Abstract
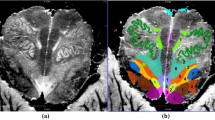
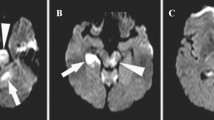
The human brainstem is a highly complex structure where even small lesions can give rise to a variety of symptoms and outward sings. Localising the area of dysfunction within the brainstem is often a difficult task. To make localisation easier, a neural net system has been developed which uses 72 clinical and neurophysiological data inputs to provide a display (using 5268 voxels) on a three-dimensional model of the human brainstem. The net was trained by means of a back-propagation algorithm, over a pool of 580 example cases. Assessed on 200 test cases, the net correctly localised 83.6% of the target voxels; furthermore the net correctly localised the lesions in 31 out of 37 patients. Because this computer-assisted method provides reliable and quantitative localisation of brainstem areas of dysfunction and can be used as a 3D interactive functional atlas, it is expected to prove useful as a diagnostic tool for assessing focal brainstem lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accornero, N., andCapozza, M. (1995): ‘OPTONET: neural network for visual field diagnosis”,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,33, pp. 223–226
Anshelevich, V. V., Amirikian, B. R., Lukashin, A. V., andFrank-Kamenetskii, M. D. (1989): ‘On the ability of neural networks to perform generalization by induction’,Biol. Cybern.,61, pp. 125–128
Arendt-Nielsen, L. (1994): ‘Characteristics, detection and modulation of laser-evoked vertex potentials’,Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand.,38, pp. 1–36
Armoni, A. (1998): ‘Use of neural networks in medical diagnosis’,MD Comput.,15, (2), pp. 100–104
Baum, E. B., andHaussler, D. (1989): ‘What size net gives valid generalization?’Neural Comput.,1, (1), pp. 151–160
Bishop, M. C. (1995): ‘Neural networks for pattern recognition’, (Oxford University Press, New York)
Bromm, B., andTreede, R. D. (1991): ‘Laser evoked potentials in the assessment of cutaneous pain sensitivity in normal subjects and patients’,Rev. Neurol.,147, pp. 625–643
Byrne, J. V., Kendall, B. E., Kingsley, D. P., andMoseley, I. F. (1989): ‘Lesions of the brain stem: assessment by magnetic resonance imaging’,Neuroradiology,31, (2), pp. 129–133
Caplan, L., Gutmann, L., Besser, R., andHopf, H. C. (1993): ‘Brain-stem localization and function’ (Springer, Heidelberg/New York)
Capra, R., Mattioli, F., Vignolo, L. A., Antonelli, A. R., Bonfioli, F., Cappiello, J., Nicolai, P., Peretti, G., andOrlandini, A. (1989): ‘Lesion detection in MS patients with and without clinical brainstem disorders: magnetic resonance imaging and brainstem auditory evoked potentials compared’,Eur. Neurol.,29, (6), pp. 317–322
Cruccu, G., andDeuschl, G. (2000): ‘The clinical use of brainstem reflexes and hand-muscle reflexes’,Clin. Neurophysiol.,111, pp. 371–387
Cruccu, G., andOngerboer de Visser, B. W. (1999): ‘The jaw reflexes’,Electroencephalogr: Clin. Neurophysiol. suppl.52, pp. 243–247
Deuschl, G., andEisen, A. (Eds) (1999): ‘Recommendations for the practice of clinical neurophysiology: guidelines of the international federation of clinical neurophysiology, 2nd edn, (Elsevier, Amsterdam)
Feldman, J., andBallard, D. (1982): ‘Connectionist models and their properties’,Cognitive Sci.,6, pp. 205–254
Grossberg, S. (1988): ‘Nonlinear neural networks: principles, mechanisms, and architectures’,Neural Networks,1, pp. 17–61
Harnad, S., Doty, R. W., Goldstein, L., Jaynes, J., andKrauthamer, G. (1977): ‘Lateralization in the nervous system’ (Academic Press, New York)
Hopf, H. C. (1994): ‘Topodiagnostic value of brain stem reflexes’,Muscle Nerve,17, pp. 475–484
Kimura, J., Daube, J., Burke, D., Hallett, M., Cruccu, G., Ongerboer de Visser, B. W., Yanagisawa, N., Shimamura, M., andRothwell, J. (1994): ‘Human reflexes and late responses. Report of an IFCN committee’,Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol.,90, pp. 393–403
Kohonen, T. (1990): The self-organizing map’,Proc. IEEE,78, pp. 1464–1480
Kretschmann H. J., andWeinrich, W. (1998): ‘Neurofunctional systems-3D reconstructions with correlated neuroimaging’ (George Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart)
Masiyama, S., Niizuma, H., andSuzuki, J. (1985): ‘Pontine haemorrhage: a clinical analysis of 26 cases’,J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry,48, pp. 658–662
Miller, A. S., Blott, B. H., andHames, T. K. (1992): ‘Review of neural network applications in medical imaging and signal processing’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,30, pp. 449–464
Ongerboer de Visser, B. W., Cruccu, G., Manfredi, M., andKoelman, J. H. (1990): ‘Effects of brainstem lesions on the masseter inhibitory reflex. Functional mechanisms of reflex pathway’,Brain,113, (3), pp. 781–792
Ongerboer de Visser, B. W., andCruccu, G. (1993): ‘Neurophysiologic examination of the trigeminal, facial, hypoglossal, and spinal accessory nerves in cranial neuropathies and brain stem disorders’ inBrown, W. F., andBolton, C. F. (Eds): ‘Clinical electromyography, 2nd edn, (Butterworth-Heinemann, Boston), pp. 61–92
Ormerod, I. E., Roberts, R. C., Du Boulay, E. P., McDonald, W. I., Callanan, M. M., Halliday, A. M., Johnson, G., Kendall, B. E., Logsdall, S. J., andMacManus, D. G. (1984). ‘NMR in multiple sclerosis and cerebral vascular disease’,Lancet,8415, (2), pp. 1334–1335
Paxinos, G., andHuang, X. F. (1995): ‘Atlas of the human brain-stem’ (Academic Press, San Diego)
‘Learning internal representations by error propagation’ inRumelhart, D. E., andMcClelland, J. L. (Eds): ‘Parallel distributed processing: explorations in the microstructure of cognition. Vol. 1, Foundations’ (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA), pp. 318–362
Shaltenbrand, G., andWahem, W. (1977). ‘Atlas for sterotaxy of the human brain’ (Thieme, Stuttgart)
Sharpe, P. K., andCaleb, P. (1994): ‘Artificial neural networks within medical decision support systems’,Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. Suppl.,219, pp. 3–11
Simpson, P. K. (1990): ‘Artificial neural systems’ (Pergamon Press, New York)
Turano, G., Jones, S. J., Miller, D. H., Du Boulay, G. H., Kakigi, R., andMcDonald, W. I. (1991): ‘Correlation of SEP abnormalities with brain and cervical cord MRI in multiple sclerosis’,Brain,114 (Pt 1B), pp. 663–81
Yang, T. F., Devine, B., andMacFarlane, P. W. (1994): ‘Artificial neural networks for the diagnosis of atrial fibrillation’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,32, (6), pp. 615–619
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capozza, M., Iannetti, G.D., Mostarda, M. et al. Three-dimensional mapping of brainstem functional lesions. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 38, 639–644 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344869
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344869