Abstract
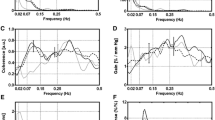
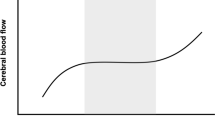
In a man with orthostatic and effort syncopes due to primary dysautonomia, we measured cerebral blood flow (CBF) — by the 133-Xenon inhalation method — in supine and in sitting positions, and after the i.v. administration of Acetazolamide, a potent cereral vasodilator.
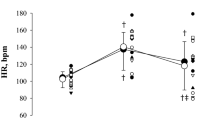
Heart rate (HR) and blood pressure (BP) were monitored over the 24 hours by a non-invasive device. The CBF was normal in supine position and significantly reduced when the patient was sitting. Despite che sympathetic denervation, good response to acetazolamide infusion was seen.
BP changed with the position of the subject according to gravity, and HR was unresponsive to orthostatic and effort stimuli.
Sommario
Abbiamo misurato il Flusso Ematico Cerebrale (FEC) — con il metodo inalatorio allo Xenon-133 — in clinostatismo, in posizione seduta e dopo la somministrazione e.v. di Acetazolamide, un potente vasodilatatore cerebrale, in un uomo affetto da Sindrome Disautonomica Primitiva con ipotensione severa, ortostatica e da sforzo.
Inoltre, abbiamo monitorato per 24 ore la Pressione Arteriosa (PA) e la Frequenza Cardiaca (FC) per mezzo di metodica non-invasiva.
I nostri risultati dimostrano che il FEC è ridotto in posizione seduta, ma è normale in clinostatismo, e che mantiene la capacità di reagire a stimoli vasodilatatori, nonostante la denervazione simpatica. La PA è risultata dipendente dalla forza gravitazionale, mentre la FC è “fissa”, cioè non risponde agli stimoli ortostatici e allo sforzo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blauentein U.W., Halsey J.S., Wilson E.M., Wills E.:133-Xenon method, analysis of reproducibility: some of its physiological implications. Stroke 8: 92–102, 1977.
Brooks D.J., Remond S., Mathias C.J., Bannister R., Symon L.:The effect of orthostatic hypotension on cerebral blood flow and middle cerebral artery velocity in autonomic failure, with observations on the action of ephedrine. J. Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52: 962–966, 1989.
Caronna J., Plum:Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in idiopathic autonomic insufficiency. Neurology 22: 308, 1972.
Depresseux J.C., Rousseau J.J., Franck, G.:The autoregulation of cerebral blood flow, the cerebrovascular reactivity and their interaction in the Shy-Drager syndrome. Eur Neurol. 18: 295–301, 1979.
Dowie N.M., Heat R.W.:Basic stratistical method. New York: Haper and Row (Eds), 1974.
Mann S., Altman D.G.:Raftery E.B., Bannister R.:Circadian variation of blood pressure in autonomic failure. Circulation 68: 477–483, 1983.
Millar-Craig M.W., Bishop C.N., Rafitery E.B.:Circadian variation of blood pressure. Lancet 1: 795–799, 1978.
Obrist W.D., Thompson H.K., Wag H.S., Wilkinson W.E.:Regional cerebral blood flow estimated by 133-Xenon inhalation. Stroke 6: 245–256, 1975.
Risberg J., Ali Z., Wilson E.M., Halsey J.H.:Regional cerebral blood flow by 133 xenon inhalation: preliminary evaluation of an initial slope index in patients with unstable flow compartments. Stroke 6: 142–148, 1975.
Stradgaard S.:Autoregulation of cerebral blood flow in hypertensive patients. Circulation 53: 720–727, 1975.
Thomas J.E., Schirger A., Fealey R.D., Sheps S.G.:Orthostatic hypotension. Mayo Clin Proc 56: 117–125, 1981.
Ziegler M.G., Lake C.R., Kopin I.J.:The symphatetic-nervous-system defect in primary orthostatic hypotension. N Engl J Med 296: 293–297, 1977.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nobili, F., Francione, S., Marenco, S. et al. Primary dysautonomia: cerebral blood flow and hemodynamic findings. Case report.. Ital J Neuro Sci 11, 281–288 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02333859
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02333859