Abstract
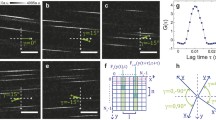
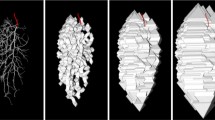
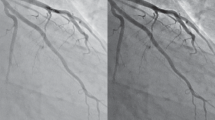
Blood flow through a frog mesenteric microvessel, consisting of one loop and two successive bends, was recorded by a video-microscopic system and analysed by a PC-based image processing system. After preprocessing, these images were analysed by the image velocimetry, axial tomography and image processing procedures. The blood flow in the microvessel had a Reynolds number of 0.033, and the Dean number varied from 0.004 in the loop to 0.007 in the bend, showing an increase in secondary flow in the bend region. These changes led to outward shifts in the peaks of velocity and concentration profiles, with an increase in the thickness of the outer walls (of about three times) compared with that of the inner walls. The mean velocity and mean cellular concentration showed a similar pattern. The variation in the cellular concentration in the microvessel was visualised by concentration contours and grey-scale images of the cellular distribution. At the inner wall of the complex geometry, the velocity reduced to zero, whereas the cellular concentration varied from 2 to 5%. In the high shear stress regions in the complex geometry, the vessel wall thickness was two-three times more than that in low shear stress regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal, J. K., andNandkumar, N. (1988): ‘On the computation of motion from sequence of images—A review’,Proc. IEEE,76, pp. 917–935
Baker, M., andWayland, H. (1974): ‘On-line volume flow rate and velocity profiles measurement for blood flow in microvessels’,Microvas. Res.,7, pp. 131–143
Berger, S. A., Talbot, L., andYacv, L. S. (1983): ‘Flow in curved pipes’,Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech.,15, pp. 461–512
Boesiger, P., Maier, S. E., Kecheng, L., Scheidegger, M. B., andMeier, D. (1992): ‘Visualization and quantification of the human blood flow by magnetic resonance imaging’,J. Biomech.,25, pp. 55–67
Carr, R. T., andWickham, L. L. (1991): ‘Influence of vessel diameter on red cell distribution at microvascular bifurcations’,Microvas. Res.,41, pp. 184–196
Cornelius, N. H., andKanade, T. (1983): ‘Adopting optical flow to measure object motion in reflectance and x-ray image sequences’, Proc. ACM SIGGRAPH/SIGART Workshop on Motion, Representation, and reception, Toronto, Canada, pp. 50–58
Douglas, M. A., andTrus, B. L. (1989): ‘An introduction to image processing in medical microscopy’,Med. Prog. Technol.,15, 109–140
Gonzalez, R. C., andWoods, R. E. (1993): ‘Digital image processing’ (Addison-Wesley Publ., New York, 1993), pp. 191–195
Hitt, D. L., andLowe, M. L. (1999): ‘Confocal imaging of flow in artificial venular bifurcations’,J. Biomech. Eng.,121, pp. 170–178
Hoogstraten, H. W., Kootstra, J. G., Hillen, B., Krijger, J. K. B., andWensing, P. J. W. (1996): ‘Numerical simulation of blood flow in an artery with two successive bends’,J. Biomech.,29, pp. 1075–1083
Horn, B. K., andSchunck, B. G. (1981): ‘Determination of optical flow’,Artif. Intell.,17, pp. 185–203
Houle, S., andRoach, M. R. (1981): ‘Flow studies in a rigid model of an aorta-renal junction’,Atherosclerosis,40, pp. 231–244
Jain, A. K. (1989): ‘Fundamentals of digital image processing’ (Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 1989), pp. 342–430
Kak, A. C. (1979): ‘Computerised tomography with X-ray emission and ultrasound sources’,Proc. IEEE,67, pp. 1345–1372
Kak, A. C., andSlaney, M. (1987): ‘Principles of computed tomographic imaging’ (IEEE Press, New York, 1987), pp. 1345–1372
Lie, M., Klineserener C., andTruskey, G. A. (1995): ‘Numerical investigation and prediction of atherogenic sites in branch arteries’,J. Biomech. Eng.,117, pp. 350–357
Liepsch, D. (1986): ‘Flow in tubes and arteries—a comparison’,Biorheology,23, pp. 395–433
Lipowski, H. H., Usami, S., andChien, S. (1980): ‘In vivo measurement of apparent viscosity and microvessel hematocrit in the mesentery of cat’,Microvas. Res.,19, pp. 297–319
Lominadze, D., andMchedlishvili, G. (1999): ‘Red blood cell behavior at low flow rate in microvessels’,Microvas. Res.,58, pp. 187–189
Maarek, T. M., Tarry, G., Cosnac, B., de., Lansiart, A., andHung, B. M. (1984): ‘A simulation method for the study of laser transillumination of biological tissue’,Ann. Biomed. Eng.,12, pp. 281–303
Moravec, S., andLiepsch, D. W. (1983): ‘Flow visualization in a model of a three dimensional human artery with Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids’,Biorheology,20, pp. 745–759
Nerem, R. M. (1992): ‘Vascular fluid mechanics, the arterial wall and atherosclerosis’,ASME J. Biomech. Eng.,114, pp. 274–282
Prakash, B., andSingh, M. (1996): ‘Optimum kinetic energy dissipation in blood flow in glass capillaries by flow field determination: Analysis of curvature effect by axial tomography and image velocimetry techniques’,Biorheology,33, pp. 59–74
Pries, A. R., Ley, K., Claussen, M., andGaehtgens, P. (1989): ‘Red cell distribution at microvascular bifurcations’,Microvas. Res.,38, pp. 81–101
Pries, A. R., andGaehtgens, P. (1987): ‘Digital video image shearing devices for continuous microvascular diameter measurement’,Microvas. Res.,34, pp. 260–267
Pries, A. R., Secomb, T. W., Gaehtgens, P., andGross, J. F. (1990): ‘Blood flow in microvascular networks. Experiments and simulation’,Circulation Res.,67, pp. 826–834
Rosenfeld, A., andKak, A. C. (1982): ‘Digital picture processing’ (Academic Press, New York, 1982)
Sato, M., andOhshima, N. (1988): ‘Velocity profiles in microvessels measured by ten channel dual sensor method’,Biorheology,25, pp. 279–288
Scarborough, J. B. (1966): ‘Numerical mathematical analysis’ (Oxford and IBH Publ. New Delhi, 1966)
Schunck, B. G. (1984): ‘Motion segmentation and estimation by constraint line clustering’. Proceedings of Workshop on Computer vision. Annapolis, Maryland, pp. 58–62
Seki, J., andLipowski, H. H. (1989): ‘In vivo andin vitro measurement of red cell velocity under epifluorescence microscopy’,Microvas. Res.,38, pp. 110–124
Shibata, M., Kawamura, T., Sohirad, M., andKamiya, A. (1995): ‘A new fluorescence microscopy for tomographic observation of microcirculation by using dual-beam slit laser illumination’,Microvas. Res.,49, pp. 300–314
Singh, S. S., andSingh, M. (2002): ‘Detection of pulsatile blood flow cycle in microvessels by image velocimetry’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,40, pp. 269–272
Smith, R. W. (1987): ‘Computer processing of line images—A survey’,Pattern recognition,20, pp. 7–15
Stehbens, W. E. (1990): ‘The lipid hypothesis and the role of hemodynamics in atherosclerosis’,Prog. Cardiovas. Diseases,339, pp. 119–139
Umrani, J., Prakash, B., andSingh, M. (1997): ‘Computerised multiparametric analysis from images of blood flow through frog mesenteric arterial bifurcation’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,35, pp. 373–380
Yan, Z. Y., Acrivos, A., andWeinbaum, S. (1991): ‘A Three-dimensional analysis of plasma skimming at microvascular bifurcations’,Microvas. Res.,42, pp. 17–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manjunatha, M., Singh, M. Computerised visualisation from images of blood flow through frog mesenteric microvessels with multiple complexities. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 40, 634–640 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345301
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345301