate region. 2. Photosynthesis, respiration and gross production. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 102: 521–32.
Koizumi H. & Oshima Y. (1985) Seasonal changes in photosynthesis of four understory herbs in deciduous forest. Bot. Mag. Tokyo 98: 1–13.
Lundegárdh H. (1957) Klima und Boden in ibrer Wirkung auf das Pflanzenlben Gustave Fischer Verlag. Jena.
Monsi, M. & Saeki T. (1953) Uber die Lichtfaktor in den Pflanzengesellschften und seine Bedeuting fur die Stoffproduktion. Jpn. J. Bot., 14: 22–52.
Numata M. & Asano S. (1970) Biological Flora of Japan vol. 2, Sympetalae-2. Tsukiji shokann, Tokyo (in Japanese).
Oberbacer M. J., Clark D. B., Clark D. A. & Quesada, M. A. (1988) Crown light environments of saplings of two species of rain forest emergent trees. Oecologia 75: 207–12.
Pearcy R. W. (1983) The light environment and growth of C3 and C4 tree species in the understory of a Hawaiian forest. Oecologia 58: 19–25.
Pearcy R. W. (1987) Photosynthetic gas exchange responses of Australian tropical forest trees in canopy, gap and understory micro-environments. Func. Ecol. 1: 169–78.
Pearcy R. W. (1988) Photosynthetic utilisation of lightflecks by understory plants. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 15; 223–38.
Pearcy R. W. & Calkin H. (1983) Carbon dioxide exchange of C3 and C4 tree species in the understory of a Hawaiian forest. Oecologia 58: 26–32.
Richards P. W. (1952) The Tropical Rain Forest. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Sasaki S. (1983) Physiological studies on seedling of Dipterocarps with particular reference to Shorea ovalis (red meranti) and Shorea talura (white meranti). FRI Kepong Res. Pampblet 92: 1–66.
Tang Y. H., Washitani I. & Iwaki H. (1992a), Seasonal variations of microsite light availability within a Miscanthus sinensis canopy Ecol. Res. 7: 97–106.
Tang Y. H., Washitani I. & Iwaki H. (1992b) Effects of microsite light availability on the survival and growth on oak seedlings within a grassland. Bot. Mag. Tokyo. 105: 281–8.
Tang Y. H., Washitani I., Tsuchiya T. & Iwaki H. (1988) Fluctuation of photosynthetic photon flux density within a Miscanthus simensis canopy. Ecol. Res. 3: 253–66.
Ustin S. L., Woodward, R. A., Barbour M. G. & Hatfield J. L. (1984) Relationship between sunfleck dynamics and red fir seedling distribution. Ecology 65: 1420–8.
Weber J. A., Jurik T. W., Tenhunen J. D. & Gates D. M. (1985) Analysis of gas exchange in seedlings of Acer saccharum: Integration of field and laboratory studies. Oecologia 65: 338–47.
Yoda K. (1974) Three-dimensional distribution of light intensity in a tropical rain forest of west Malaysia. Jpn. J. Ecol. 24: 247–54.
Young D. R. & Smith W. K. (1979) Influences of sunflecks on the temperature and water relations of two subalpine understory congeners. Oecologia 43: 195–205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Koizumi, H., Oshima, Y. Light environment and carbon gain of understory herbs associated with sunflecks in a warm temperate deciduous forest in Japan. Ecol. Res. 8, 135–142 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02348525
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02348525